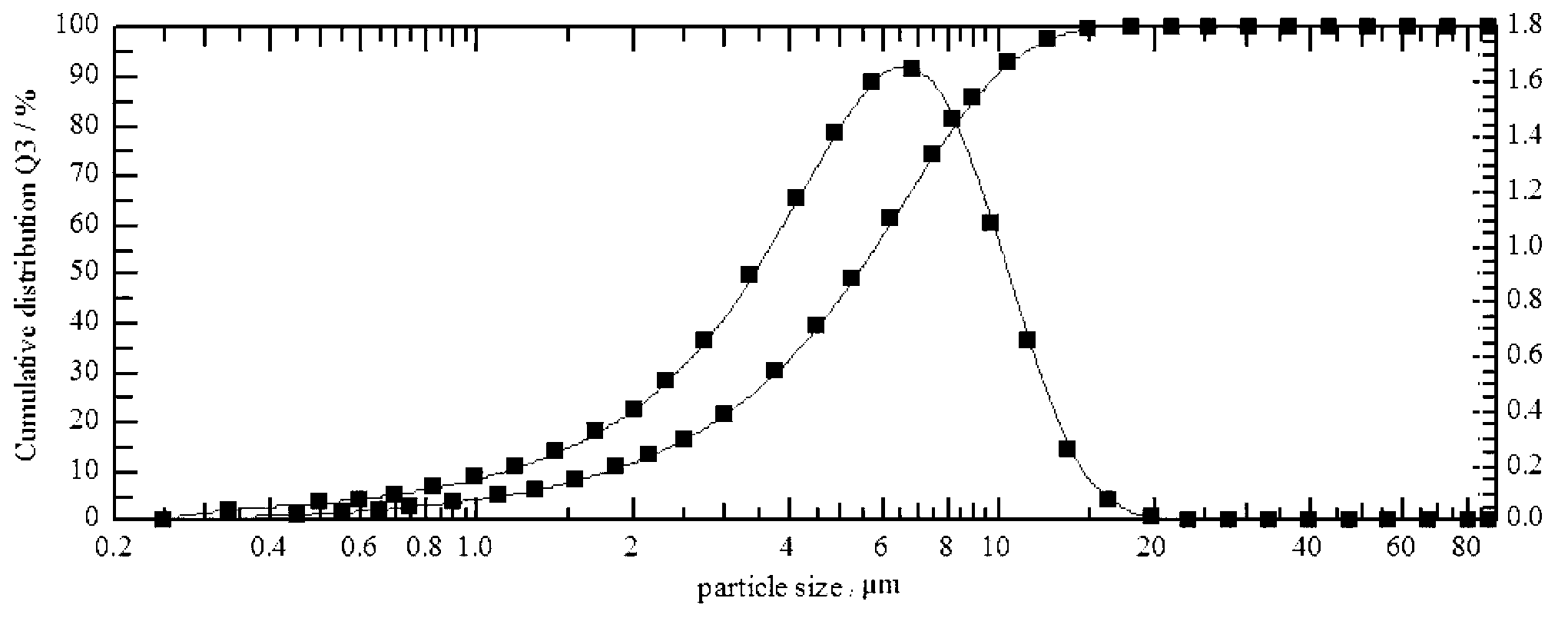
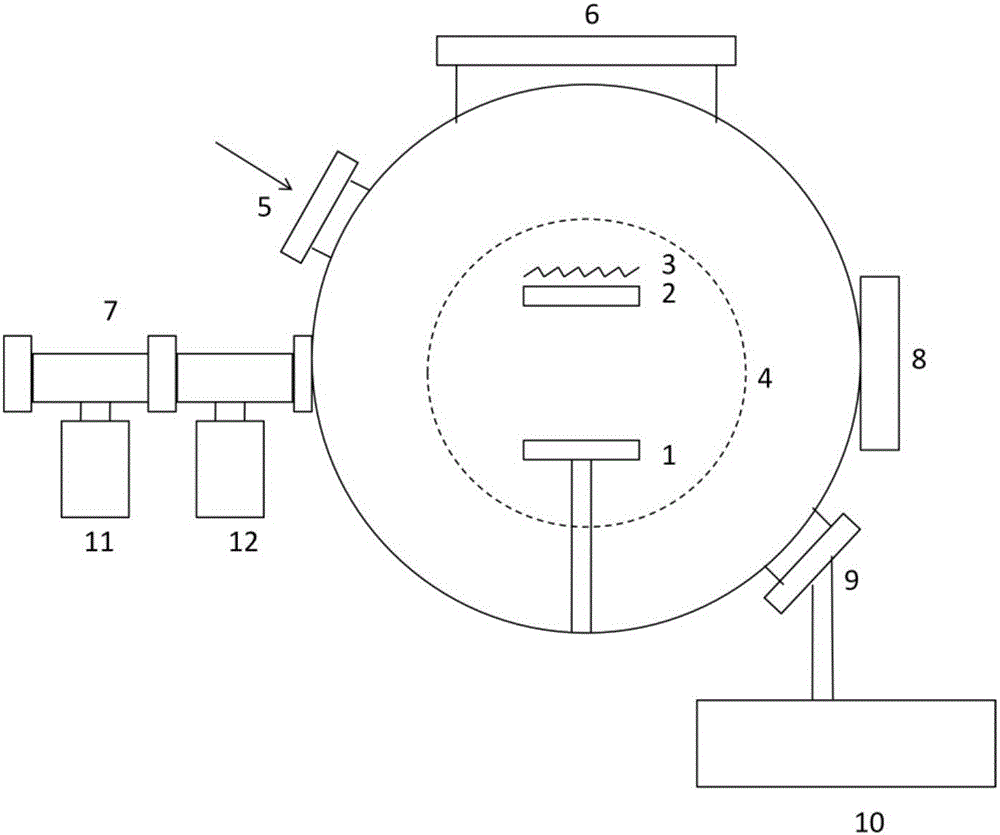
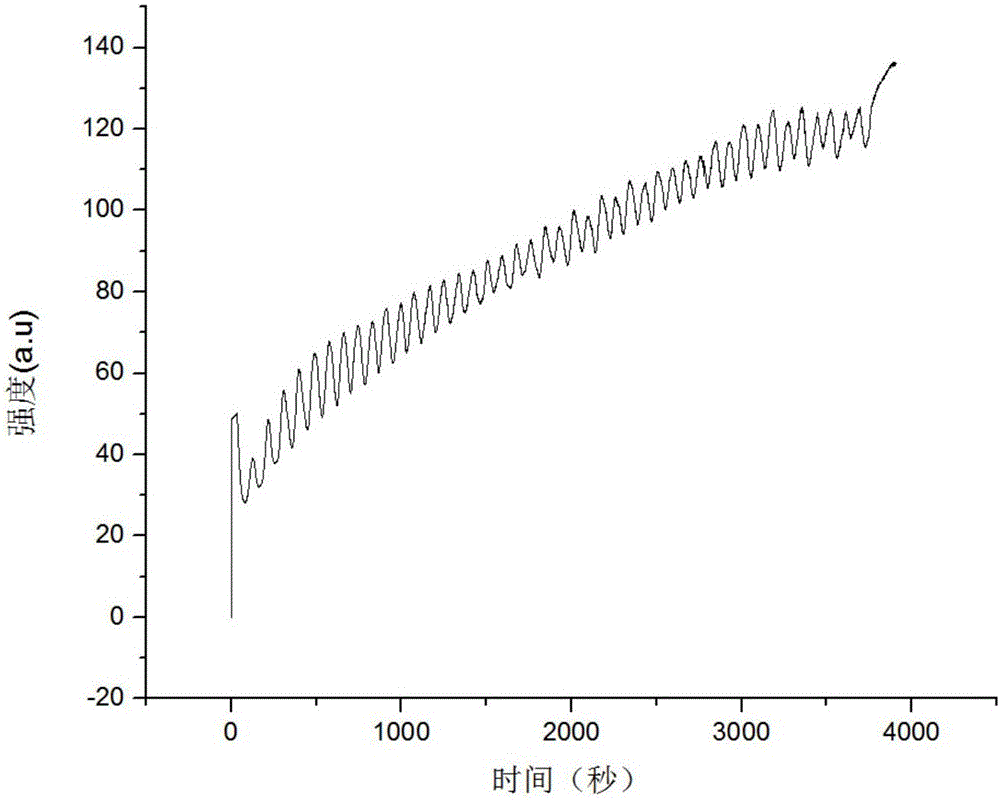
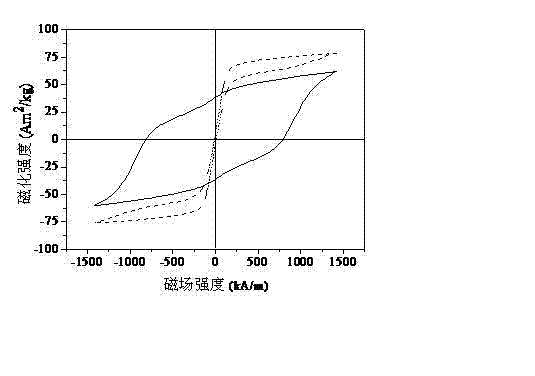
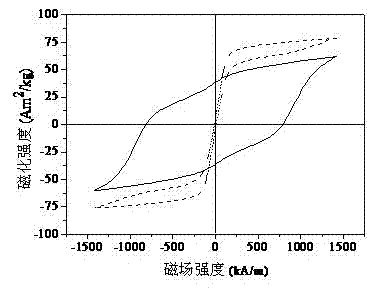
Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Good coercivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron nitride powder, method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20090087688A1Excellent magnetic propertiesSuited to high-density recordingPretreated surfacesRecord information storageMischmetalIron nitride
An aspect of the present invention relates to an iron nitride powder. The iron nitride powder is comprised chiefly of Fe16N2 and comprises, on at least a portion of the powder surface, a coating layer comprising at least one element selected from the group consisting of rare earth metal elements, aluminum, and silicon, and cobalt-containing ferrite having a composition denoted by (CoxFe1−x)Fe2O4, wherein 0<x≦1. The present invention further relates to a method of manufacturing iron nitride powders and a magnetic recording medium comprising the iron nitride powder.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Dust core, ferromagnetic powder composition therefor, and method of making
InactiveUS6102980AImprove stressGood coercivityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureShell moldingUltimate tensile strength
A ferromagnetic powder composition for dust cores contains a ferromagnetic metal powder and 0.1-15% by volume based on the powder of titania sol and / or zirconia sol. The composition is pressure molded and desirably annealed into a dust core which exhibits a high magnetic flux density, low coercivity, low loss and high mechanical strength.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20180358046A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove scratch resistanceMaterials with cobaltRecord information storageTO-18Greek letter epsilon
Provided is a magnetic recording medium including: a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including particles of at least one kind of epsilon type iron oxide-based compound selected from the group consisting of ε-Fe2O3 and a compound represented by Formula (1), an abrasive, and a binding agent, at least on one surface of the non-magnetic support, in which an average equivalent circle diameter of the particles of the epsilon type iron oxide-based compound is 7 nm to 18 nm, an average equivalent circle diameter of the abrasive in a plan view of the magnetic layer is 20 nm to 1,000 nm, and a coefficient of variation of the equivalent circle diameter of the abrasive is 30% to 60%. In Formula (1), A represents at least one kind of metal element other than Fe and a satisfies a relationship of 0<a<2.ε-AaFe2-aO3 (1)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of improving coercivity of sintering Nd-Fe-B magnetic material
ActiveCN103056370AImprove crushing efficiencyImprove particle size uniformityMagnetic materialsHydrogenShielding gas
The invention discloses a method of improving the coercivity of sintering Nd-Fe-B magnetic materials. The method includes the following steps of using hydrogen to crush Nd-Fe-B alloy, powder processing, compression moulding, sintering and tempering under the protection of vacuum or protective gases. The sintering condition consists of heating to 300 to 600 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 5 to 6 hours to dehydrogenize, heating once again to 1060 to 1120 DEG C, sintering for 1 to 60 minutes under high temperature, finally decreasing the temperature to 1000 to 1050 DEG C, keeping sintering for 1 to 4 hours under the temperature and cooling. The method adopts the steps of sintering for a short period under high temperature to precipitate the liquid phase and then sintering under lower temperature. The liquid phase is rapidly precipitated under high temperature, thereby improving the sintering process of the magnetic materials, promoting the performance of sintering process, controlling the grain size through sintering under lower temperature, inhabiting grain growth and benefiting obtaining an excellent coercivity of magnetic materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGHANG NEW MATERIAL
