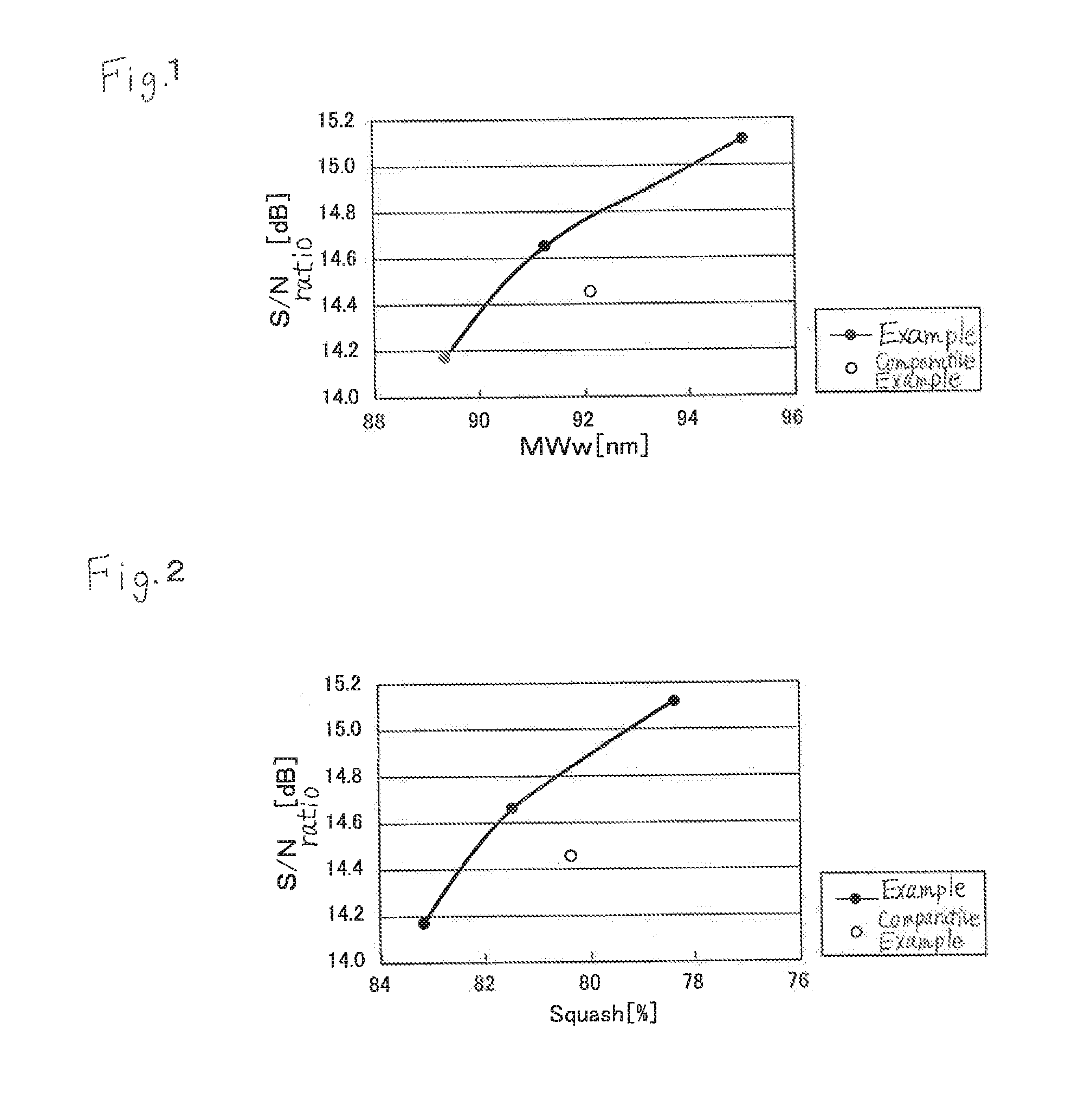
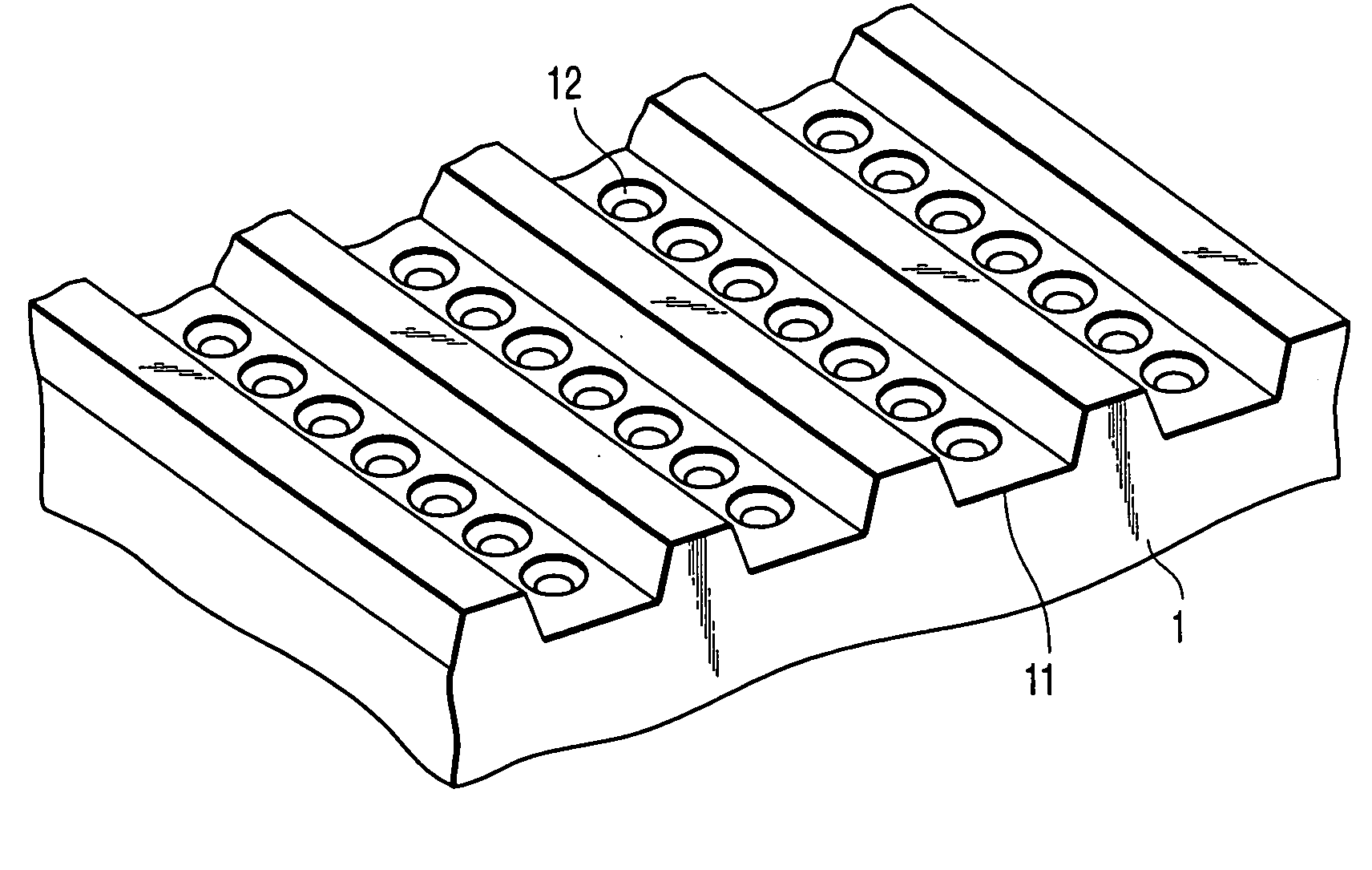
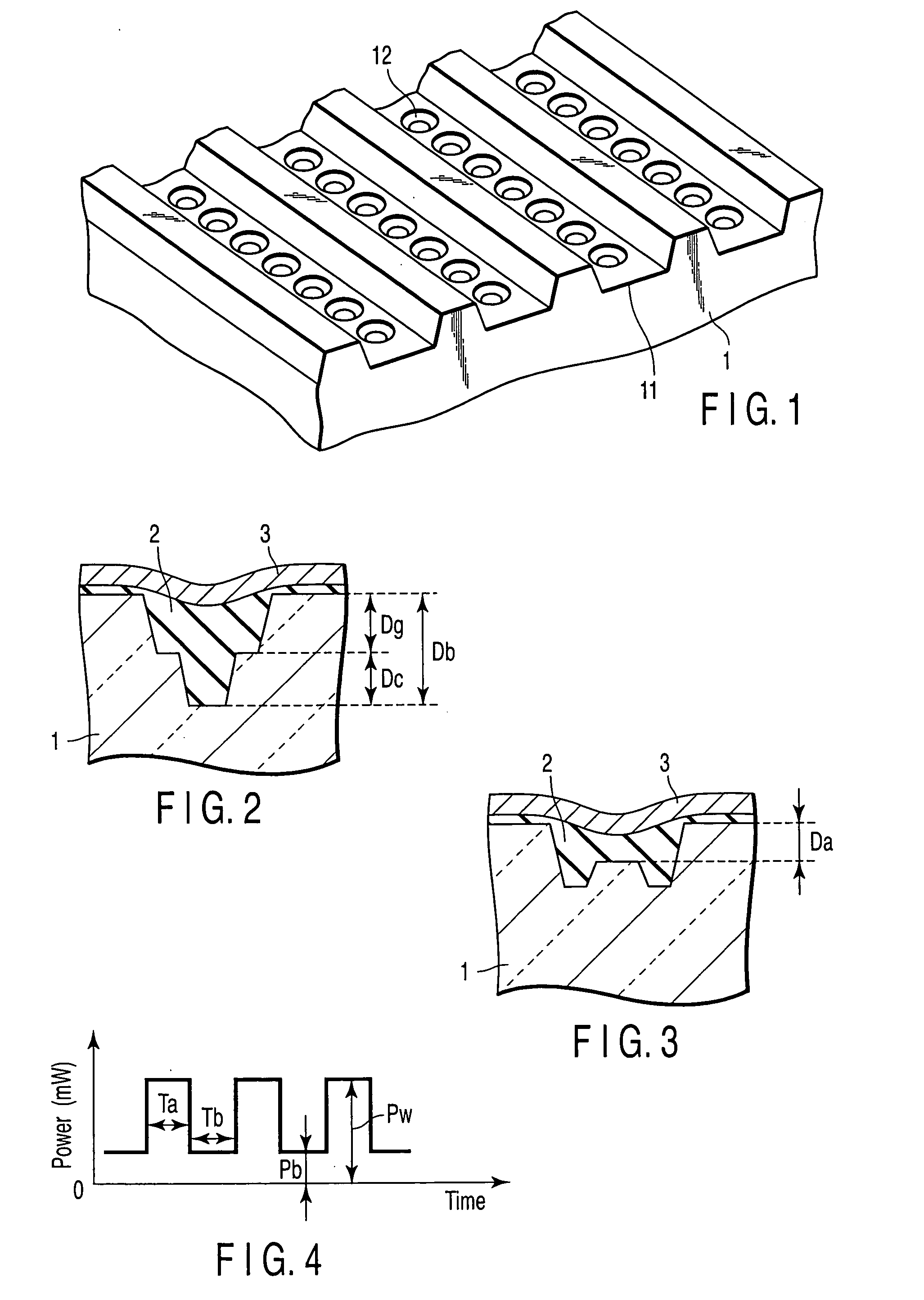
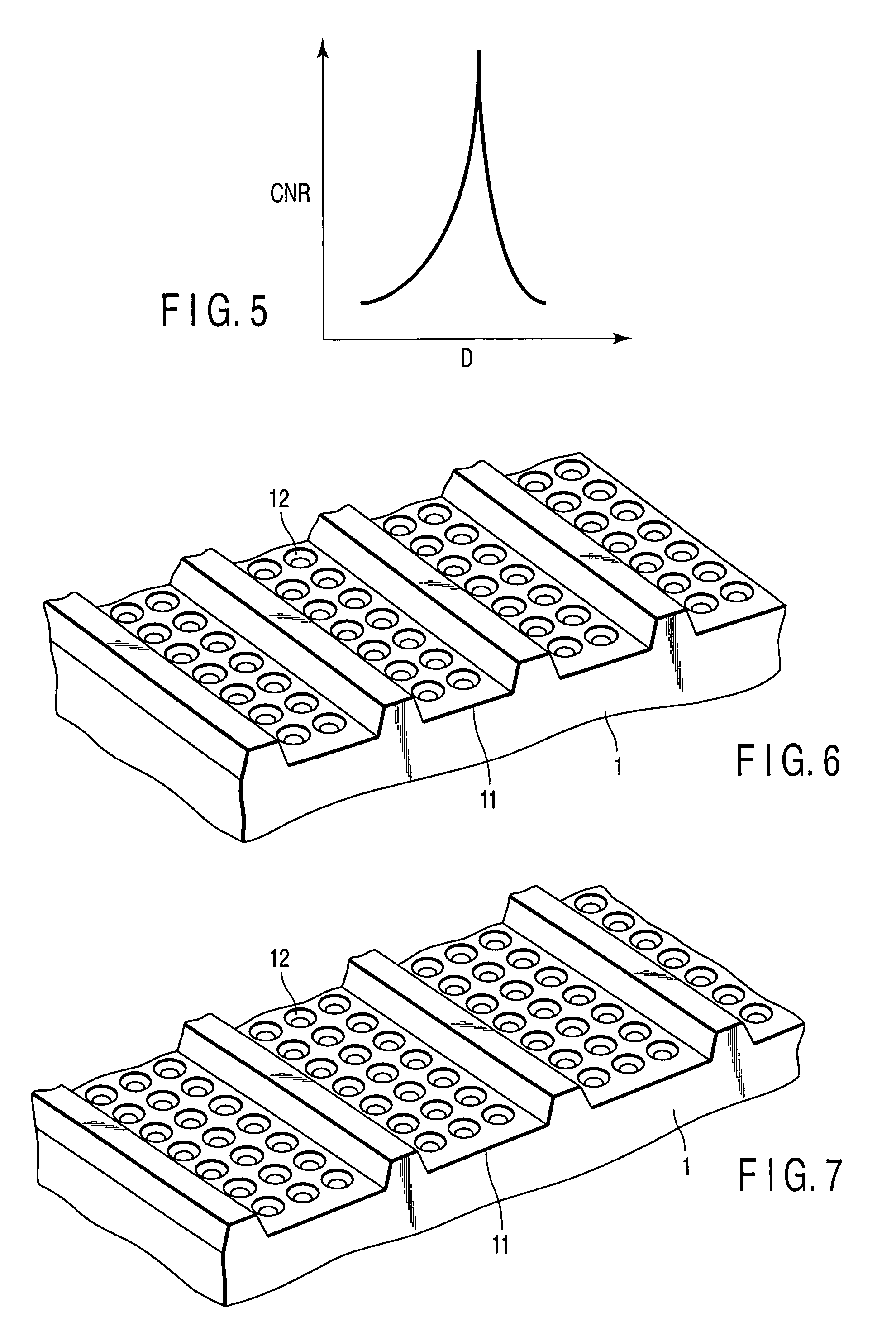
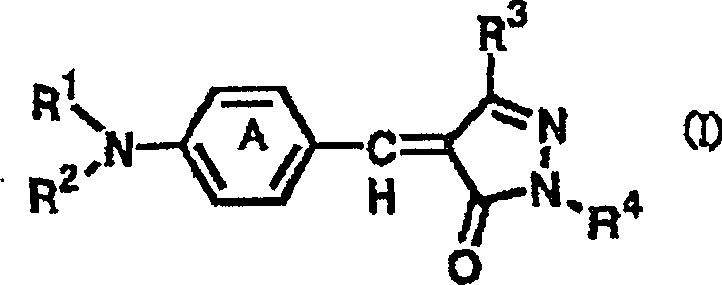
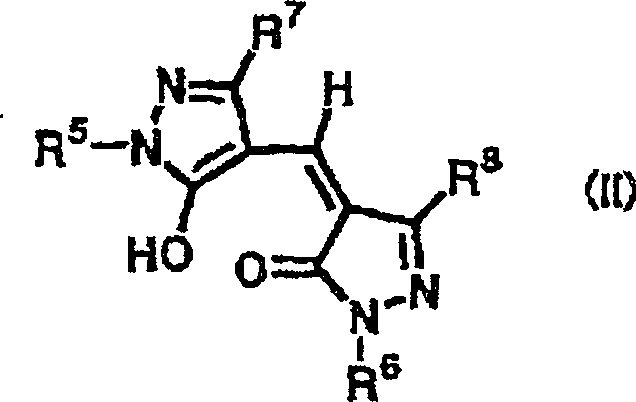
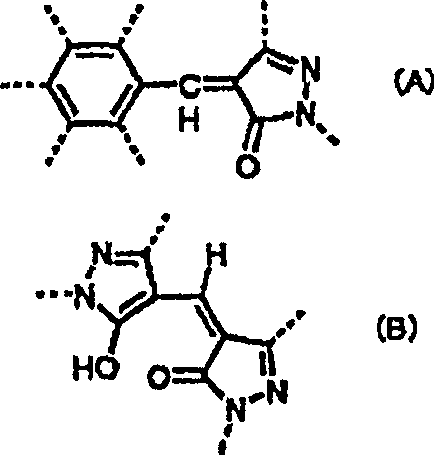
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "High recording density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
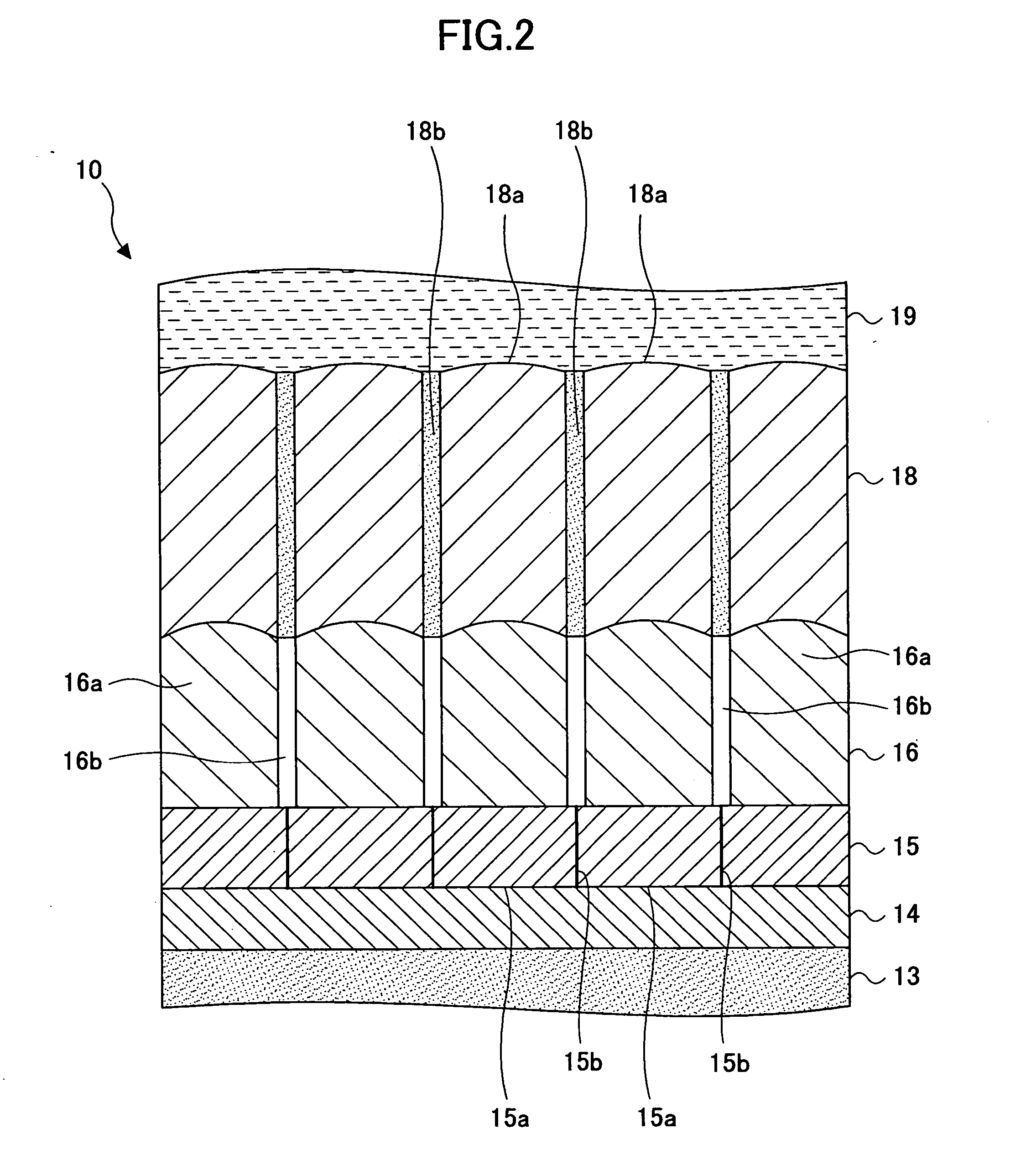
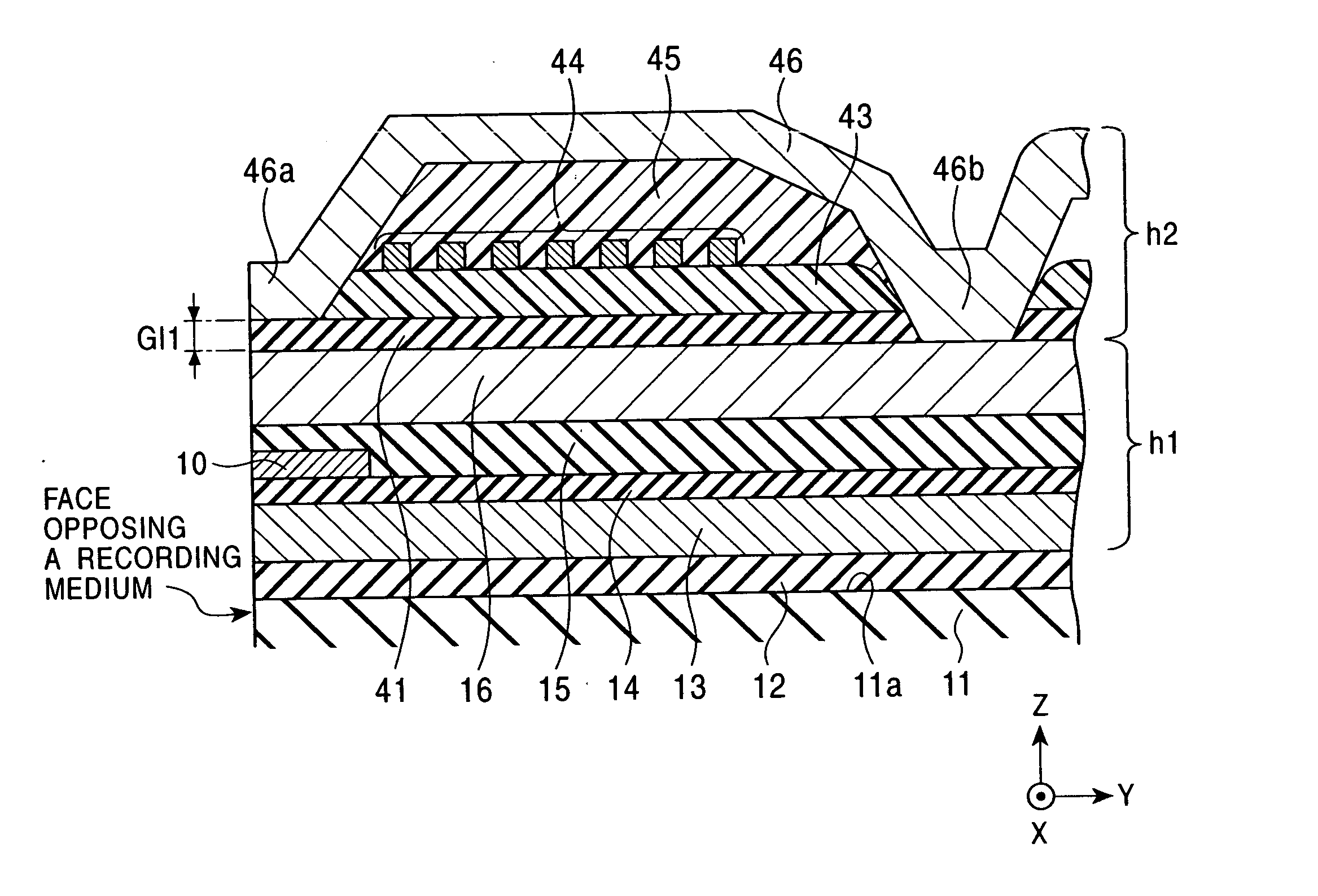
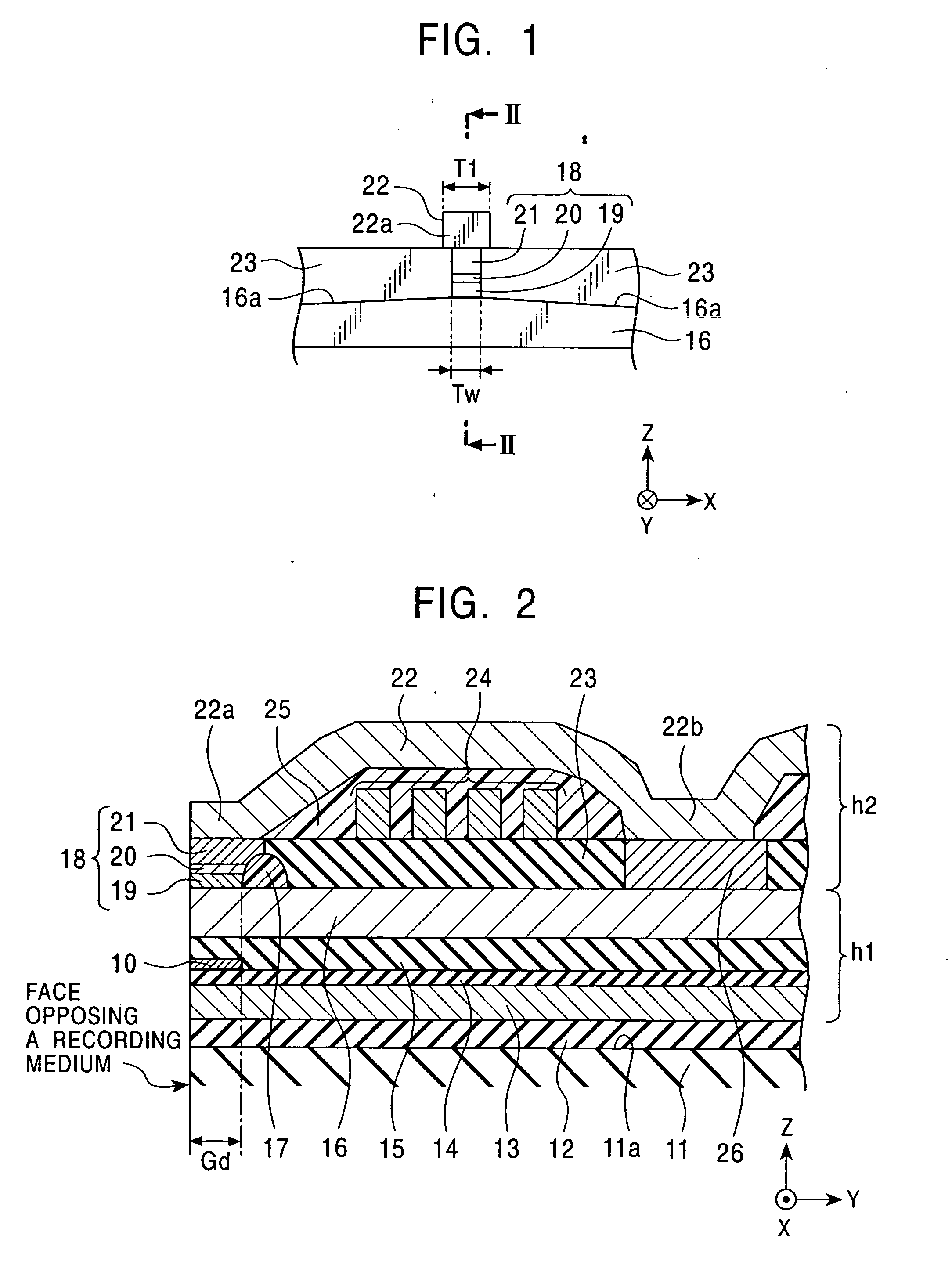
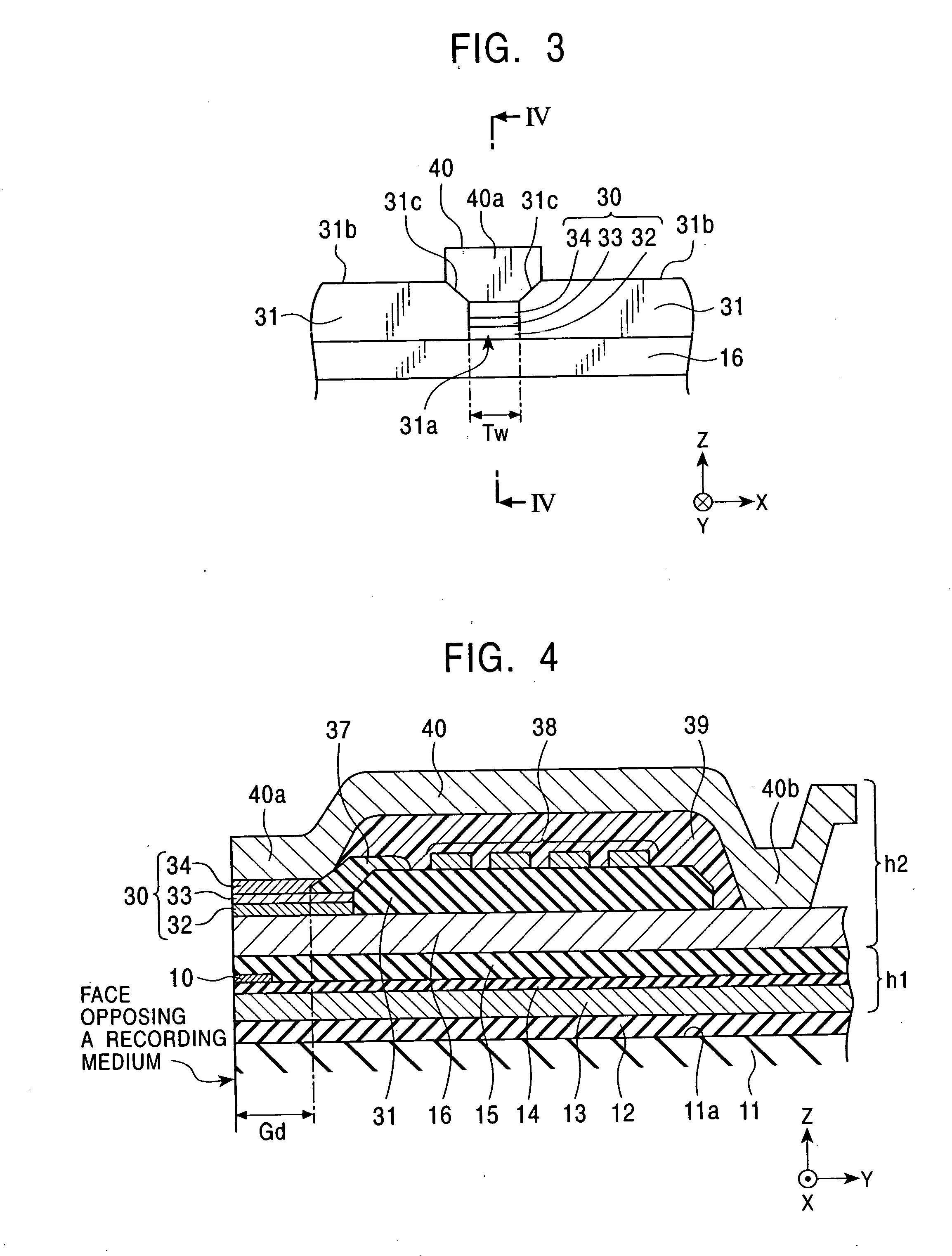
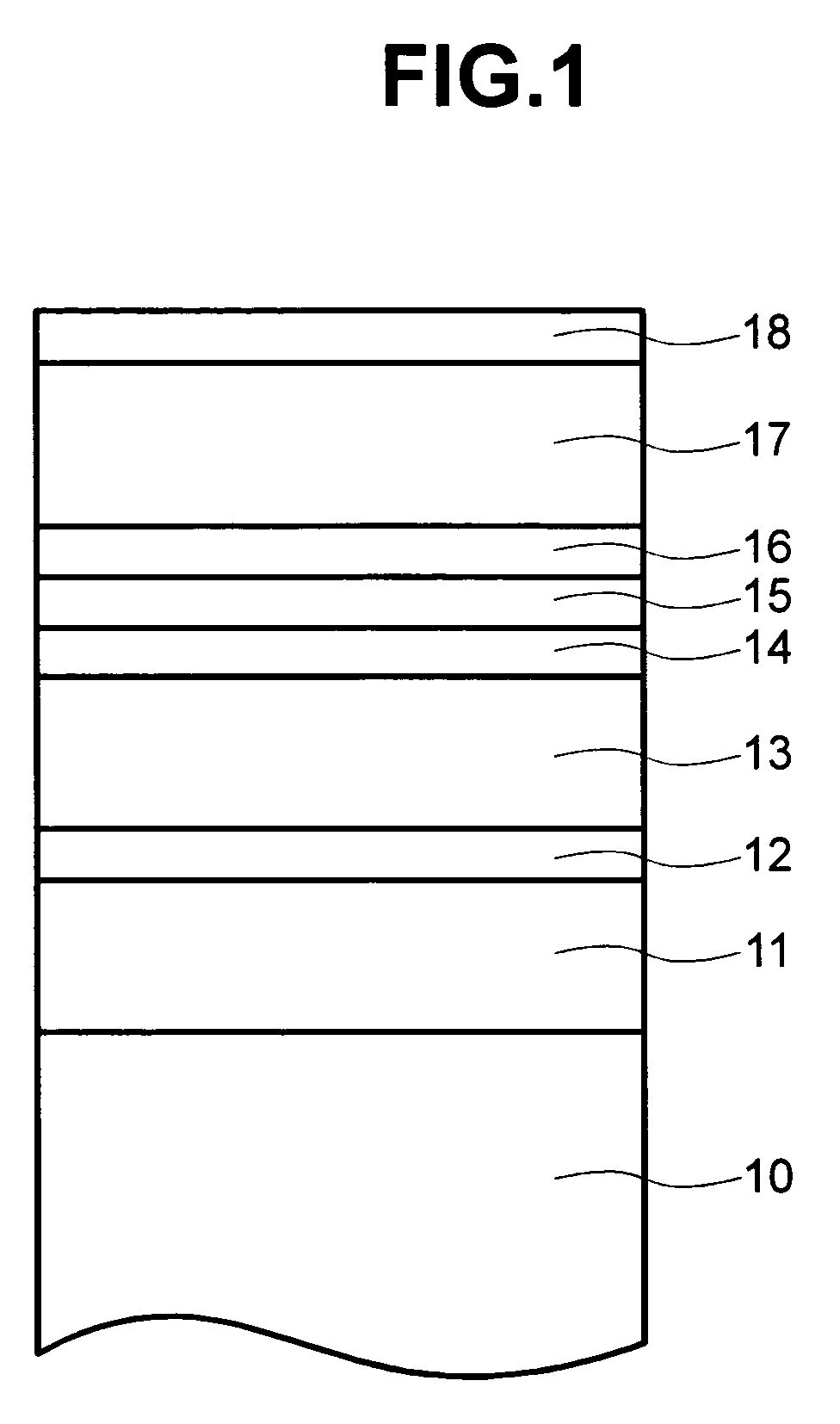
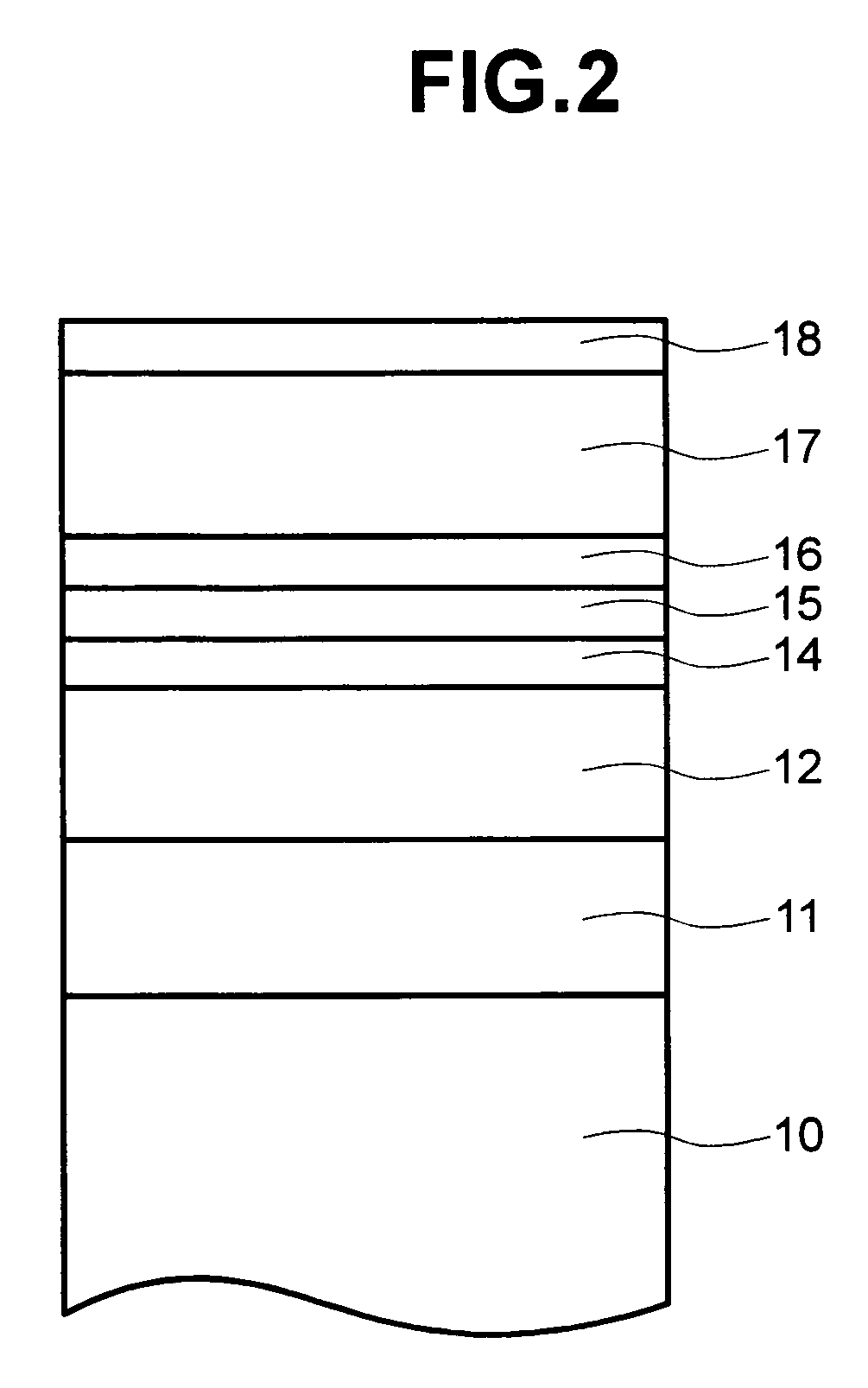
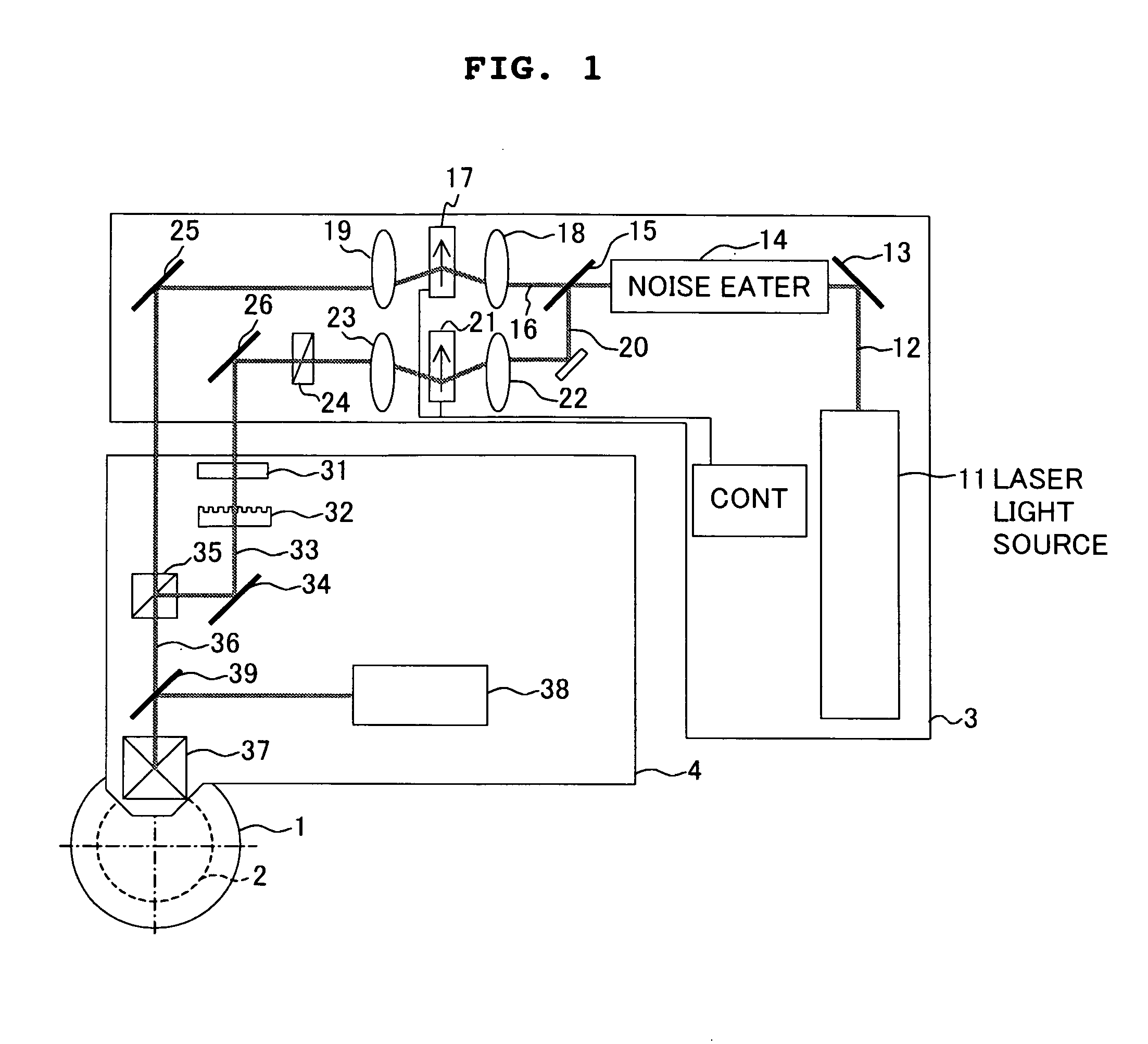
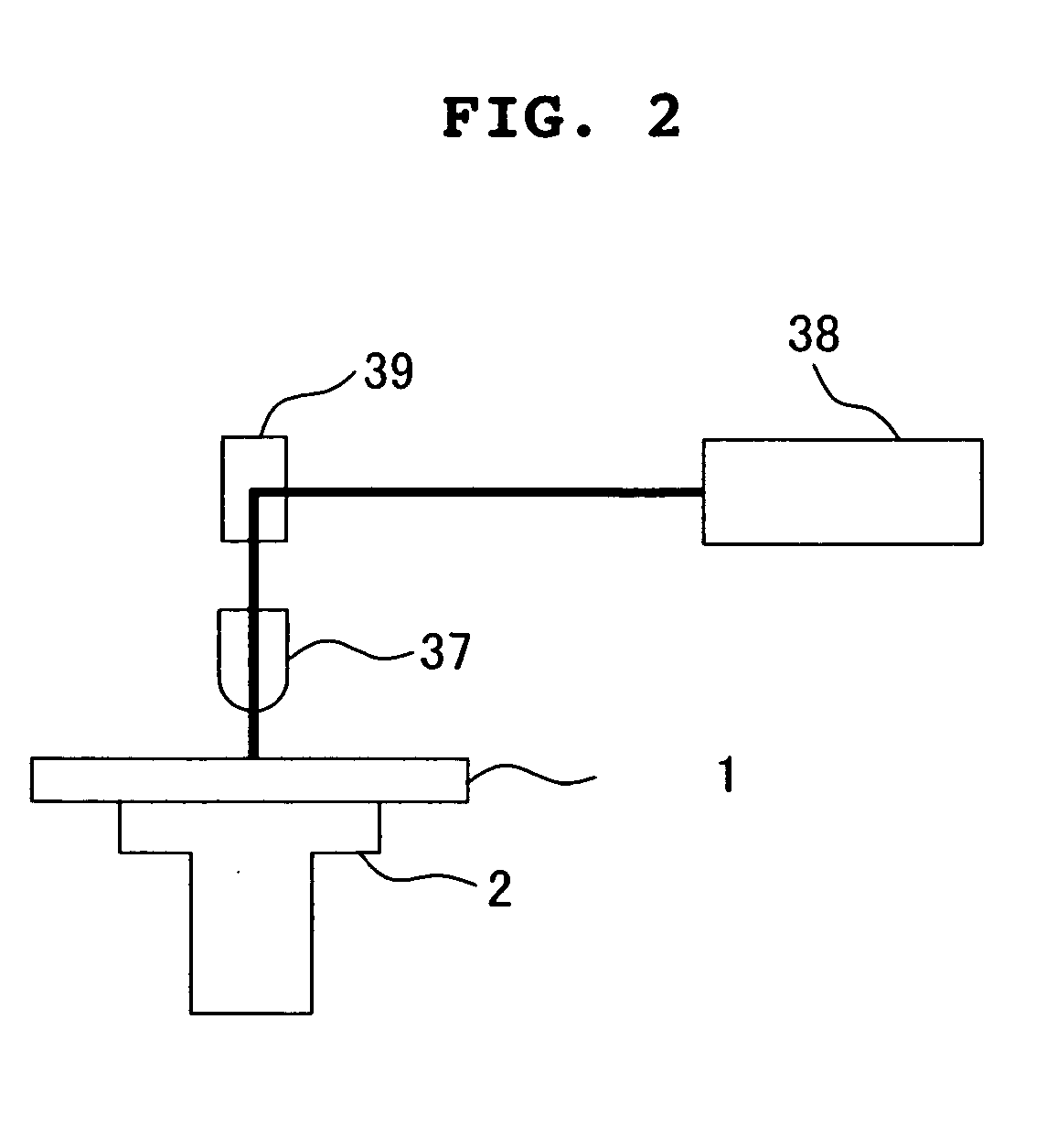
