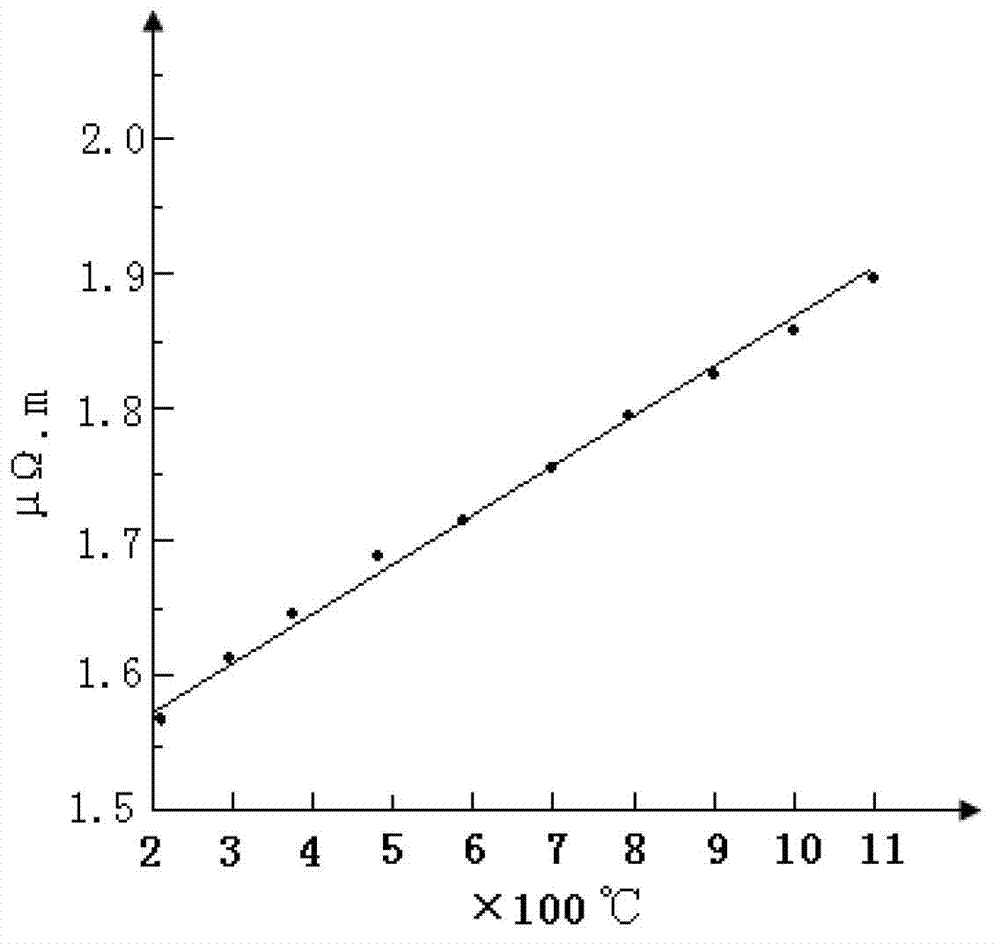
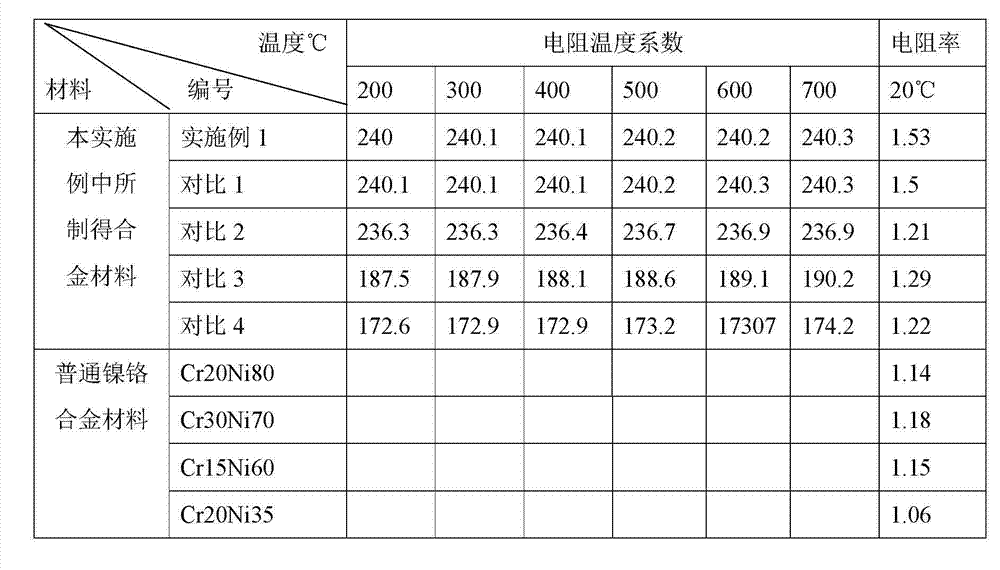
Alloy material with high temperature coefficient of resistance and preparation method thereof
A technology of alloy material and temperature coefficient, which is applied in the field of heating resistance wire material, can solve the problems of unstable welding weight, long time required, long distance of temperature conduction, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding cold drawing broken wire and improving dispersion ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] In the present embodiment, first weigh 100 kilograms of nickel-cadmium alloy, GeO 2 1 kg, CeO 2 0.5 kg, ZrO 2 1 kg, TiO 2 4 kg, Al 2 o 3 2.2 kg and 10 kg of Fe powder, heating the nickel-chromium alloy in a vacuum furnace to melt to prepare molten steel for use, the heating temperature is 1600°C. Then the remaining six components are mixed and fully ground for 2 hours to make additives in powder form; the molten steel is tapped and poured into the furnace, and the powdered additives are added to the furnace when the steel is tapped between 1 / 5-4 / 5 and stirred with a magnetic stirrer at a temperature of 1600 °C for 1 hour. Finally, the molten steel is poured into a billet with a diameter of 120mm, cooled and rolled into a profile with a diameter of 20mm, and finally a filament with a diameter of 0.5mm is obtained after multiple cold drawing.
[0016] In the alloy material prepared in this example, the mass percentages of each component are: Ni component: 65%,...
Embodiment 2
