Preparation method of human milk fat substitute
A human milk fat substitute and oil technology, applied in food preparation, edible oil/fat, food science, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of fatty acid, high price of tripalmitin, and difficulty in downstream deacidification of increased cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
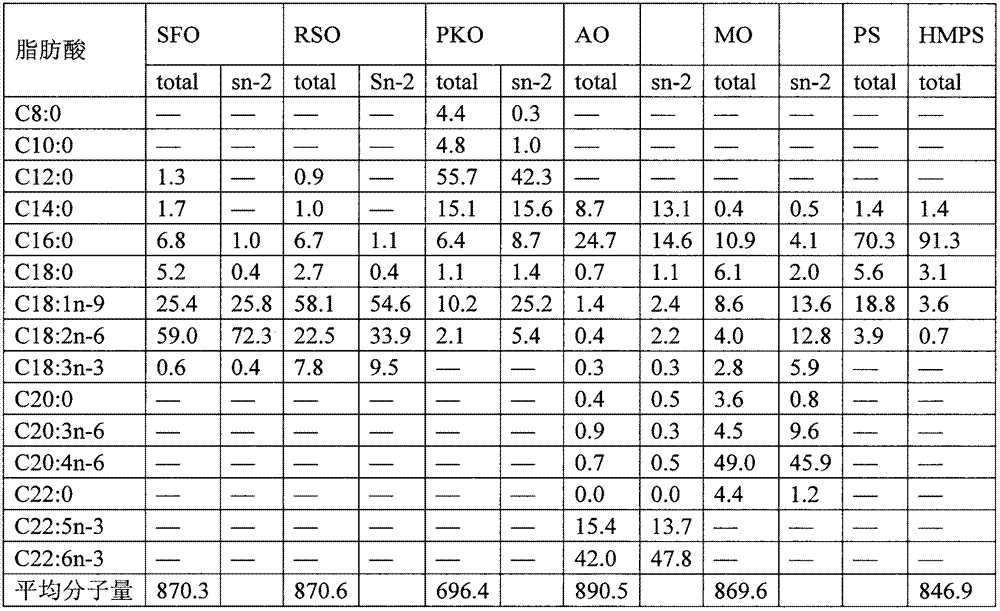
[0026] Take by weighing 20g high-melting-point palm stearin in the round-bottomed flask, and mix with the free fatty acid that comes from rapeseed oil with the ratio of 1: 10 in molar ratio, add the Lipozyme RM IM of 10wt% in the mixed system (in total substrate weight), and reacted for 4 hours in water at 60° C. and a stirring rate of 250 rpm. After the obtained reaction substrate was centrifuged at 4000rpm to remove the enzyme, the fatty acid was removed by molecular distillation. The molecular distillation conditions were: evaporation temperature, 185°C; heat exchanger temperature, 60°C; rotational speed, 120rpm; absolute pressure, 2Pa. The composition and distribution of fatty acids are shown in the table.
[0027] Fatty acid composition and distribution of table 2 intermediate product
[0028] fatty acid
total
sn-2
%sn-2 a
sn-1,3 b
C12:0
0.3
0.1
11.1
0.4
C14:0
0.4
0.1
8.3
0.6 ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Take by weighing 20g high-melting-point palm stearin in the round-bottomed flask, and mix with the free fatty acid that comes from rapeseed oil with the ratio of 1: 12 in molar ratio, add the Lipozyme RM IM of 8wt% in the mixing system (in total substrate weight), and reacted for 3 hours in water at 65° C. and a stirring rate of 250 rpm. After the obtained reaction substrate was centrifuged at 4000rpm to remove the enzyme, the fatty acid was removed by molecular distillation. The molecular distillation conditions were: evaporation temperature, 185°C; heat exchanger temperature, 60°C; rotational speed, 120rpm; absolute pressure, 2Pa. The composition and distribution of fatty acids are shown in the table below.
[0059] Fatty acid composition and distribution of table 4 intermediate product
[0060] fatty acid
total
sn-2
%sn-2
sn-1,3
C12:0
0.3
0.1
11.1
0.4
C14:0
0.4
0.1
8.3
0.6
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com