Method of producing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium
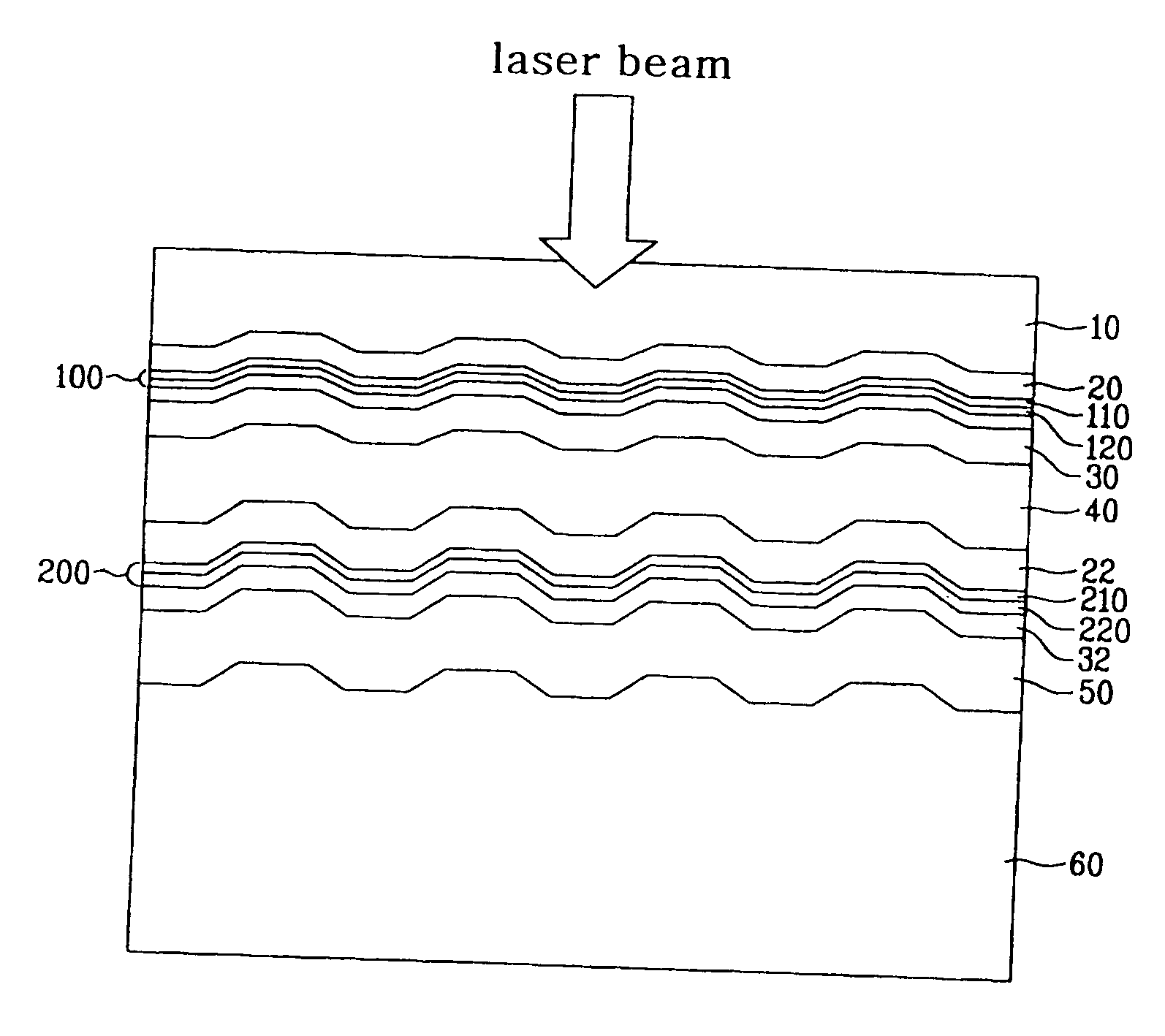
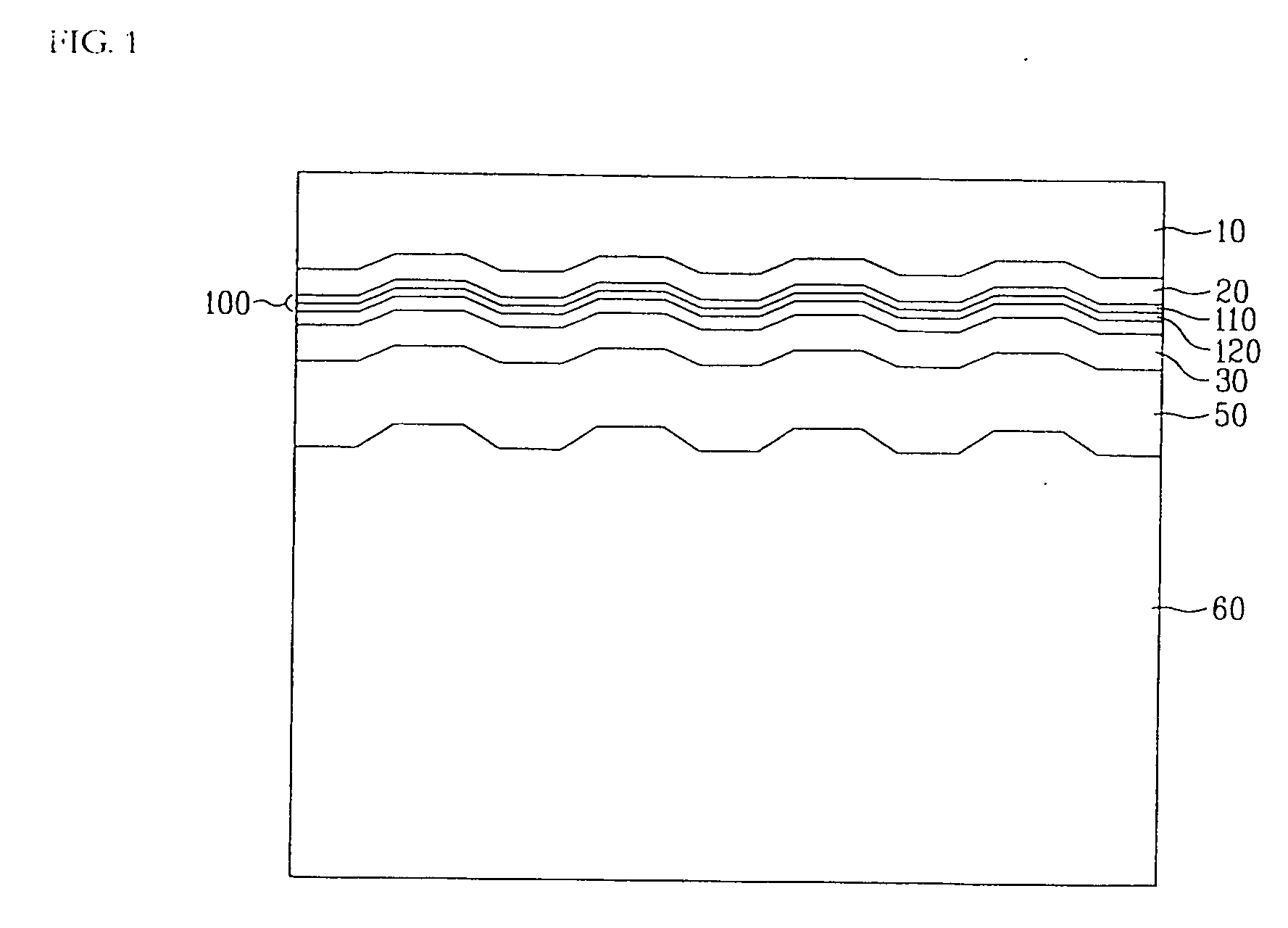
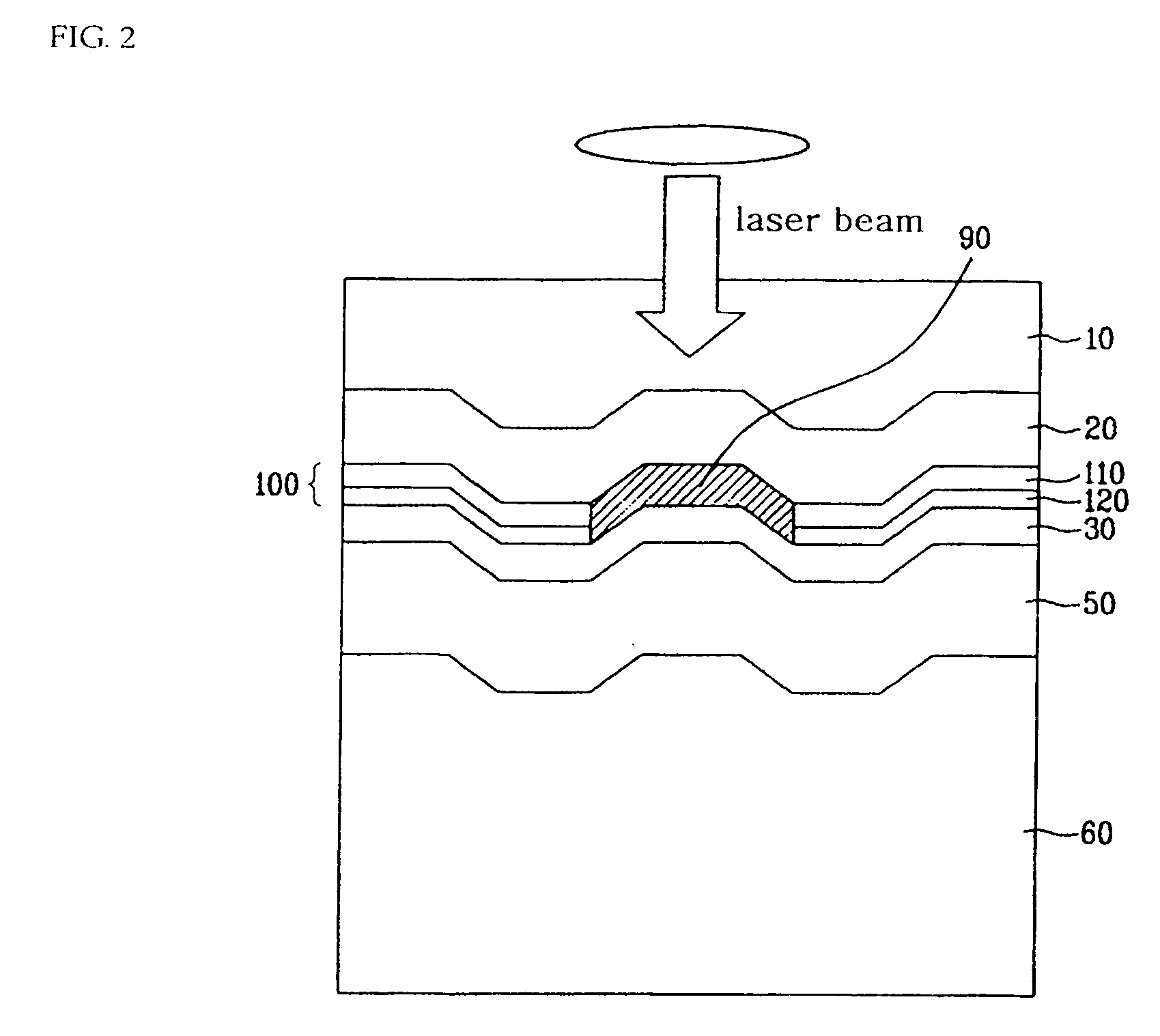
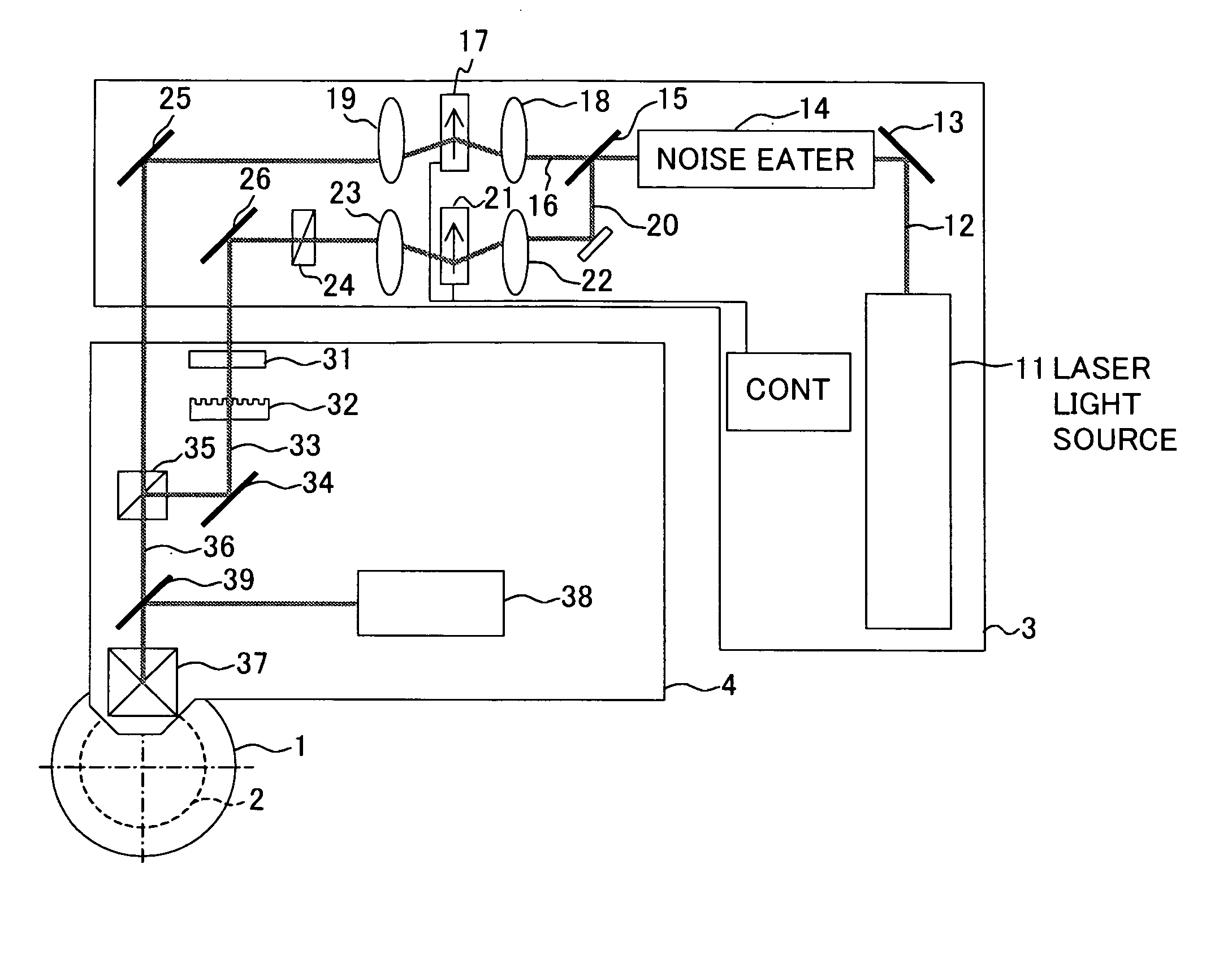
InactiveUS20120175243A1Improved propertyHigh recording densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingRecording densitySputter deposition
To provide a method for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium which has improved electromagnetic conversion characteristics, and thus making it possible to achieve the much higher recording density.Disclosed is a method for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium to be used for recording information by a perpendicular magnetic recording system, the perpendicular magnetic recording medium