[0027] In the present embodiment, first weigh 80 kilograms of nickel-cadmium alloy, GeO 2 0.6 kg, CeO 2 0.4 kg, ZrO 2 0.9 kg, TiO 2 3.2 kg, Al 2 o 3 1.6 kilograms and 13.3 kilograms of Fe powder, nickel-chromium alloy is heated to melting in vacuum furnace to make molten steel for subsequent use, and heating temperature is 1600 ℃. Then mix the remaining six components and fully grind them into powder to make additives; tap the molten steel and pour it into the furnace, and add the powdered additives into the furnace when the steel is tapped between 1 / 5-4 / 5, And stirred with a magnetic stirrer at a temperature of 1600° C. for 1 hour. Finally, the molten steel is poured into a billet with a diameter of 120mm, cooled and rolled into a profile with a diameter of 20mm, and finally a filament with a diameter of 0.5mm is obtained after multiple cold drawing.
[0028] In the alloy material prepared in this example, the mass percentages of each component are: Ni component: ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] In the present embodiment, first weigh 75.9 kilograms of nickel-cadmium alloy, GeO 2 0.3 kg, CeO 2 0.5 kg, ZrO 2 0.3 kg, TiO 2 3.5 kg, Al 2 o 3 2 kilograms and 17.5 kilograms of Fe powders, the nickel-chromium alloy is heated to melting in a vacuum furnace to make molten steel for subsequent use, and the heating temperature is 1600°C. Then mix the remaining six components and fully grind them into powder to make additives; tap the molten steel and pour it into the furnace, and add the powdered additives into the furnace when the steel is tapped between 1 / 5-4 / 5, And stirred with a magnetic stirrer at a temperature of 1600° C. for 1 hour. Finally, the molten steel is poured into a billet with a diameter of 120mm, cooled and rolled into a profile with a diameter of 20mm, and finally a filament with a diameter of 0.5mm is obtained after multiple cold drawing.
[0032] In the alloy material prepared in this example, the mass percentages of each component are: Ni ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com