Acryl-based copolymers and optical film including the same
A kind of copolymer and acrylate technology, applied in the field of optical film, can solve the problems of complex process and high price, and achieve the effects of excellent compatibility, excellent heat resistance, excellent delay and durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
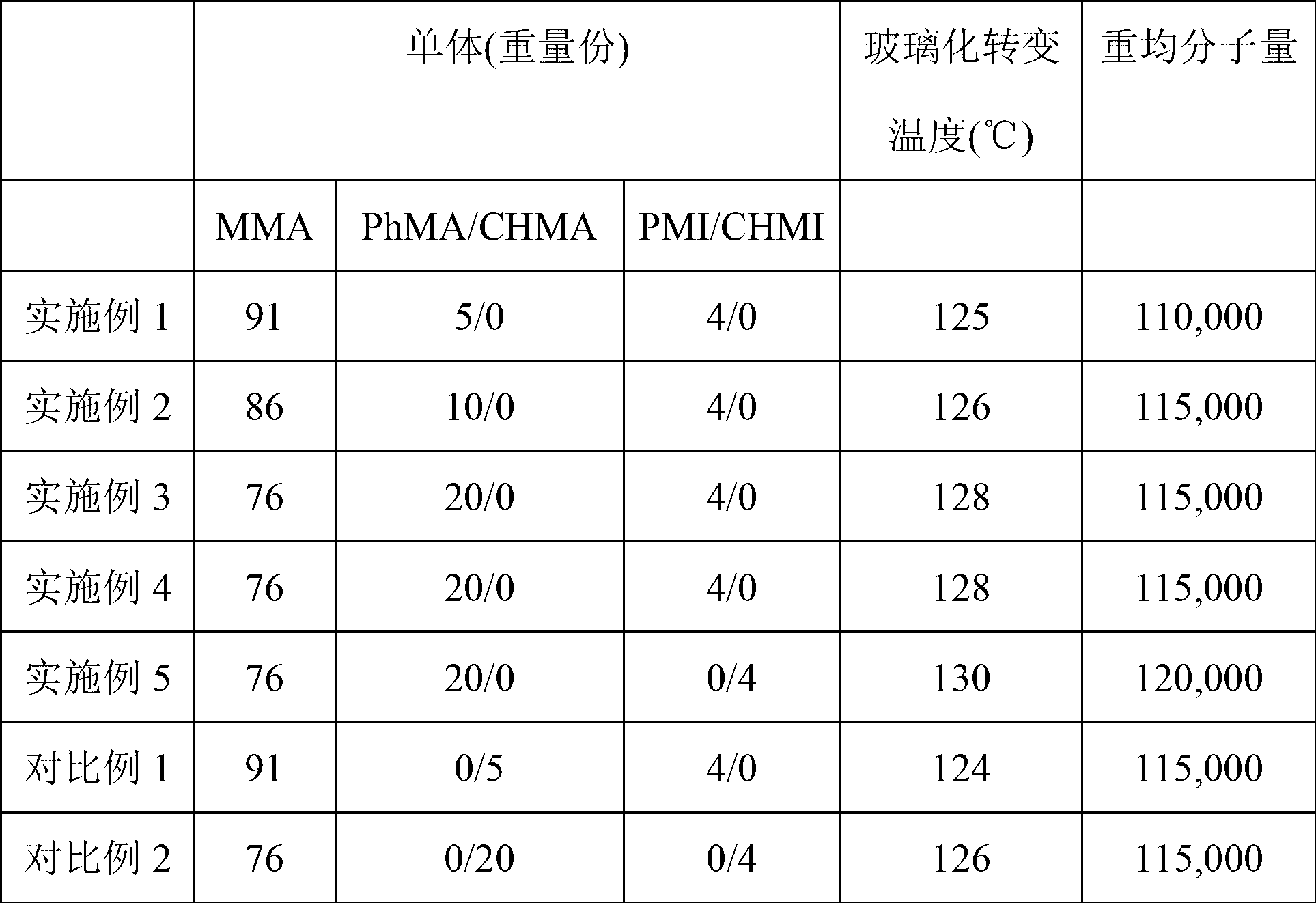
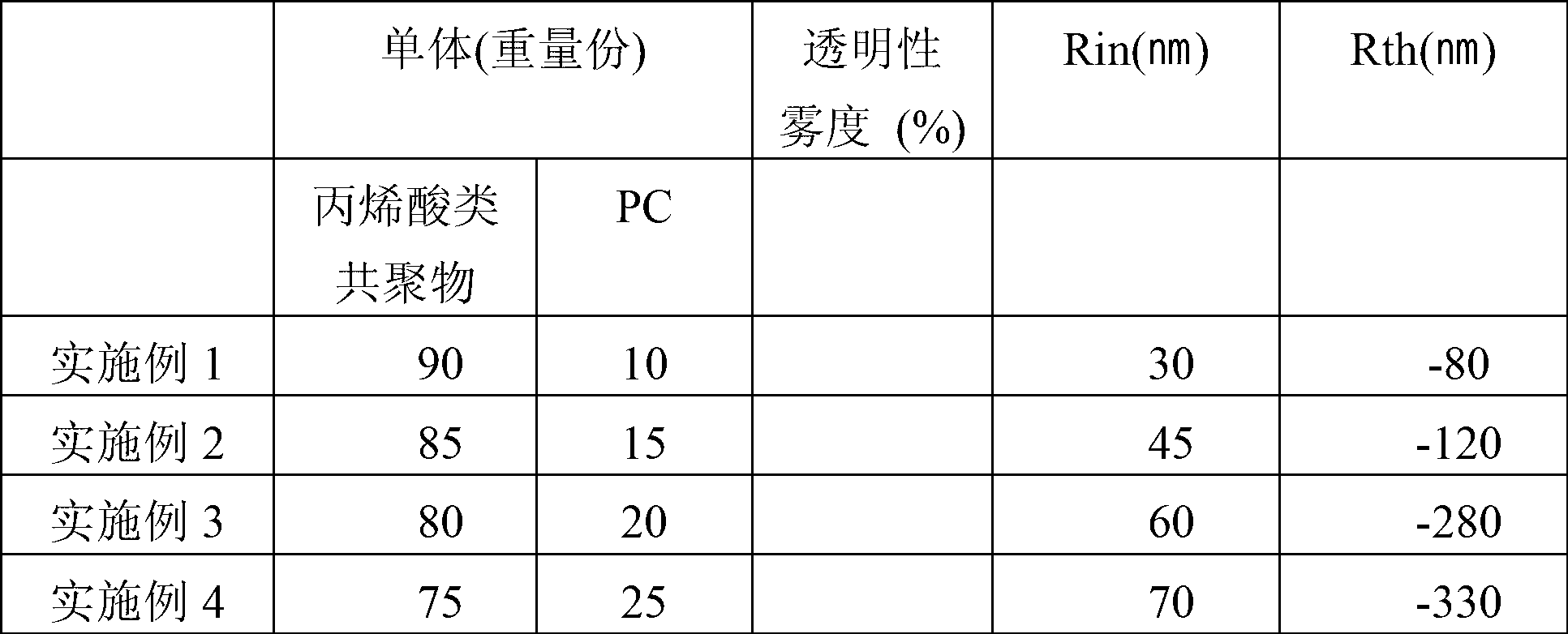
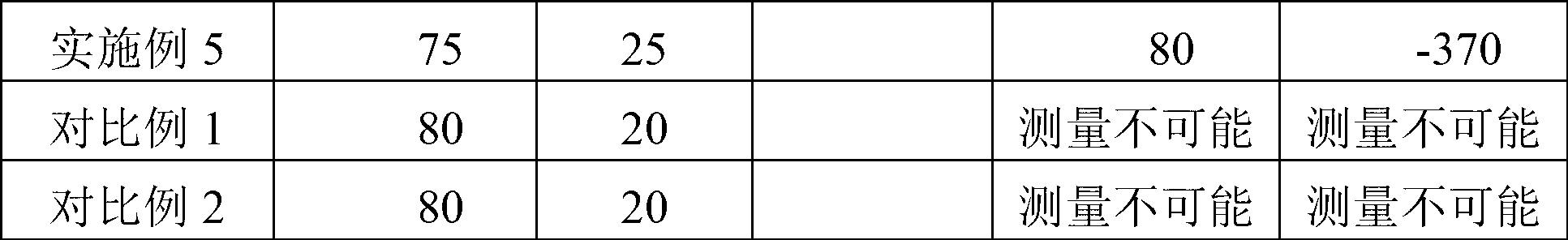
[0072] An acrylic copolymer resin was prepared using 91 parts by weight of methyl methacrylate, 5 parts by weight of phenyl methacrylate and 4 parts by weight of phenylmaleimide monomer. The glass transition temperature and molecular weight of the obtained resin were measured, and as a result, a resin having a glass transition temperature of 125° C. and a weight average molecular weight of 110,000 was obtained. 90 parts by weight of the above resin and 10 parts by weight of polycarbonate were mixed to prepare a final resin composition. The above resin composition was formed into a film using a solution casting method, and then stretched at a glass transition temperature to measure the retardation value of the film. As a result, the in-plane retardation value / thickness retardation value were 30 / -80, respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0074] An acrylic copolymer resin was prepared using 86 parts by weight of methyl methacrylate, 10 parts by weight of phenyl methacrylate and 4 parts by weight of phenylmaleimide monomer. The glass transition temperature and molecular weight of the obtained resin were measured, and as a result, a resin having a glass transition temperature of 126° C. and a weight average molecular weight of 115,000 was obtained. 85 parts by weight of the above resin and 15 parts by weight of polycarbonate were mixed to prepare a final resin composition. The above resin composition was formed into a film using a solution casting method, and then stretched at a glass transition temperature to measure the retardation value of the film. As a result, the in-plane retardation value / thickness retardation value were 45 / -120, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0076] An acrylic copolymer resin was prepared using 76 parts by weight of methyl methacrylate, 20 parts by weight of phenyl methacrylate and 4 parts by weight of phenylmaleimide monomer. The glass transition temperature and molecular weight of the obtained resin were measured, and as a result, a resin having a glass transition temperature of 128° C. and a weight average molecular weight of 115,000 was obtained. 80 parts by weight of the above resin were mixed with 20 parts by weight of polycarbonate to prepare a final mixed resin. The above mixed resin was formed into a film using a solution casting method, and then stretched at a glass transition temperature to measure the retardation value of the film. As a result, the in-plane retardation value / thickness retardation value were 60 / -280, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com