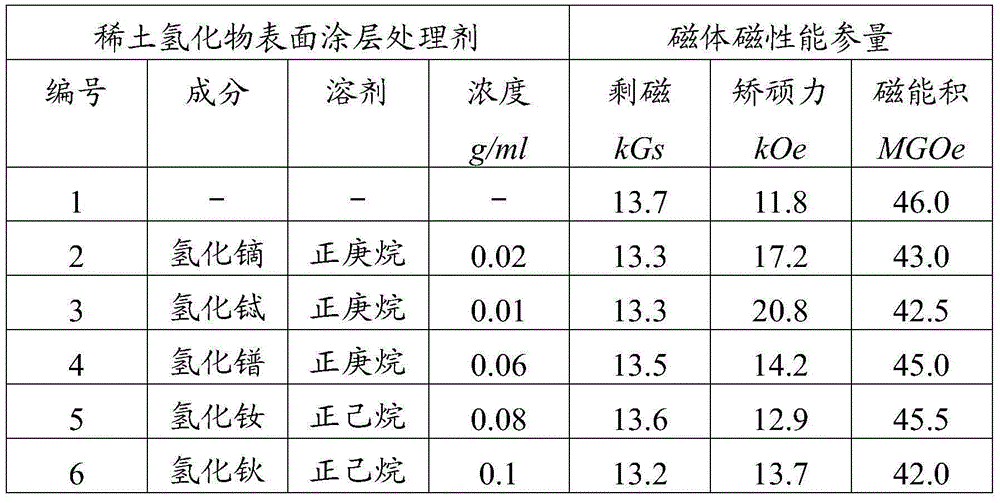
Treating agent and electro-deposition method for forming rare earth hydride particle coating
ActiveCN103556208AImprove magnetic propertiesStrong magnetismElectrolytic coatingsMagnetic materialsRare-earth magnetHeptane
The invention relates to a treating agent and an electro-deposition method for forming a rare earth hydride particle coating, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials. Rare earth hydride particles are dispersed in a dispersing agent, wherein n-hexane or n-heptane is taken as the dispersing agent; the rare earth is at least one element of Pr, Nd, Tb, Dy and Ho. The hydride particles are deposited on the surface of a sintered NdFeB rare earth magnet by using the electro-deposition method so as to form the uniform and dense coating with controllable thickness. The rare earth hydride particle coating can be used for obviously improving the magnetic property of the sintered NdFeB rare earth magnet and especially the coercivity of the magnet. As the method is adopted, the usage amounts of heavy rare earths in the sintered NdFeB rare earth is decreased on the premise of guaranteeing good magnetic property of the magnet, so that the manufacturing cost of the magnet with high coercivity is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
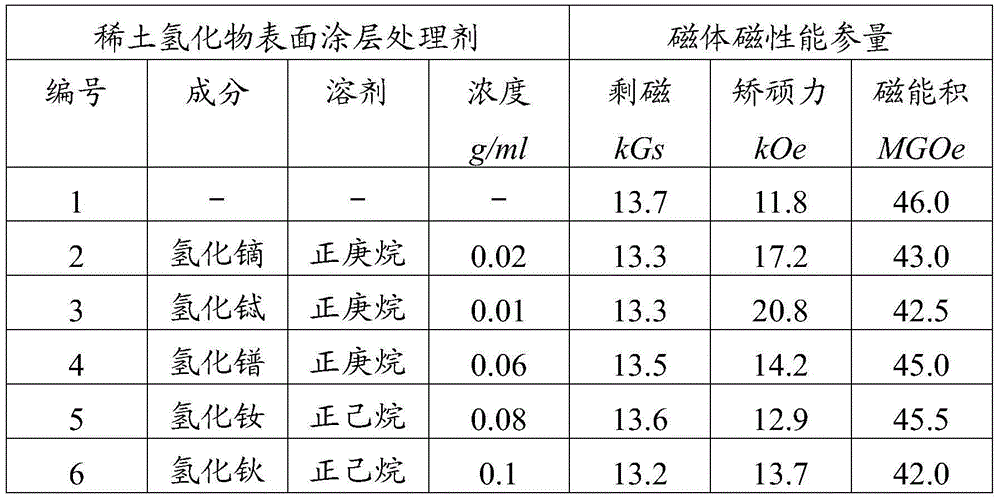
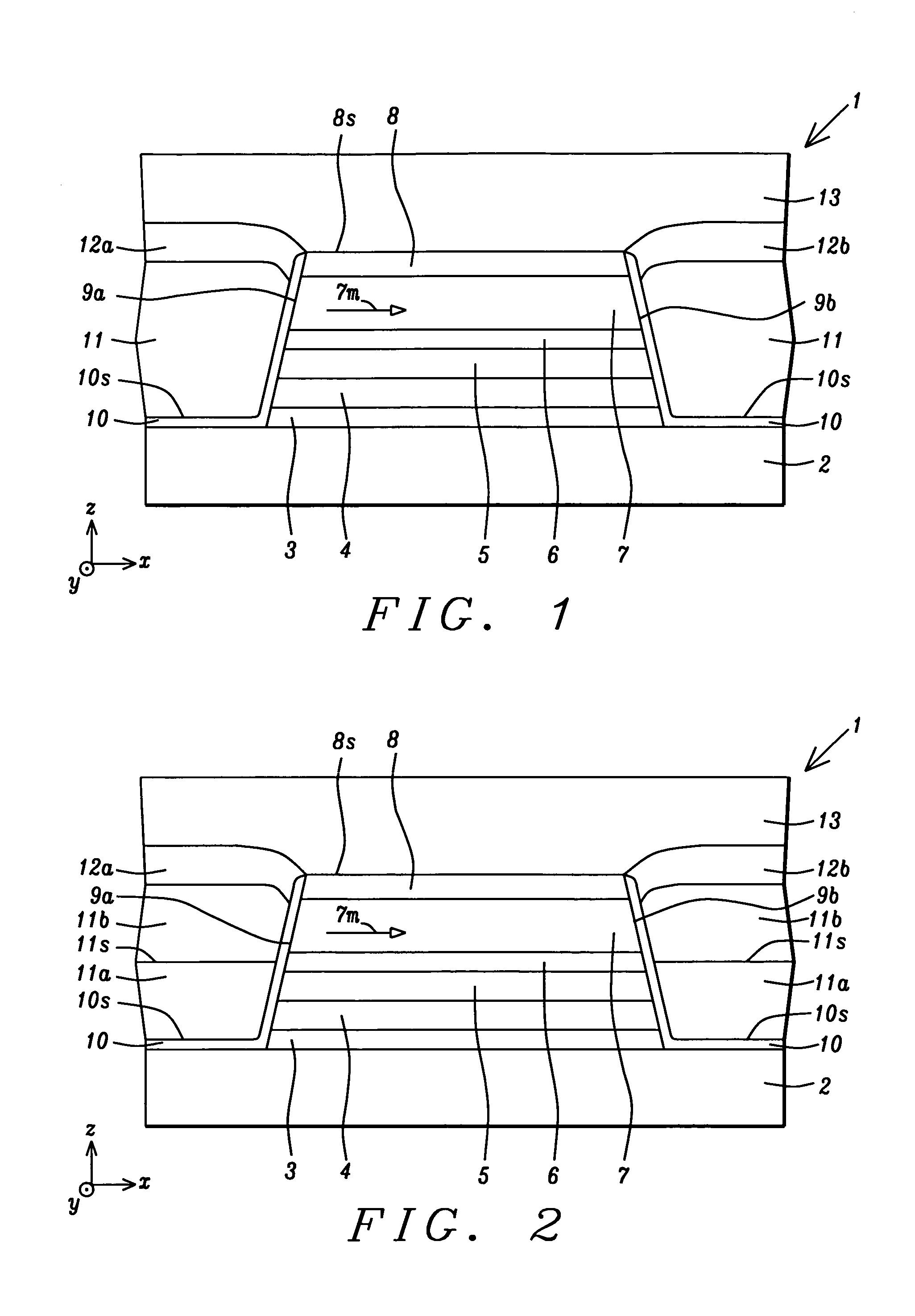
Method for fabricating a high coercivity hard bias structure for magnetoresistive sensor
ActiveUS20100276272A1High recording densityGreat coercivityMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingCrystalliteHigh concentration
A hard bias (HB) structure for longitudinally biasing a free layer in a MR sensor is disclosed that includes a mildly etched seed layer and a hard bias (HB) layer on the etched seed layer. The HB layer may contain one or more HB sub-layers stacked on a lower sub-layer which contacts the etched seed layer. Each HB sub-layer is mildly etched before depositing another HB sub-layer thereon. The etch may be performed in an IBD chamber and creates a higher concentration of nucleation sites on the etched surface thereby promoting a smaller HB average grain size than would be realized with no etch treatments. A smaller HB average grain size is responsible for increasing Hcr in a CoPt HB layer to as high as 2500 to 3000 Oe. Higher Hcr is achieved without changing the seed layer or HB material and without changing the thickness of the aforementioned layers.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Preparation method of high-performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet
ActiveCN111243806AHigh densityEnhanced remanence and maximum energy productTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMagnetic powderHot pressing
A preparation method of a high-performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnet belongs to the technical field of rare earth permanent magnet materials and comprises the following steps: preparing single alloy or main alloy and auxiliary alloy micro powder by adopting vacuum rapid hardening melt-spinning and hydrogen decrepitation processes; adding a lubricating agent, an antioxidant and a dispersing agent, and mixing; grinding powder by airflow, adding a lubricant into magnetic powder, mixing, orienting the magnetic powder in a magnetic field, pressing and molding, and carrying out isostaticcool pressing treatment; carrying out heat preservation and deflation treatment in three temperature sections; cooling to 300-500 DEG C, introducing high-purity argon with the pressure intensity of 2-10 MPa, and carrying out hot pressing treatment; sintering at high temperature, naturally cooling to 800-900 DEG C, introducing room-temperature argon or liquid argon, and performing rapid cooling; and then carrying out two-stage heat treatment and argon rapid cooling respectively. According to the invention, the density of the final magnet is improved by improving the density before high-temperature sintering, so that the residual magnetism and the maximum magnetic energy product are enhanced. By reducing the sintering temperature, the coercive force can be obviously improved under the conditions of high residual magnetism and high magnetic energy product. The method has good economic benefits and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