including at least a soft magnetic layer, an underlayer, and a magnetic recording layer on a substrate. In the method, the underlayer is formed by sputtering deposition, including a low-gas-pressure deposited layer deposited at a low gas pressure during the deposition, and a high-gas-pressure deposited layer deposited at a high gas pressure during the deposition. The high-gas-pressure deposited layer is formed of a multilayer deposited by decreasing a deposition rate in a stepwise manner.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Write-once optical recording medium
InactiveUS20050052986A1High record speedHigh recording densityLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringOrganic dye
A write-once optical recording medium has a transparent resin substrate having a concentric groove or a spiral groove and having recessed cells defining recording regions that are arranged in the groove, a recording film comprising an organic dye formed to fill the cells, and a metal reflection film formed on the recording film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
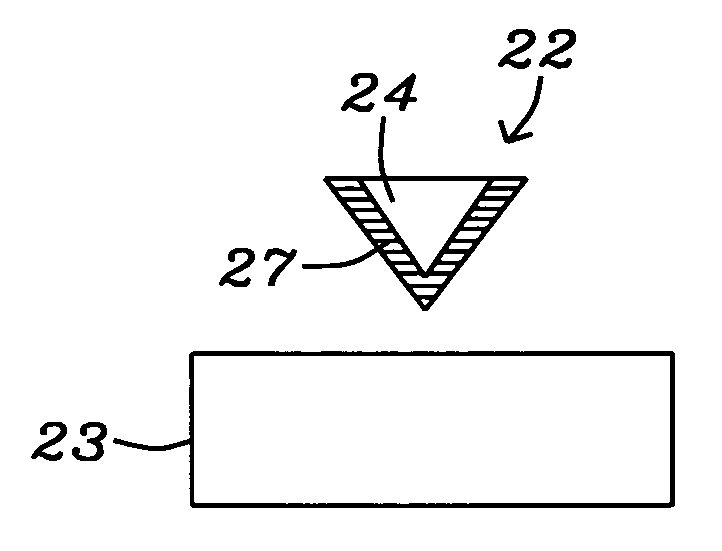
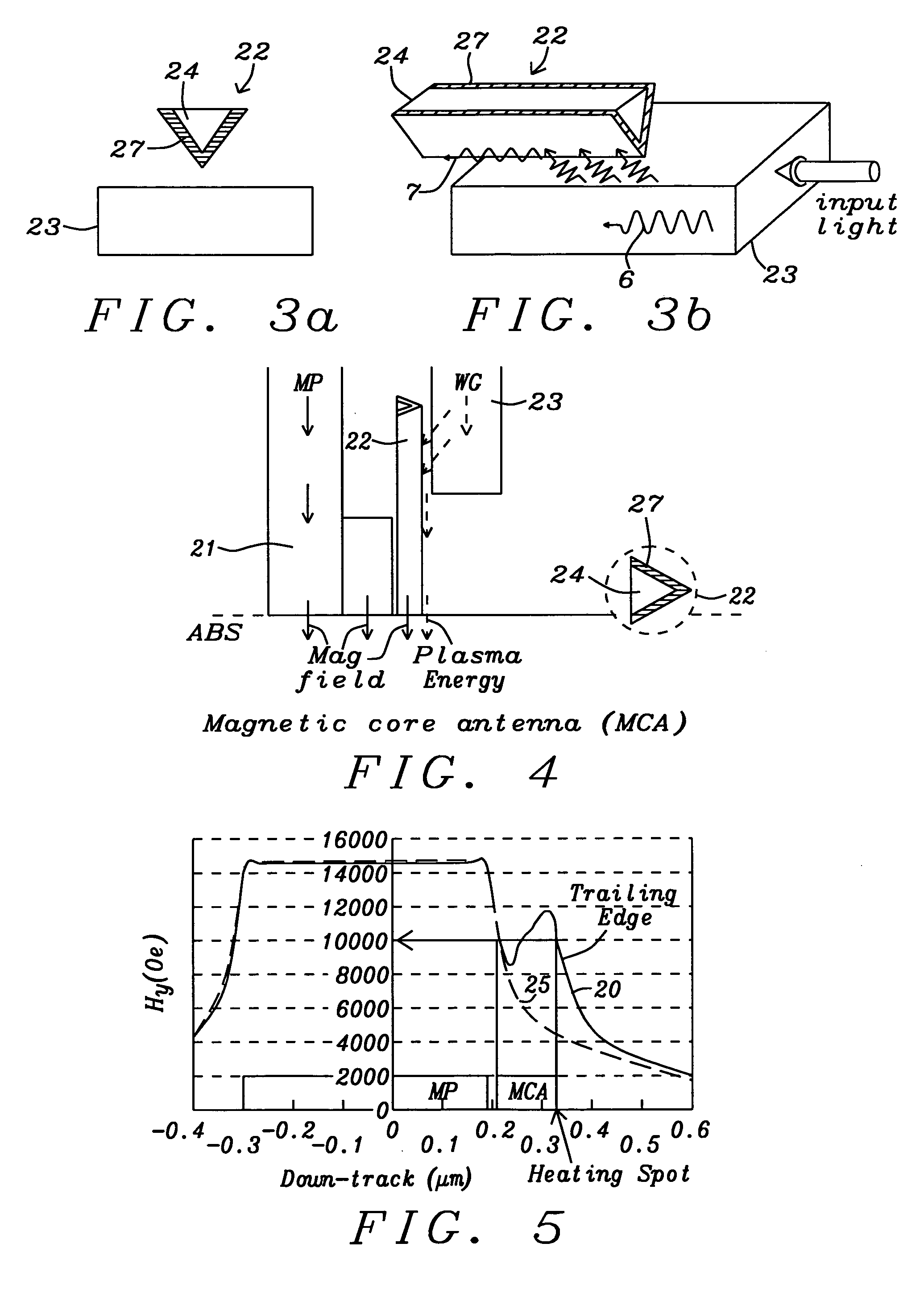
Plasmon antenna with magnetic core for thermally assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20100315735A1Enhance effective record field gradientHigh recording densityCombination recordingRecord information storageMagnetic coreNuclear magnetic resonance
A TAMR (Thermal Assisted Magnetic Recording) write head uses the energy of optical-laser generated plasmons in a plasmon