Method of improving coercivity of sintering Nd-Fe-B magnetic material
A magnetic material, neodymium iron boron technology, applied in the field of sintered neodymium iron boron magnetic materials, can solve the problems of reduction, rare earth consumption, and drop, and achieve the effect of ensuring high magnetic energy product, reducing average particle size, and narrow particle size distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
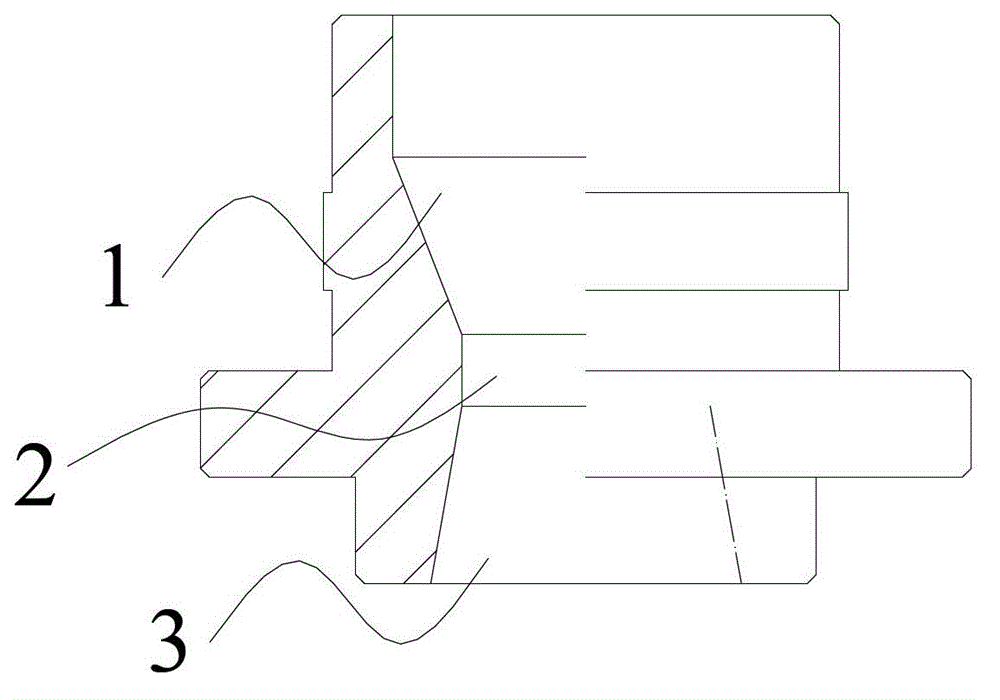
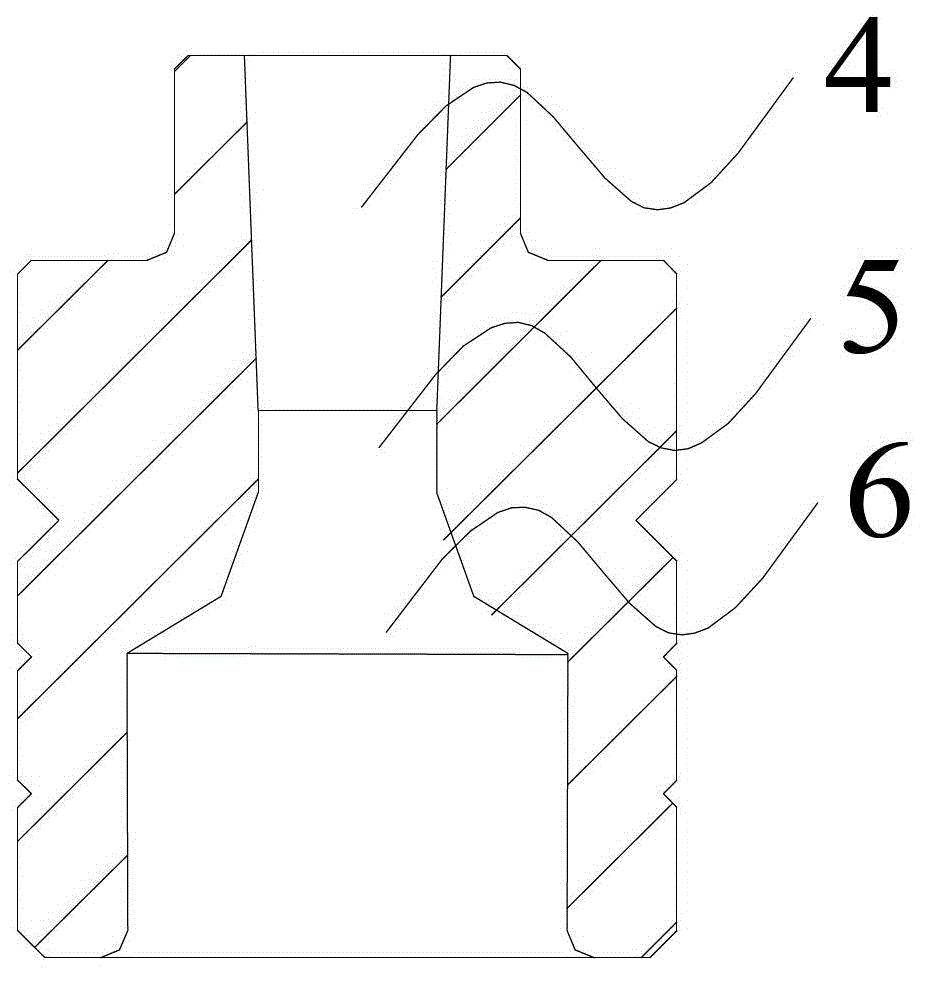
[0036] The retractable airflow mill system of the present invention includes a bottom nozzle with an internal airflow channel and a side nozzle with an internal airflow channel. like figure 1 As shown in the figure, the bottom nozzle is composed of a first converging section 1, a first throat section 2 and a first diffusing section 3 which are connected in sequence; the specific connection method is as follows: the end with the smaller opening of the first converging section 1 is connected to the first throat section. The section 2 is connected, and the end with the smaller opening of the first diffuser section 3 is connected with the first throat section 2 . like figure 2 As shown, the side nozzle is composed of a second converging section 6, a second throat section 5 and a second diffusing section 4 which are connected in sequence; the specific connection method is as follows: the smaller end of the second converging section 6 is connected to the second throat section. Th...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Homogenized magnetic powder + high temperature liquid phase low temperature sintering