R-t-b rare earth sintered magnet and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140314612A1Excellent coercivityIncrease in coercivityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementSintered magnets
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Epitaxial growth method of yttrium iron garnet film
ActiveCN106048726AInsulationRoom temperature ferromagneticPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHigh energyRoom temperature
An epitaxial growth method of a yttrium iron garnet film comprises the following steps: vacuumizing a vacuum cavity with a treated yttrium iron garnet substrate to be 8.6+ / -1*10-6 Pa, and heating the yttrium iron garnet substrate to the constant temperature which is 736 DEG C; in a heating process, feeding ozone when heating to the temperature of 250 DEG C; after heating to the temperature of 736 DEG C, maintaining air pressure of the vacuum cavity, adjusting the mass fraction of the ozone to be 40%, meanwhile insulating for half a hour, and starting a reflective high-energy electron diffraction instrument (RHEED) to adjust so as to obtain diffraction spots of a substrate; maintaining real-time and in-situ monitoring of the RHEED in the whole process, and focusing laser onto a YIG target through a lens by using a KrF excimer laser of which the wavelength is 248 nm; after growth of the film is finished, maintaining the temperature of the substrate unchanged, annealing in situ for 15 minutes, then naturally cooling the film to the temperature about 250 DEG C, stopping protective gas and cooling to the room temperature. The obtained YIG film has uniform components, is controllable in thickness and good in process repeatability, and has high preparation efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A Fe-based bulk permanent magnet alloy with excellent coercive force and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an Fe-based bulk permanent magnet alloy with excellent coercive force and a preparation method thereof. The composition (atomic percentage) of the Fe-based bulk permanent magnet alloy of the present invention is: Fe55-75%, Nd5-15%, Nb1-7%, B18-30%. The preparation process is as follows: (1) The industrial pure metal raw materials Fe, Nd, Nb and FeB alloy are mixed according to the above formula, and then smelted in a vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace under the protection of argon, and the alloy is smelted repeatedly for 3~ 5 times, the master alloy was obtained; (2) after remelting the master alloy, it was poured by copper mold negative pressure suction casting method, and the Fe-based bulk amorphous alloy was obtained. (3) Vacuum annealing the above bulk amorphous alloy at 580-850°C and a vacuum degree of 3-5×10-3Pa for 10-35 minutes to obtain Fe with excellent coercive force Base bulk permanent magnet alloy. The Fe-based alloy of the present invention has soft magnetic properties in the as-cast state. After vacuum annealing, the alloy changes from soft magnetic to hard magnetic, with saturation magnetization Ms=61Am2 / kg and coercive force jHc=819kA / m.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
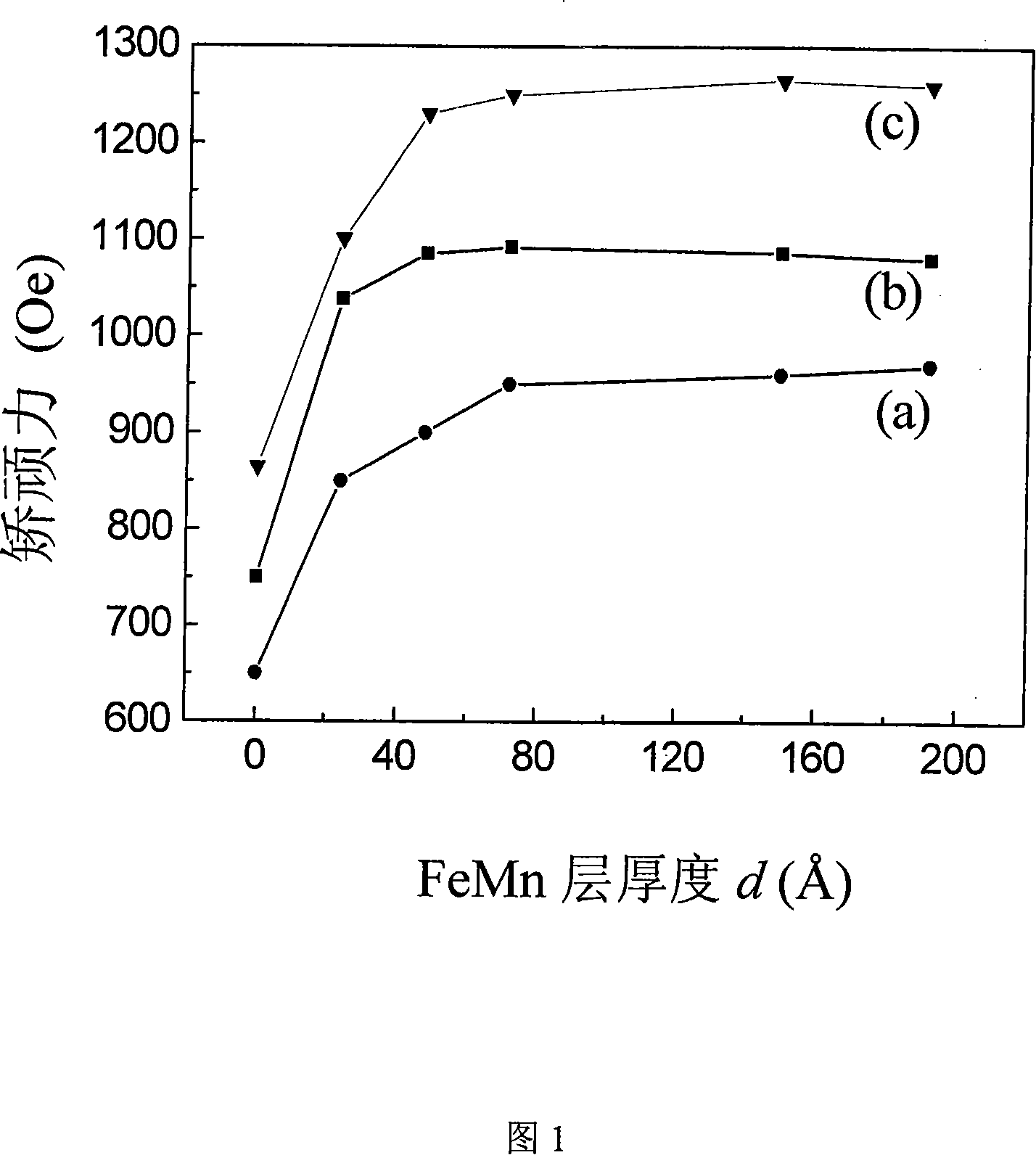
Method for increasing metal magnetic multilayer film coercive force
InactiveCN101148751AEnhanced perpendicular magnetic anisotropyImprove coercive forceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingVolumetric Mass DensityFuture application