antenna to locally heat a magnetic recording medium and reduce its coercivity and magnetic anisotropy. To enable the TAMR head to operate most effectively, the maximum gradient of the magnetic recording field should be concentrated in the small region being heated. Typically this does not occur because the spot being heated by the antenna is offset from the position at which the magnetic pole concentrates its magnetic field. The present invention incorporates a magnetic core within a plasmon antenna, so the antenna effectively becomes an extension of the magnetic pole and produces a magnetic field whose maximum gradient overlaps the region being heated by edge plasmons being generated in a conducting layer surrounding the antenna's magnetic core.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
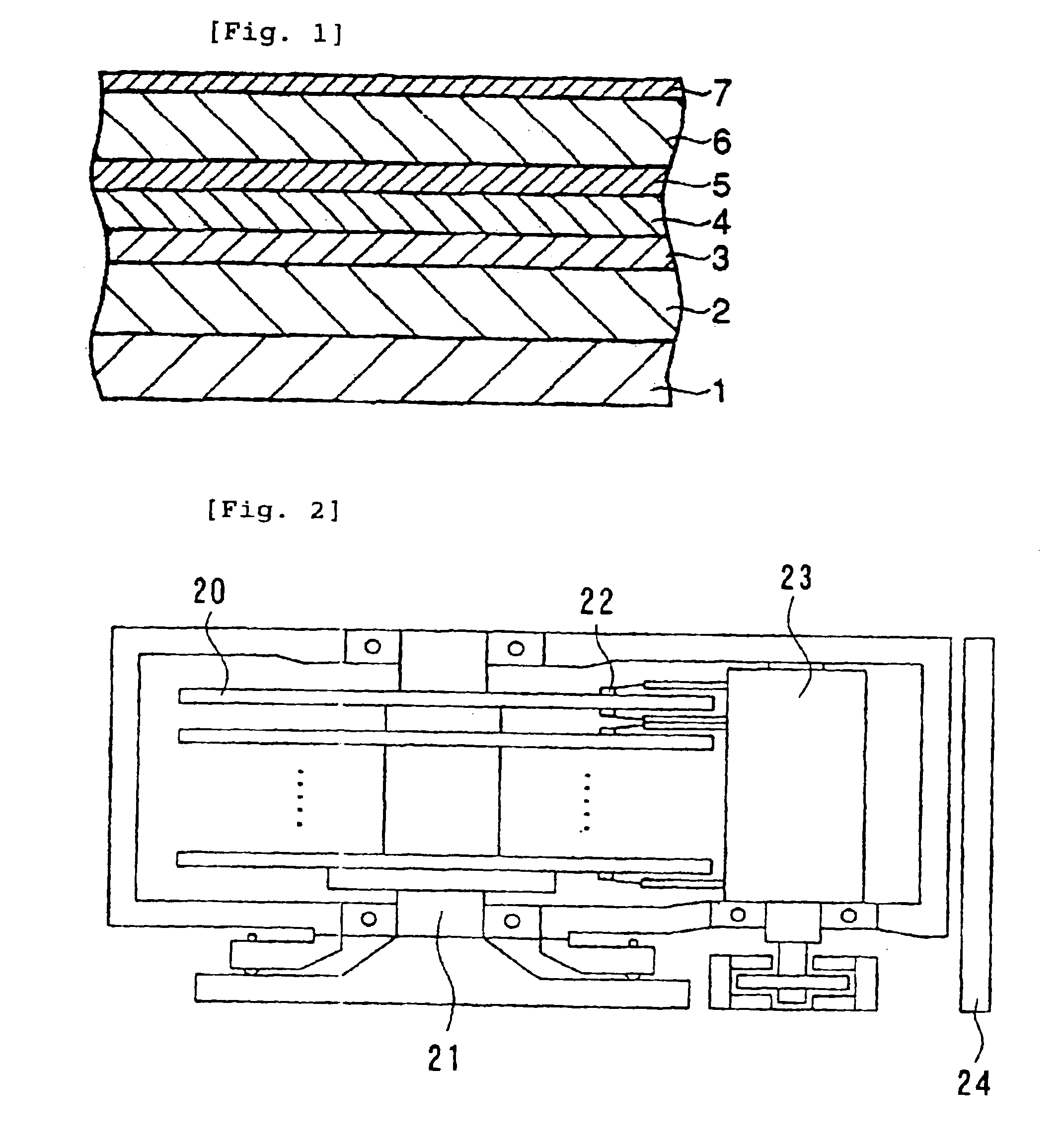
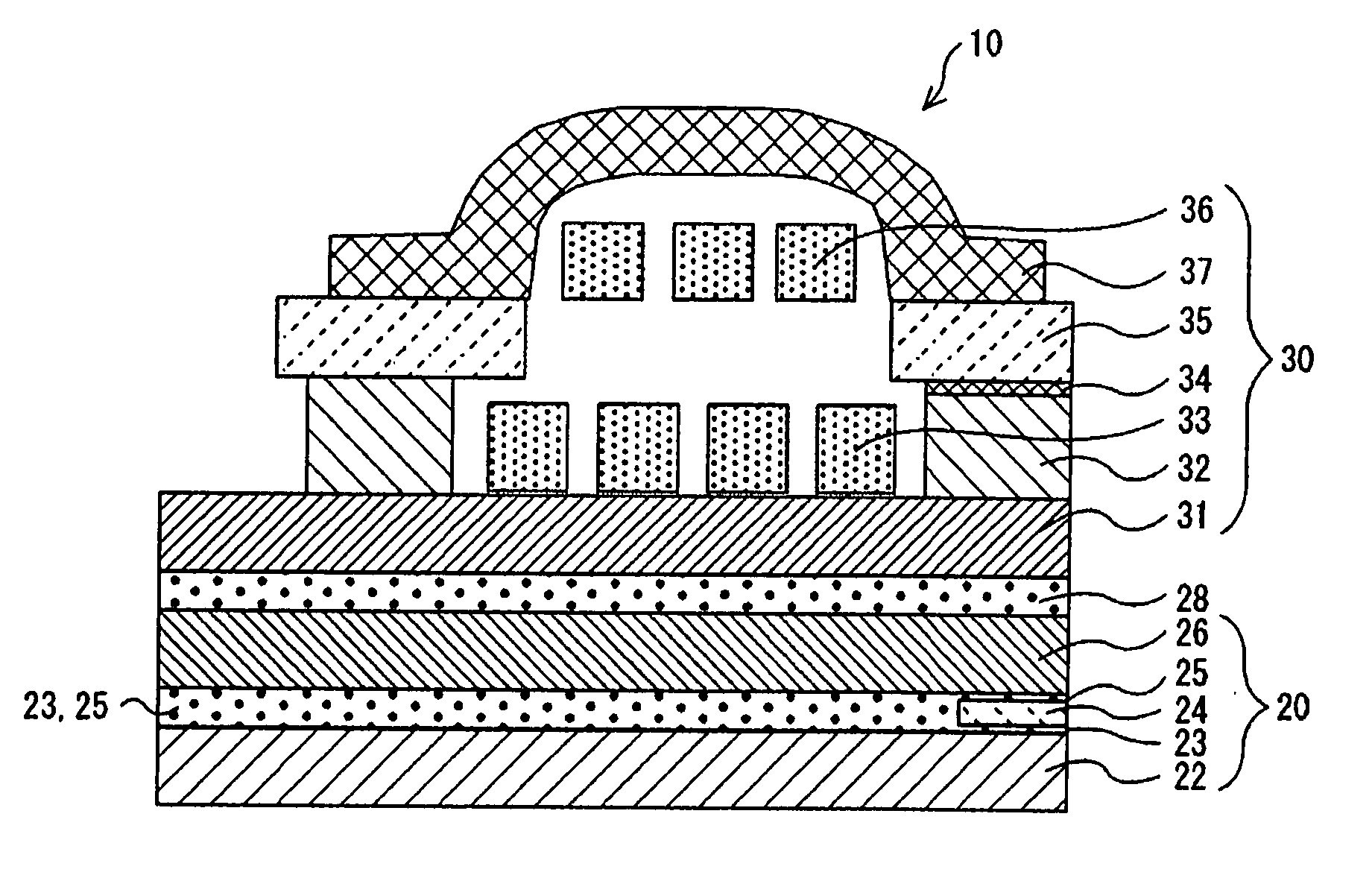
Magnetic recording medium, production process thereof, and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS6942933B2High recording densityHigh coercive forceBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMagnetic layerMaterials science
A magnetic recording medium comprises a non-magnetic substrate, a non-magnetic undercoat layer, a magnetic layer, and a protective film, the layers and film being successively formed on the substrate. The non-magnetic undercoat layer has a multi-layer structure formed of at least two layers and contains a layer A formed of a material selected from a Cr—Ta based alloy, a Cr—Nb-based alloy, a Cr—Ti based alloy, a Cr—Zr-based