Laser production process of radio frequency identification antenna
A radio frequency identification and production process technology, applied in the field of electronic radio frequency identification, can solve the problems of limited selection of substrates, complex production process, unstable performance, etc., to achieve easy control of the production process, low requirements for storage conditions, and low-carbon production efficiency Environmentally friendly effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings, so that the advantages and features of the present invention can be more easily understood by those skilled in the art, so as to make a clearer and clearer definition of the protection scope of the present invention.
[0049] See Figure 1 to Figure 18 , The embodiment of the present invention includes:
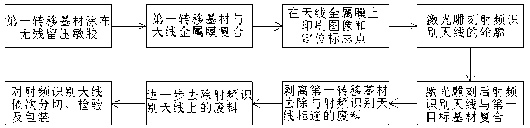
[0050] A laser production process for radio frequency identification antennas, and includes the following steps:
[0051] a) Provide the first substrate;
[0052] b) Spread the adhesive evenly on the first substrate;
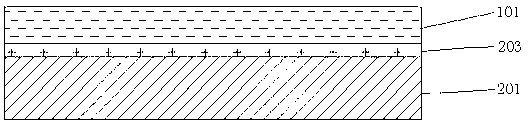
[0053] c) Laminating the first substrate and the antenna metal film 101 through an adhesive;
[0054] d) Use the viscous ink 102 to print an image and several positioning mark points on the antenna metal film 101, and the position of each positioning mark point is determined by referring to the outline of the radio frequency identificati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com