The present invention is method of raising the coercive force of multilayer magnetic metal film with antiferromagnetic material. Multilayer Pt / [CoCr / Pt]5 / FeMn / Pt film is formed through depositing on cleaned glass substrate by means of using one magnetically controlled sputtering instrument. The multilayer magnetic metal film has the advantages of small thickness, excellent vertical magnetic anisotropy and high coercive force, and is suitable for use in ultrahigh density vertical magnetic record. In addition, the deposited film needs no annealing treatment, so that the present invention has also the advantages of low cost, simple preparation, etc and is suitable for future application.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
R-T-B series magnetic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111599564AGood remanenceGood coercivityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementRemanence
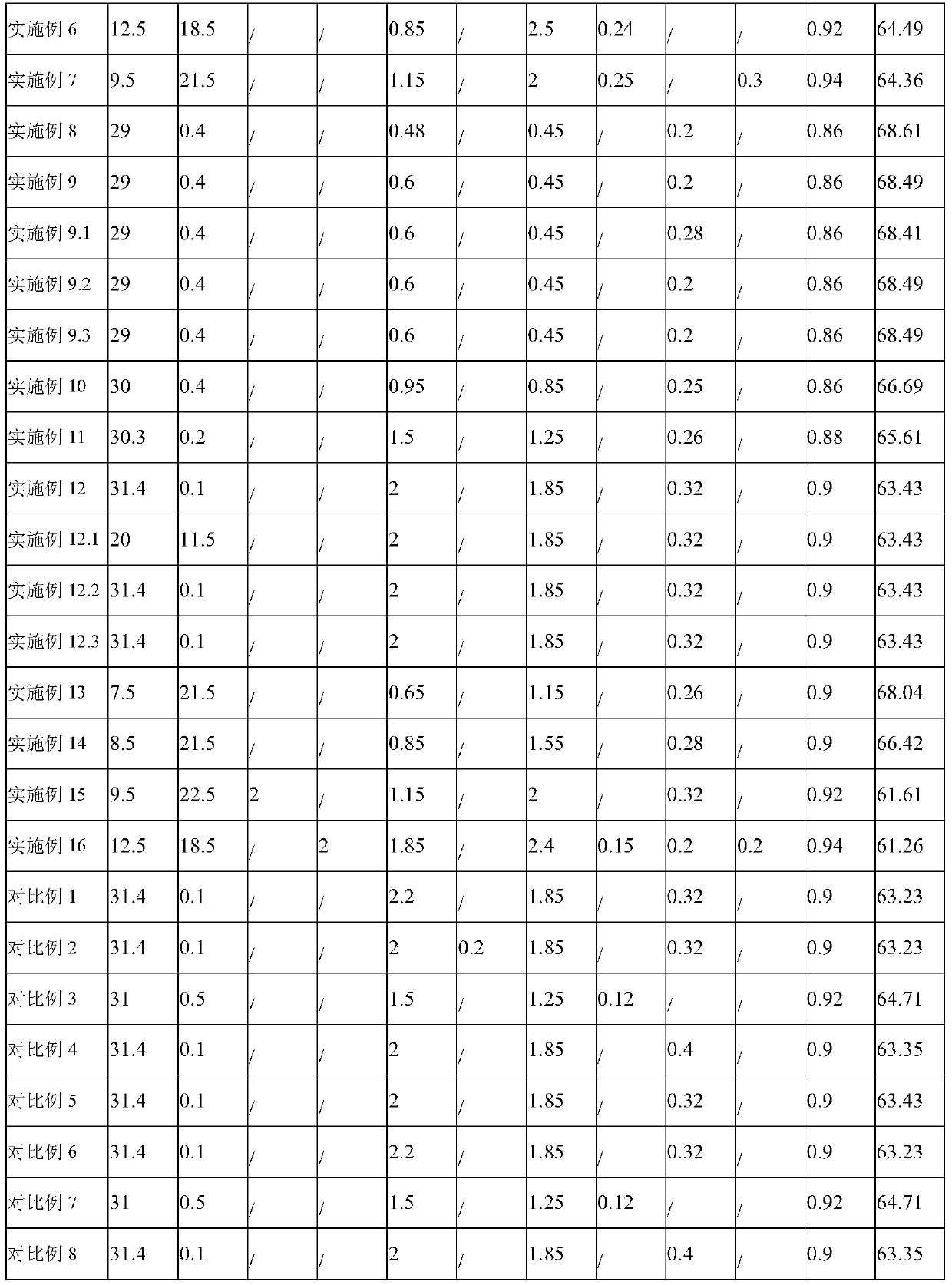
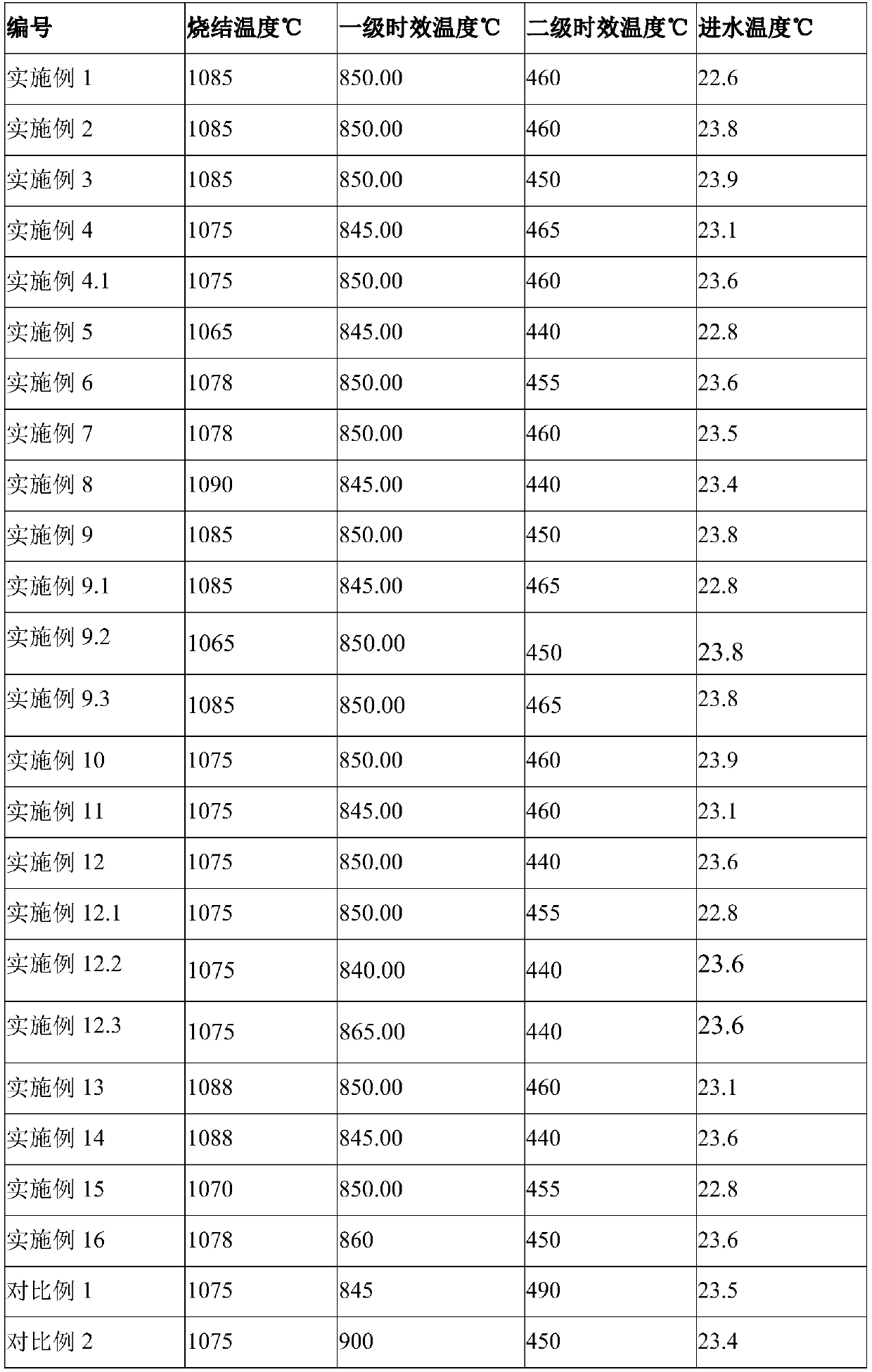
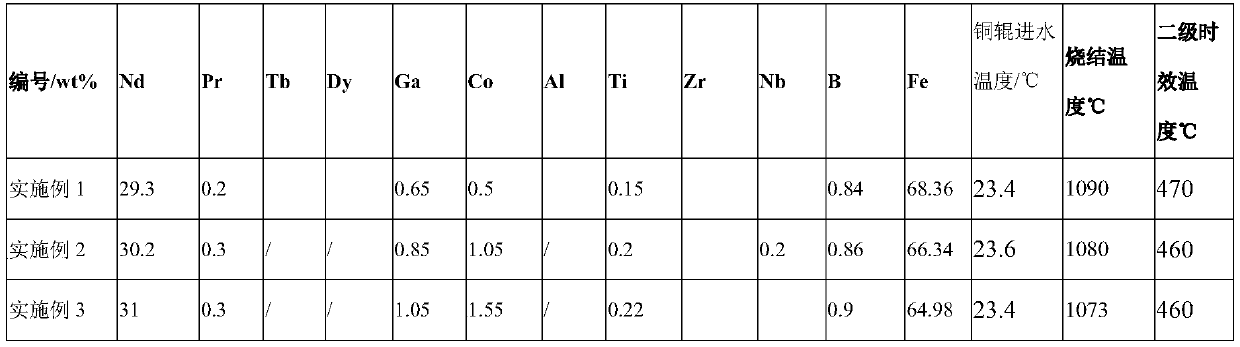
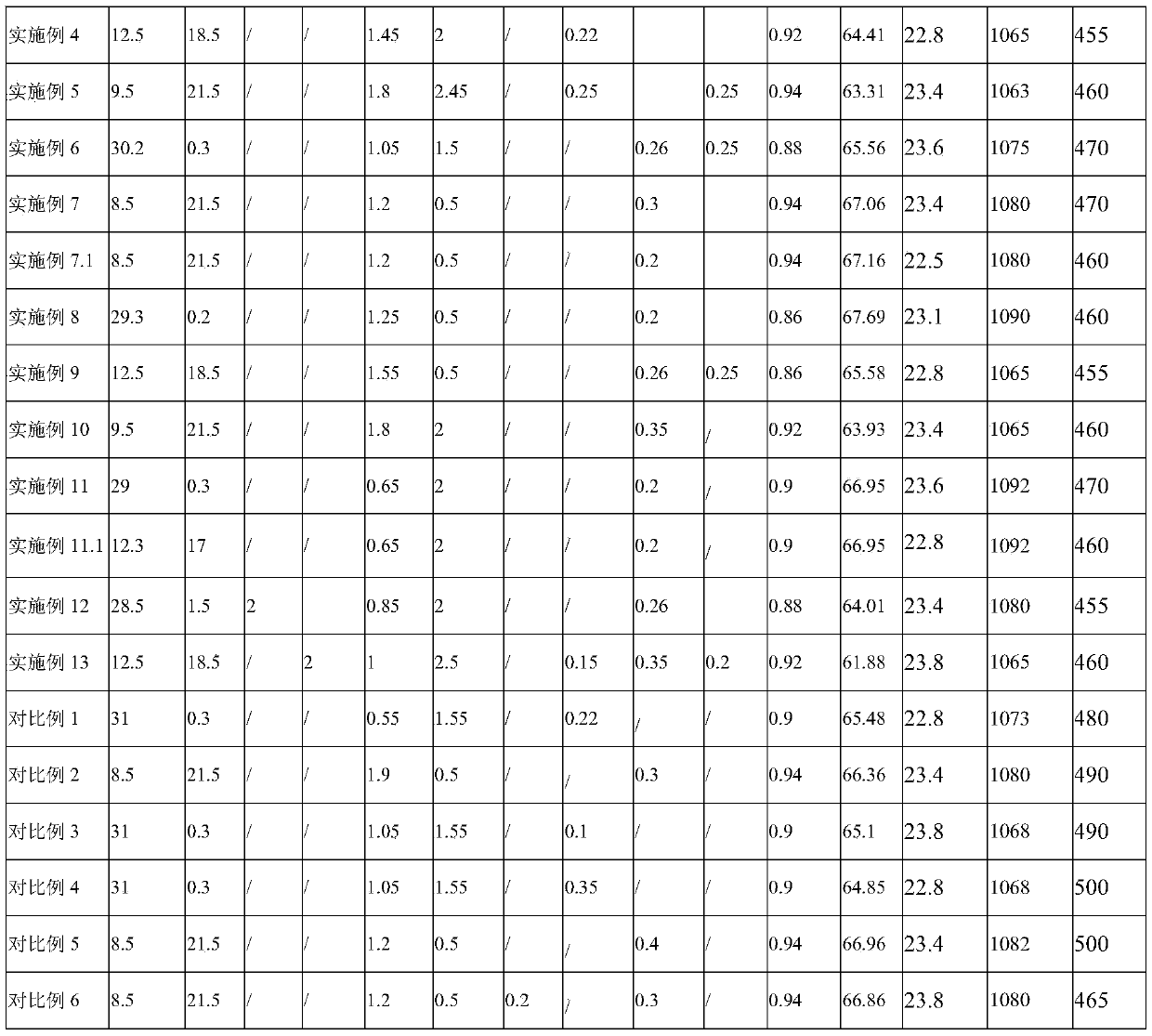
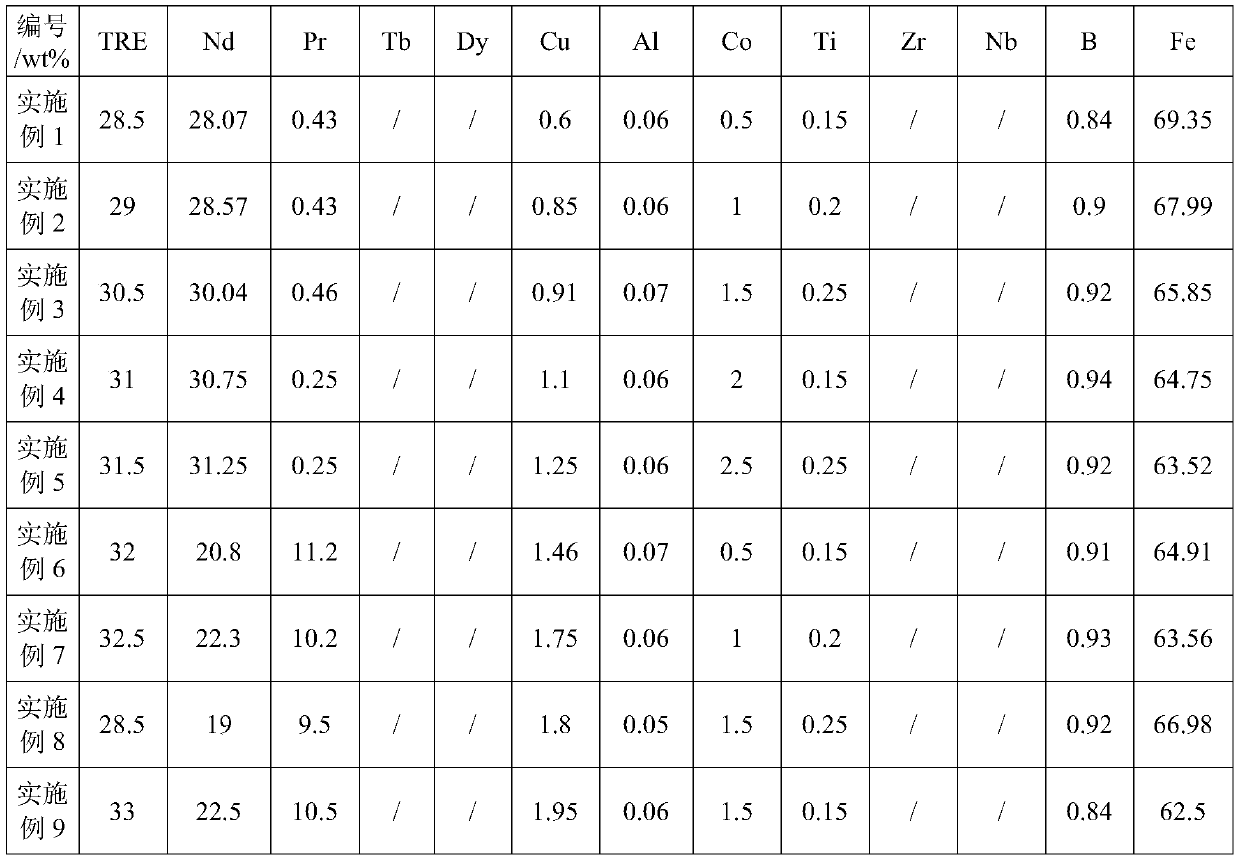
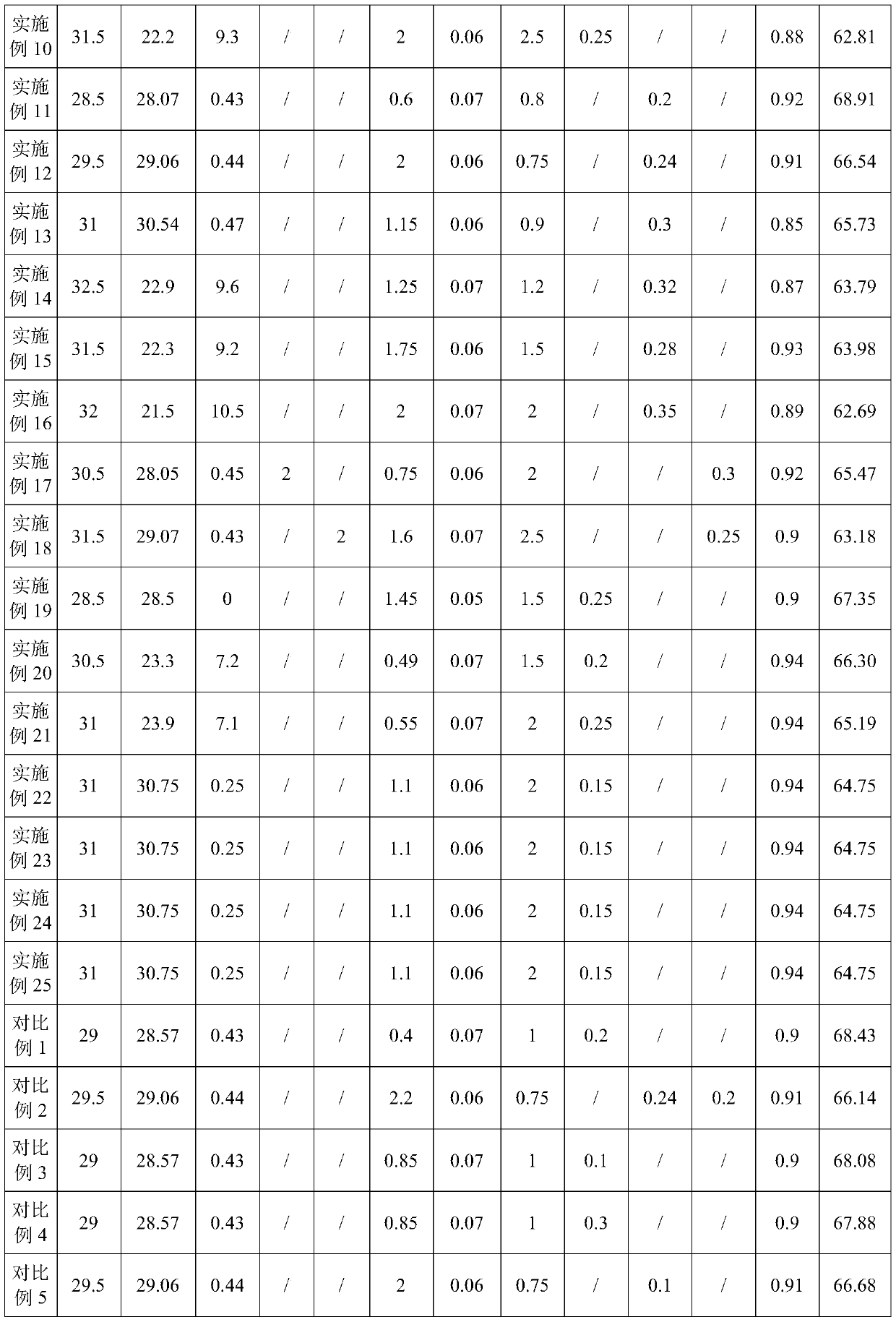
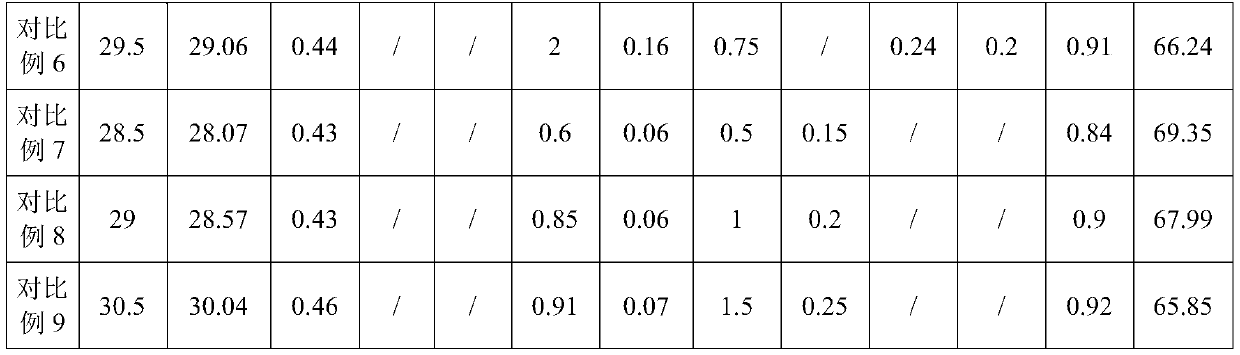
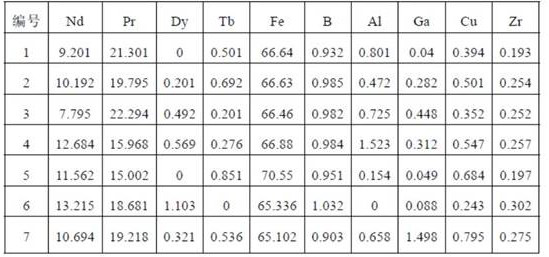
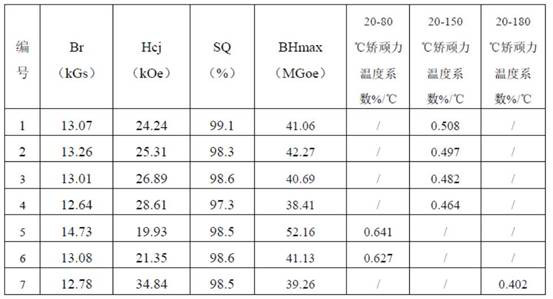
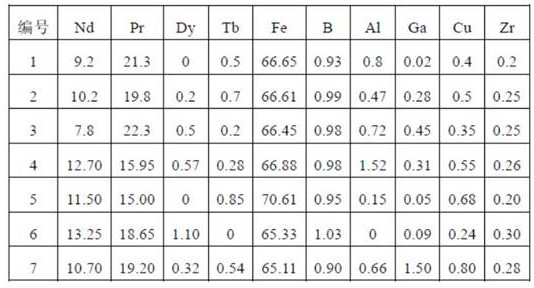
The invention discloses an R-T-B series magnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The R-T-B series magnetic material provided by the invention comprises the following components (1) to (6) in percentage by weight: (1) 29.50wt.% to 33.00wt.% of R, wherein R is a rare earth element and comprises Pr and RH, Pr is greater than or equal to 15.00wt.%, and RH comprises Tb and / or Dy; (2) 0.24wt.% to 0.80wt.% of Cu; (3) 0.05wt.% to 0.50wt.% of Ti, and / or 0.10wt.% to 1.20wt.% of Nb; (4) 0wt.% to 1.52wt.% of Al; (5) 0.90wt.% to 1.03wt.% of B; and (6) 0.05wt.% to 1.50wt.% of Ga. The material hasgood residual magnetism, coercive force and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111326304AGood remanenceGood coercivityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMagnetMetallurgy
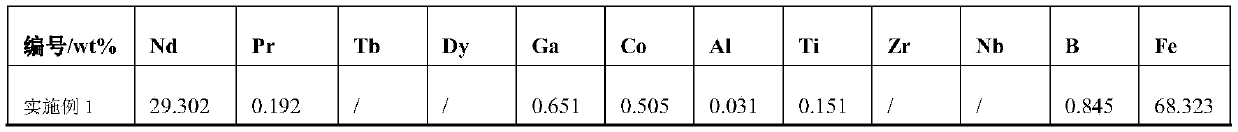
The invention discloses a rare earth permanent magnet material and a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the rare earth permanent magnet material comprises thefollowing components in percentage by mass: 28.5-33.0% of R, 0.5%-1.8% of Ga, but not 0.5 wt% of Ga, 0.84%-0.94% of B, 0.05 to 0.07% of Al, and <=2.5% but not 0 of Co, 62-69% of Fe; N is one or moreof Ti, Zr and Nb; when N contains Ti, the content of Ti is 0.15%-0.25%; when N contains Zr, the content of Zr is 0.2%-0.35%; when N contains Nb, the content of Nb is 0.2%-0.5%; and the percentage is the mass percentage of each component in the total mass of the raw material composition. The rare earth permanent magnet material has better magnetic properties (residual magnetism, coercive force, squareness and temperature stability), and the magnetic properties of the same batch of products are uniform.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
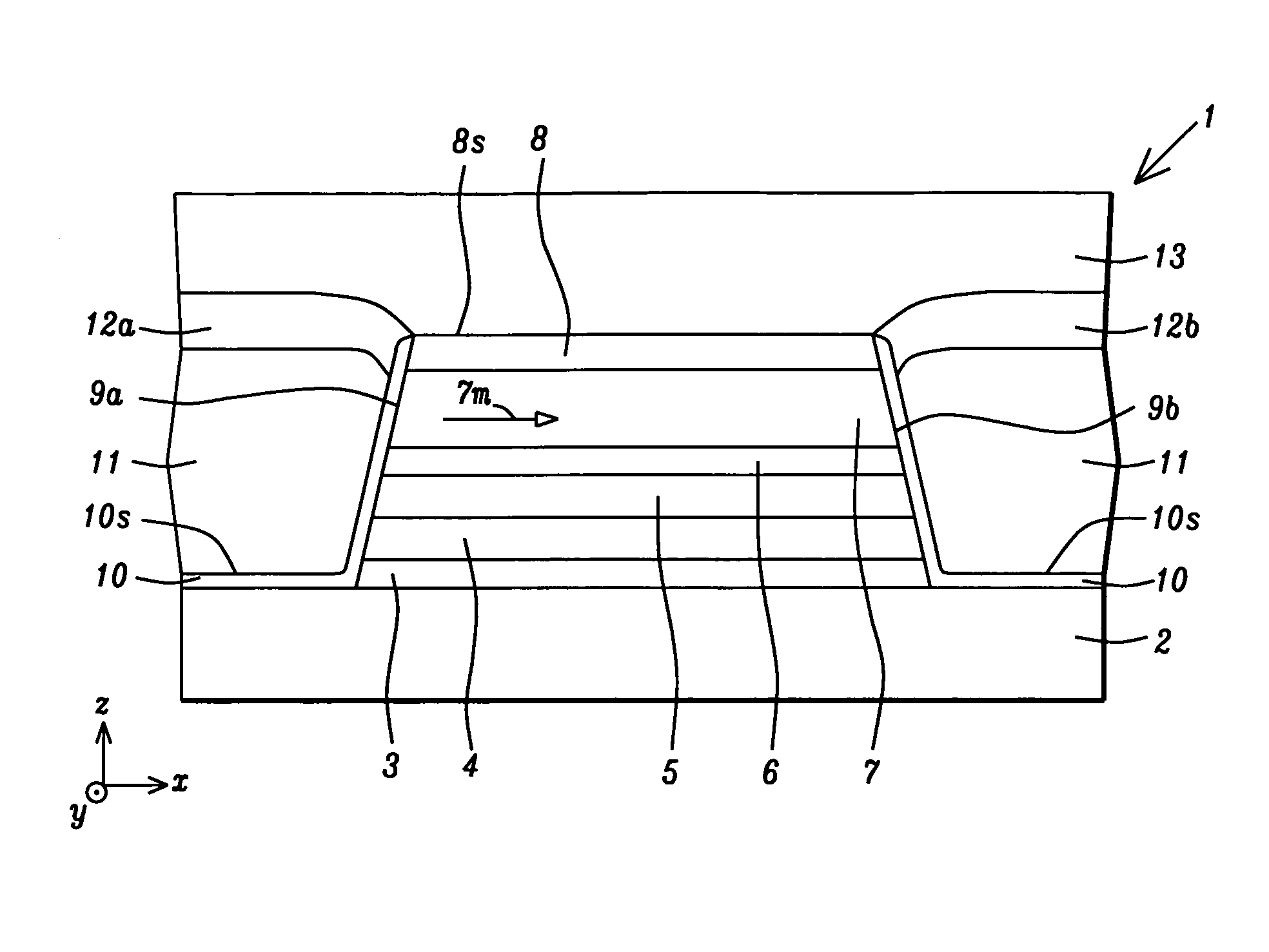
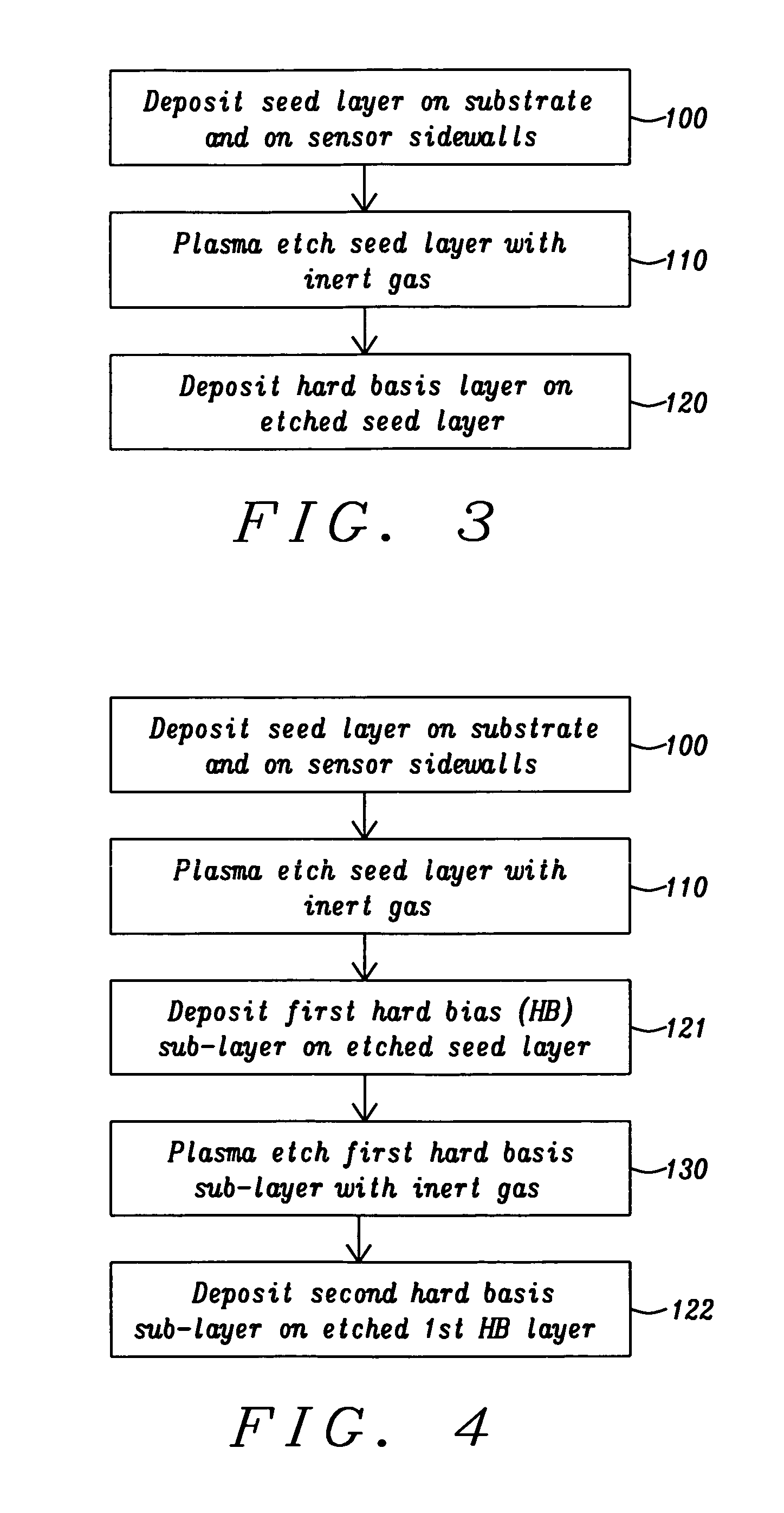
Method for fabricating a high coercivity hard bias structure for magnetoresistive sensor
ActiveUS9034149B2Good coercivityImprove recording densityMagnetic measurementsHeads using thin filmsHigh concentrationEngineering
A hard bias (HB) structure for longitudinally biasing a free layer in a MR sensor is disclosed that includes a mildly etched seed layer and a hard bias (HB) layer on the etched seed layer. The HB layer may contain one or more HB sub-layers stacked on a lower sub-layer which contacts the etched seed layer. Each HB sub-layer is mildly etched before depositing another HB sub-layer thereon. The etch may be performed in an IBD chamber and creates a higher concentration of nucleation sites on the etched surface thereby promoting a smaller HB average grain size than would be realized with no etch treatments. A smaller HB average grain size is responsible for increasing Hcr in a CoPt HB layer to as high as 2500 to 3000 Oe. Higher Hcr is achieved without changing the seed layer or HB material and without changing the thickness of the aforementioned layers.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
