Treating agent and electro-deposition method for forming rare earth hydride particle coating
A rare earth hydride and treatment agent technology, applied in coatings, circuits, electrolytic coatings, etc., can solve the loss of magnet saturation magnetization, the thickness and distribution uniformity of hydride nanoparticle coatings are difficult to control, and the coating effect is unstable. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
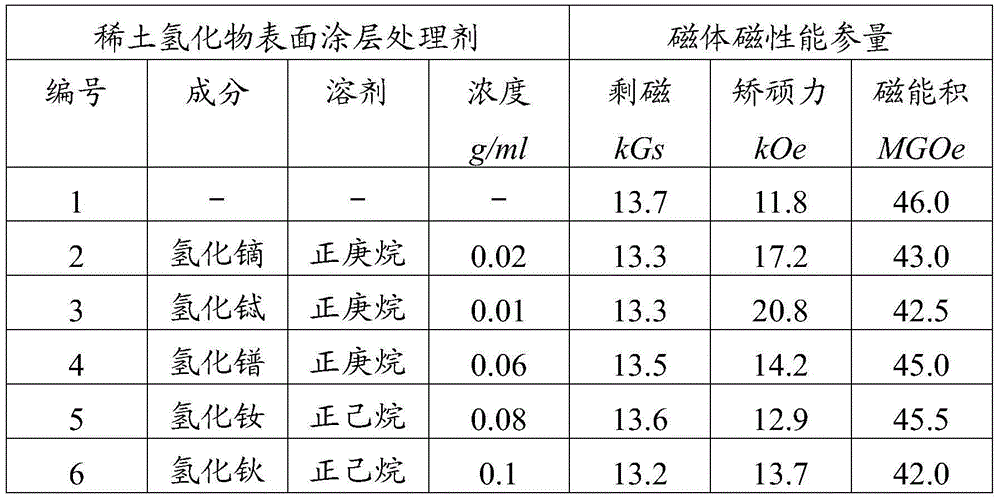
[0014] Mix 20 g of rare earth dysprosium hydride particles with a particle diameter of 100 nanometers and 1000 ml of n-heptane solution evenly, so that dysprosium hydride is uniformly dispersed in n-heptane, and electromagnetic stirring is used to ensure that the concentration of each place in the electrolytic cell is consistent. The concentration of the suspension that forms the dysprosium hydride particle coating is 0.02 g / ml (since the volume of the obtained suspension is basically the same as that of the dispersant, the same below).
[0015] The sintered NdFeB magnet (see the No. 1 magnet in Table 2 for its magnetic properties) was prepared into a small piece with an outer dimension of 10×10×3.5 mm, and its surface was polished. Connect the processed magnet to the cathode, and the anode uses a stainless steel sheet with an area slightly larger than the area facing the magnet. The distance between the cathode and the anode is controlled at about 2.5cm, the electrodeposition ...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Mix 10 g of rare earth terbium hydride particles with a particle diameter of 100 nanometers and 1000 ml of n-heptane solution evenly, so that terbium hydride is evenly dispersed in n-heptane, and electromagnetic stirring is used to ensure that the concentration of each place in the electrolytic cell is consistent. A suspension of terbium hydride particle coating was formed at a concentration of 0.01 g / ml.
[0018] The sintered NdFeB magnet (see the No. 1 magnet in Table 2 for its magnetic properties) was prepared into a small piece with an outer dimension of 10×10×3.5 mm, and its surface was polished. Connect the processed magnet to the cathode, and the anode uses a stainless steel sheet with an area slightly larger than the area facing the magnet. The distance between the cathode and the anode is controlled at about 2.5cm, the electrodeposition voltage is controlled at 150v, the electrodeposition current is controlled at 40mA, and after 220 seconds of electrodeposition ...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Evenly mix 60 g of rare earth praseodymium hydride particles with a particle diameter of 150 nanometers and 1000 ml of n-heptane solution, so that praseodymium hydride is evenly dispersed in n-heptane, and electromagnetic stirring is used to ensure that the concentration in the electrolytic cell is consistent everywhere, and the preparation for A suspension of the praseodymium hydride particle coating was formed at a concentration of 0.06 g / ml.
[0021] The sintered NdFeB magnet (see the No. 1 magnet in Table 2 for its magnetic properties) was prepared into a small piece with an outer dimension of 10×10×3.5 mm, and its surface was polished. Connect the processed magnet to the cathode, and the anode uses a stainless steel sheet with an area slightly larger than the area facing the magnet. The distance between the cathode and the anode is controlled at about 2.5cm, the electrodeposition voltage is controlled at 150v, and the electrodeposition current is controlled at 40mA....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com