[0040] (1) The design component is Nd 31 Co 1 Cu 0.2 Fe 66.82 B 0.98 The quick-setting sheet is placed in a sintering furnace that can be evacuated, vacuumed, and hydrogen is introduced to keep the hydrogen pressure in the sintering furnace at 5 × 10 5 Pa, maintained for 2 hours, kept the pressure and cooled to room temperature and then dehydrogenated by vacuum. After the vacuum degree reached below 1 kPa, the temperature was raised to 500 ° C and kept for 3 hours for dehydrogenation. After the dehydrogenation was completed, it was cooled to room temperature to obtain hydrogen breakdown.
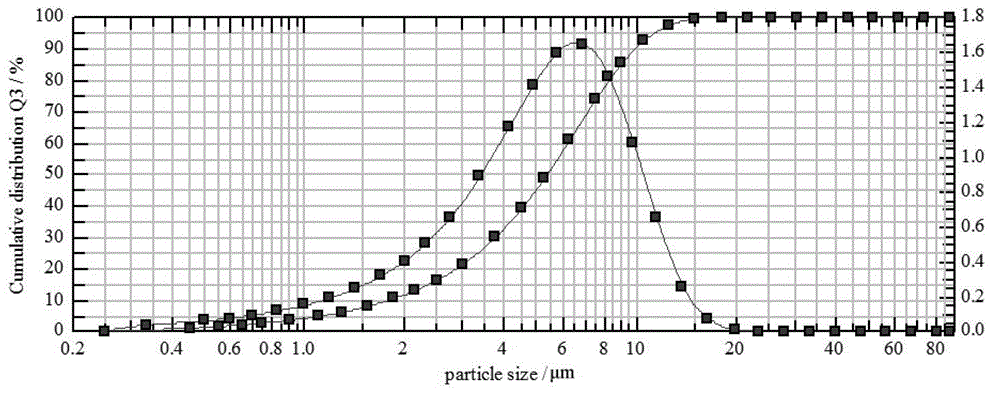
[0041] (2) Under the protection of nitrogen, place the hydrogen crusher in the jet mill of Example 1 to grind until the average particle size of the main phase alloy powder is 3.39 μm, and the powder dispersion (D90-D10) / (2D50) is less than 0.8, Obtain the magnetic powder; put the obtained mag...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Traditional grinding powder magnetic powder + high temperature liquid phase low temperature sintering
[0048] Except for step (2), under the protection of nitrogen, the hydrogen crushed material is placed in an existing jet mill with a linear gas flow acceleration mechanism, and the average particle size is 3.29 μm, and the powder dispersion is (D90-D10) / (2D50)= Except for the magnetic powder of 0.827, the rest of the operations are the same as those in Example 2, and the NdFeB magnetic material is obtained.
[0049] The obtained NdFeB magnetic material is processed into a sample of Φ10mm×10mm, and the magnet properties are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com