R-t-b based permanent magnet
ActiveUS20170278602A1Favorable coercivity and magnetization propertyIncrease ratingsTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare-earth elementCrystallite
An R-T-B based permanent magnet includes R-T-B based compounds as main-phase crystal grains. R is a rare earth element. T is iron group element(s) essentially including Fe or Fe and Co. B is boron. A two-grain boundary is contained between the two adjacent main-phase crystal grains. An average grain size of the main-phase crystal grains is 0.9 μm or more and 2.8 μm or less. A thickness of the two-grain boundary is 5 nm or more and 200 nm or less.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method of improving coercivity of sintering Nd-Fe-B magnetic material
The invention discloses a method of improving the coercivity of sintering Nd-Fe-B magnetic materials. The method includes the following steps of using hydrogen to crush Nd-Fe-B alloy, powder processing, compression moulding, sintering and tempering under the protection of vacuum or protective gases. The sintering condition consists of heating to 300 to 600 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 5 to 6 hours to dehydrogenize, heating once again to 1060 to 1120 DEG C, sintering for 1 to 60 minutes under high temperature, finally decreasing the temperature to 1000 to 1050 DEG C, keeping sintering for 1 to 4 hours under the temperature and cooling. The method adopts the steps of sintering for a short period under high temperature to precipitate the liquid phase and then sintering under lower temperature. The liquid phase is rapidly precipitated under high temperature, thereby improving the sintering process of the magnetic materials, promoting the performance of sintering process, controlling the grain size through sintering under lower temperature, inhabiting grain growth and benefiting obtaining an excellent coercivity of magnetic materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGHANG NEW MATERIAL
Neodymium iron boron material and preparation method and application thereof
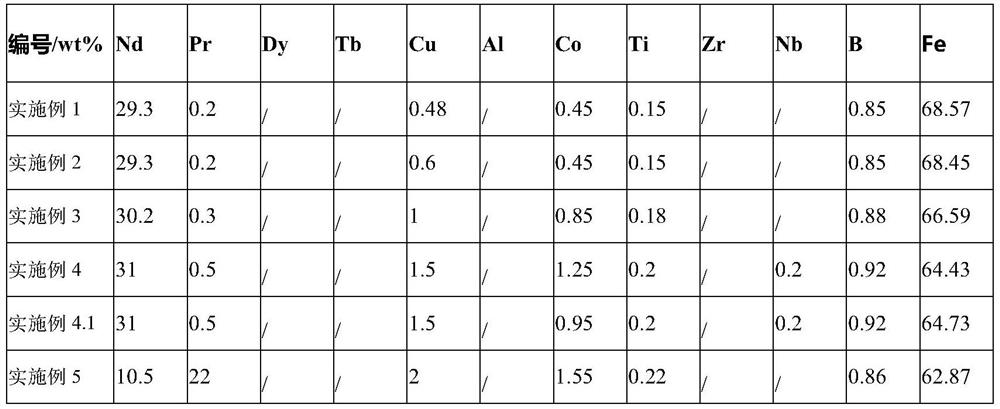
ActiveCN111312462AGood remanenceGood coercivityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementBoron
The invention discloses a neodymium iron boron material and a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the neodymium iron boron material comprises the following components by mass: 28.5-34% of R; R is a rare earth element and comprises Nd; 0.84%-0.94% of B; Cu: 0.45 < Cu < = 2%; Co: < = 2.5%, but not 0; Fe: 61 to 69 %; N, containing one or more of Ti, Zr and Nb.When N contains Ti, the content of Ti is 0.15%-0.25%. When N contains Zr, the content of Zr is 0.2%-0.35%. When N contains Nb, Nb is 0.2%-0.5%; wherein the percentage is the mass percentage of each component in the total mass of the raw material composition. According to the neodymium iron boron material, on the premise of not adding heavy rare earth elements, the neodymium iron boron material which is good in magnetic performance and uniform in magnetic performance in the same batch can still be prepared by adopting a low-boron aluminum-free system.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Rare earth permanent magnet material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111312463ARandom combinationGood remanenceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementAluminium
