Far infrared temperature jump microscope
A far-infrared and microscope technology, applied in the field of fluorescence microscopy, can solve the problems of individual damage, inability to accurately locate heating, inability to monitor the temperature of different areas in real time, etc., and achieve the effect of high penetration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
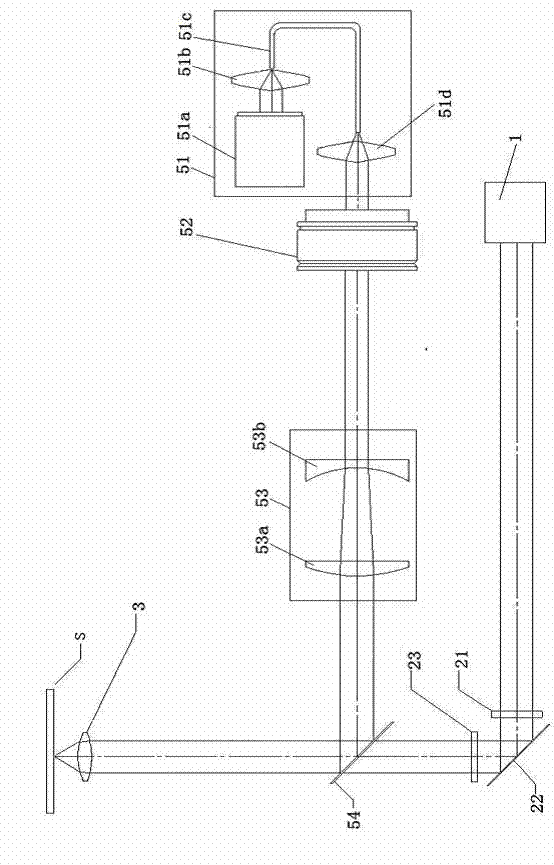
[0026] The far-infrared temperature-jumping microscope of the present invention can realize micro-area heating of biological samples, and has short heating time and high heating efficiency. The key point of the invention is to add a far-infrared laser system on the basis of the existing fluorescence microscope, and realize precise heating of the micro-region of the sample through the far-infrared laser. Since the fluorescence microscope is an existing technology, please refer to the structure of the fluorescence microscope in the prior art for the specific structural parts of the fluorescence microscope involved in this embodiment (disclosed or not disclosed in this embodiment). A preferred embodiment of the present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0027] Far-infrared temperature jump microscope of the present invention, see figure 1 , mainly including a laser light source unit 1 installed on the mirror body, a fluorescent filter com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com