Method for mixing and gasifying liquid-phase acetic acid and hydrogen
A technology of mixed gas and acetic acid, which is applied in chemical methods, chemical instruments and methods, and preparation of organic compounds for reacting liquid and gaseous media. Corrosion problems, effect of reducing requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
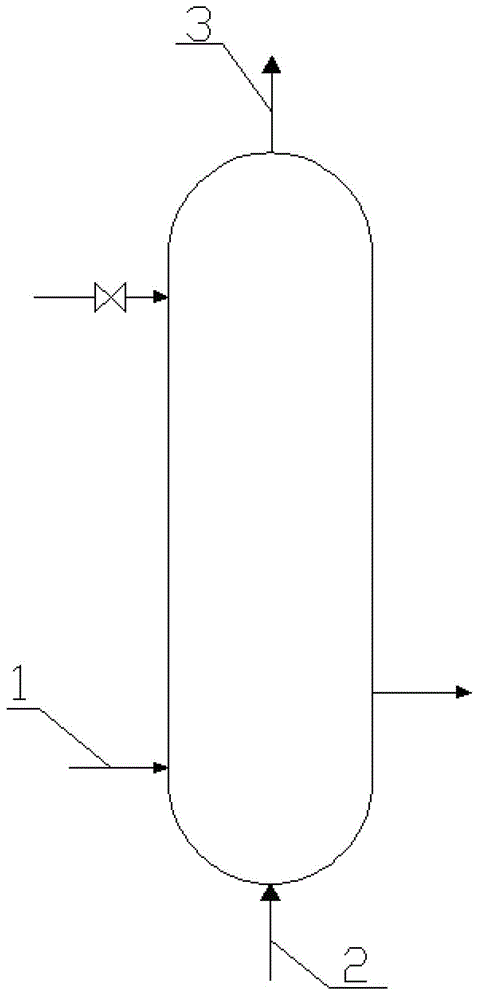
[0025] refer to figure 1 , this specific embodiment adopts the following technical solutions: temperature 160 o C. Acetic acid 1 with a pressure of 1MPa enters the evaporator from the bottom, and the acetic acid is distributed in the evaporator as a continuous phase; the temperature is 230 o C, the hydrogen-containing gas 2 with a pressure of 1 MPa passes through the acetic acid layer in the form of bubbling, and in the contact process with acetic acid, under the effect of an external heat source, by controlling the temperature of the mixed gas 3 at the top of the evaporator, the H2 / acetic acid molar ratio is obtained. 15. Mixed gas with a pressure of 1MPa. The temperature of the mixed gas 3 at the top of the evaporator under the operating pressure of 1 MPa is lower than the boiling point of acetic acid under the operating pressure.
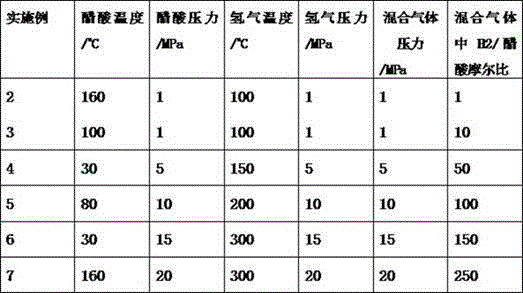
[0026] The data of each process parameter in Embodiment 2 to Embodiment 7 are shown in Table 1, and other conditions are the same as Embodimen...
Embodiment 8
[0030] temperature 30 o C. Propionaldehyde 1 with a pressure of 1MPa enters the evaporator from the bottom, and the propionaldehyde is distributed in the evaporator as a continuous phase; the temperature is 100 o C. Hydrogen-containing gas 2 with a pressure of 1 MPa passes through the propionaldehyde layer in a bubbling manner. During the contact process with propionaldehyde, under the action of an external heat source, by controlling the temperature of the mixed gas 3 at the top of the evaporator, H2 / propionaldehyde is obtained A mixed gas with a molar ratio of 1 and a pressure of 1 MPa. The temperature of the mixed gas 3 at the top of the evaporator under the operating pressure of 1 MPa is lower than the boiling point of propionaldehyde under the operating pressure.
Embodiment 9
[0032] Temperature 160 o C. Propionaldehyde 1 with a pressure of 20MPa enters the evaporator from the bottom, and the propionaldehyde is distributed in the evaporator as a continuous phase; the temperature is 300 o C. Hydrogen-containing gas 2 with a pressure of 20 MPa passes through the propionaldehyde layer in a bubbling manner. During the contact process with propionaldehyde, under the action of an external heat source, by controlling the temperature of the mixed gas 3 at the top of the evaporator, H2 / propionaldehyde is obtained A mixed gas with a molar ratio of 250 and a pressure of 20 MPa. The temperature of the mixed gas 3 at the top of the evaporator under the operating pressure of 20 MPa is lower than the boiling point of propionaldehyde under the operating pressure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com