The invention discloses a rare earth permanent magnet material and a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the rare earth permanent magnet material comprises thefollowing components: R: 28.5-33%, R beig a rare earth element and comprising Nd; B: 0.84%-0.94% of the total weight of the raw materials; Ga: 0.6 < Ga < = 1.8%; Co: < = 2.5%; Fe: 61.6-69 %; wherein Ncomprises one or more of Ti, Zr and Nb. When N contains Ti, the content of Ti is 0.15%-0.25%. When N contains Zr, the content of Zr is 0.2%-0.35%. When N contains Nb, Nb is 0.2%-0.5%, wherein the percentage is the percentage of each component in the total mass of the rare earth permanent magnet material. According to the rare earth permanent magnet material, under the condition that no heavy rareearth element is added, a low-boron aluminum-free system is adopted, the magnetic properties such as residual magnetism, coercive force, temperature stability and squareness are still good, and meanwhile the magnetic properties of permanent magnet materials of the same batch are uniform.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Neodymium iron boron material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111243811AGood remanenceGood coercivityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementMetallurgy
The invention discloses a neodymium iron boron material and a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the neodymium-iron-boron material comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 28.5-33.0% of R and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, r is a rare earth element at least containing Nd; 0.45%-2% of Cu, but not 0.45% of Cu; b: 0.84%-0.94% ofthe total weight of the raw materials; 0.05 to 0.07% of Al; co: < = 2.5% but not 0; 62 to 70 percent of Fe; n is one or more of Ti, Zr and Nb; when N contains Ti, the content of Ti is 0.15%-0.25%; when N contains Zr, the content of Zr is 0.2%-0.35%; when N contains Nb, the content of Nb is 0.2%-0.5%; wherein the percentage is the mass percentage of each component in the total mass of the raw material composition. The neodymium iron boron material is good in magnetic performance, and the magnetic performance of products of the same batch is uniform.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
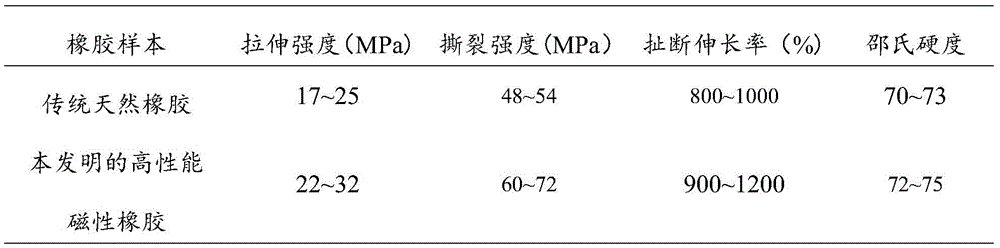
High-performance magnetic rubber and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-performance magnetic rubber and a preparation method of the high-performance magnetic rubber. The high-performance magnetic rubber is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 41.225 percent of natural rubber, 5.154 percent of SrO.6Fe2O3, 1.296 percent of peroxide vulcanizing agent, 2.945 percent of ZnO, 0.353 percent of stearic acid, 0.294 percent of accelerator, 0.353 percent of anti-aging agent, 47.114 percent of carbon black, 0.353 percent of plasticizer, 0.471 percent of paraffin and 0.442 percent of fatty acid. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the high-performance magnetic rubber. The high-performance magnetic rubber disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high strength, high temperature resistance, oil resistance, cold resistance, tensile resistance, aging resistance and good vibration damping performance, the damping characteristic of the natural rubber is enlarged, the manufacturing cost is saved, and the requirements of vibration damping products in the high-performance and high-technology field such as automobiles, engineering machinery, hydraulic transmission, aviation and navigation can be met.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Preparation method of high-strength magnetically soft alloy bar
ActiveCN113539653AHigh strengthIncrease contentInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsSolution treatmentIngot casting
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-strength magnetically soft alloy bar, wherein a high-strength magnetically soft alloy is prepared by optimizing chemical components and a process, and the high-strength magnetically soft alloy bar comprises the following components in percentage by mass: less than or equal to 0.04% of C, less than or equal to 0.30% of Si, less than or equal to 0.30% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S, less than or equal to 0.20% of Cu, less than or equal to 0.50% of Ni, 48.0-51.0% of Co, 1.80-2.10% of V, 0.1-0.2% of Mo and the balance of Fe. The preparation process comprises the steps of vacuum melting, alloy ingot casting, forging cogging, finished product hot rolling and solution treatment. According to the invention, the tensile strength of the prepared high-strength magnetically soft alloy bar 1J22MV is larger than 500 MPa, the yield strength is greater than or equal to 250MPa, B800 is greater than or equal to 1.8 T, B2400 is greater than or equal to 2.1 T, B4000 is greater than or equal to 2.15 T, B8000 is greater than or equal to 2.2 T, the coercive force Hc is less than or equal to 144A / m, the Curie point is 980 DEG C, and the saturation magnetostriction coefficient (10<-6>) is 60-100.
Owner:西安钢研功能材料股份有限公司
Preparation method of neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material
ActiveCN113096952AReduce replacementSmall residual magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementCompression molding
The invention relates to the technical field of neodymium-iron-boron magnetic materials, in particular to a preparation method of a neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material, which comprises the preparation steps of melt-spinning, hydrogen demolishing and grinding, compression molding, magnetism generation and sheet preparation, rare earth pulping, slurry coating and diffusion sintering. The diffusion of heavy rare earth elements such as dysprosium and terbium in the crystalline phase can be effectively promoted, meanwhile, diffusion of the rare earth elements into main phase grains is inhibited, the effective utilization rate of heavy rare earth elements such as dysprosium and terbium is increased, and the coercive force of the neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material is greatly improved.
Owner:宁波合力磁材技术有限公司
A treatment agent for forming rare earth hydride particle coating and electrodeposition method for forming coating
ActiveCN103556208BImprove magnetic propertiesStrong magnetismElectrolytic coatingsMagnetic materialsMetallurgyRare-earth magnet
The invention relates to a treating agent and an electro-deposition method for forming a rare earth hydride particle coating, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials. Rare earth hydride particles are dispersed in a dispersing agent, wherein n-hexane or n-heptane is taken as the dispersing agent; the rare earth is at least one element of Pr, Nd, Tb, Dy and Ho. The hydride particles are deposited on the surface of a sintered NdFeB rare earth magnet by using the electro-deposition method so as to form the uniform and dense coating with controllable thickness. The rare earth hydride particle coating can be used for obviously improving the magnetic property of the sintered NdFeB rare earth magnet and especially the coercivity of the magnet. As the method is adopted, the usage amounts of heavy rare earths in the sintered NdFeB rare earth is decreased on the premise of guaranteeing good magnetic property of the magnet, so that the manufacturing cost of the magnet with high coercivity is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
A kind of epitaxial growth method of yttrium iron garnet film
ActiveCN106048726BQuality improvementPreparation parameters are easy to adjustPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHigh energyRoom temperature
An epitaxial growth method of a yttrium iron garnet film comprises the following steps: vacuumizing a vacuum cavity with a treated yttrium iron garnet substrate to be 8.6+ / -1*10-6 Pa, and heating the yttrium iron garnet substrate to the constant temperature which is 736 DEG C; in a heating process, feeding ozone when heating to the temperature of 250 DEG C; after heating to the temperature of 736 DEG C, maintaining air pressure of the vacuum cavity, adjusting the mass fraction of the ozone to be 40%, meanwhile insulating for half a hour, and starting a reflective high-energy electron diffraction instrument (RHEED) to adjust so as to obtain diffraction spots of a substrate; maintaining real-time and in-situ monitoring of the RHEED in the whole process, and focusing laser onto a YIG target through a lens by using a KrF excimer laser of which the wavelength is 248 nm; after growth of the film is finished, maintaining the temperature of the substrate unchanged, annealing in situ for 15 minutes, then naturally cooling the film to the temperature about 250 DEG C, stopping protective gas and cooling to the room temperature. The obtained YIG film has uniform components, is controllable in thickness and good in process repeatability, and has high preparation efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A kind of r-t-b magnetic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111627633BGood remanenceGood coercivityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementRemanence
The invention discloses an R-T-B-based magnetic material, which is characterized in that, in terms of weight percentage, it comprises the following components: 27.42wt.% to 33.00wt.% of R; the R is a rare earth element , which contains Pr and R H ; said Pr≥15.00wt.%; said R H Contains Tb and / or Dy; 0.24wt.% to 0.80wt.% Cu; 0.19wt.% to 0.30wt.% Zr; 0wt.% to 1.52wt.% Al; 0.90wt.% to 1.03wt. % B; and, 0.04 wt.% to 0.09 wt.% Ga or 0.28 wt.% to 1.50 wt.% Ga. The magnetic material has better remanence, coercive force, temperature coefficient, etc.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
A kind of neodymium iron boron material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111312462BGood remanenceGood coercivityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementMetallurgy
The invention discloses a neodymium iron boron material, a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the NdFeB material includes the following components in mass content: R: 28.5-34%; R is a rare earth element, and R includes Nd; B: 0.84-0.94%; Cu: 0.45%
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGTING GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of soft magnetic alloy bar
ActiveCN113539653BHigh strengthIncrease contentInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsSolution treatmentChemical composition
Owner:西安钢研功能材料股份有限公司
Wireless charging magnetic sheet screening method
ActiveCN108558386AImprove performanceGood coercivityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic coreEnvironmentally friendly
The invention discloses a wireless charging magnetic sheet screening method which comprises the following steps: selecting and stirring ferrite powder with uniform granularity and high activity, adding TbFx and copper-tin alloy powder into a stirrer step by step for stirring, then introducing an ingredient additive, performing doping treatment and pre-sintering treatment, pressing the mixture intoa strip-type green body, and cleaning, drying, cutting and grinding the green body in sequence to obtain a magnetic core. The method is environmentally friendly and low in energy consumption; a magnetic core product is high in performance and high in reliability.
Owner:山东恒瑞磁电科技有限公司
R-T-B based permanent magnet
ActiveUS10529473B2Increase ratingsEasily magnetizedTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare-earth elementIron group
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
A kind of preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnetic material
ActiveCN113096952BReduce replacementSmall residual magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementDysprosium
This application relates to the technical field of NdFeB magnetic materials, and specifically relates to a preparation method of NdFeB magnetic materials, including melting and stripping, hydrogen crushing and grinding, compression molding, raw magnetic sheeting, rare earth pulping, coating slurry and The preparation steps of diffusion sintering can effectively promote the diffusion of heavy rare earth elements such as dysprosium and terbium in the crystalline phase, and at the same time inhibit their diffusion into the main phase grains, improve the effective utilization of heavy rare earth elements such as dysprosium and terbium, and greatly Improve the coercive force of NdFeB magnets.
Owner:宁波合力磁材技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com