alloy, and a Cr—Hf-based alloy, and a layer B formed of a material selected from a Co—W based alloy, a Co—W—B-based alloy, a Co—Mo based alloy, a Co—Mo—B based alloy, a Co—W—Mo based alloy, and a Co—W—Mo—B based alloy. The layers A and B are provided in this order from the non-magnetic substrate. A process for producing the medium comprises exposing the surface of the layer B to an oxygen atmosphere.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
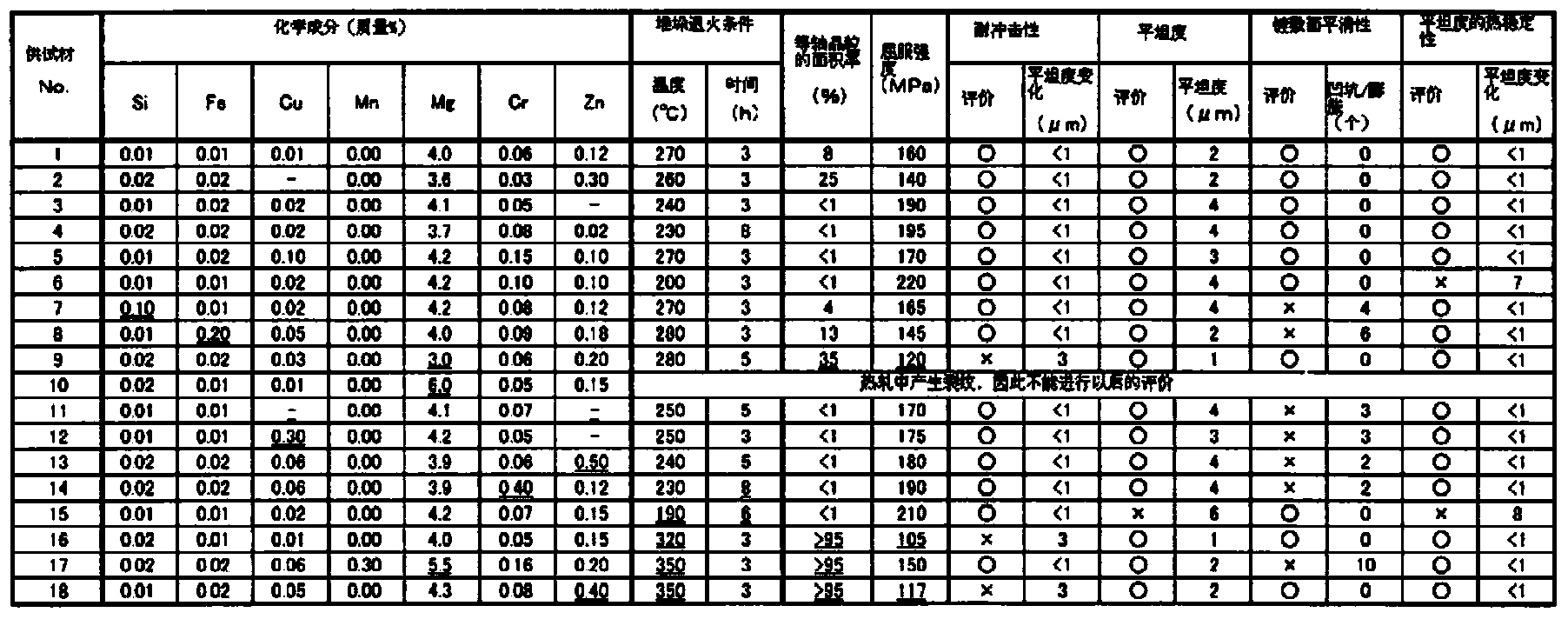
Aluminium alloy substrate used for magnetic disc, and method of manufacturing the same
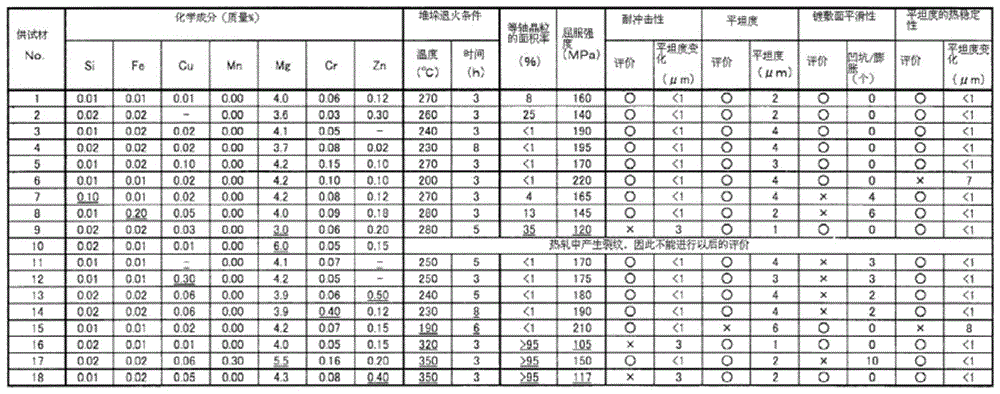
InactiveCN104109783AImprove smoothnessImprove impact resistanceBase layers for recording layersImpurityCrystallite
The present invention provides an aluminium alloy substrate used for a magnetic disc, and a method of manufacturing the same. The aluminium alloy substrate is resistant to impact, has great flatness, and has a plated surface with excellent smoothness. The aluminium alloy substrate is characterized by comprising the following aluminium alloys: below 0.03 by mass of Si, below 0.03 by mass of Fe, over 3.5 and below 4.5 by mass of Mg, below 0.2 by mass of Cr, and at least one selected from over 0.01 and below 0.20 by mass of Cu and over 0.01 and below 0.40 by mass of Zn, the balance being Al and unavoidable impurities, wherein the degree of flatness is less than 5 [mu]m, and the area rate of equiaxed grains on the surface of the substrate is less than 30%.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
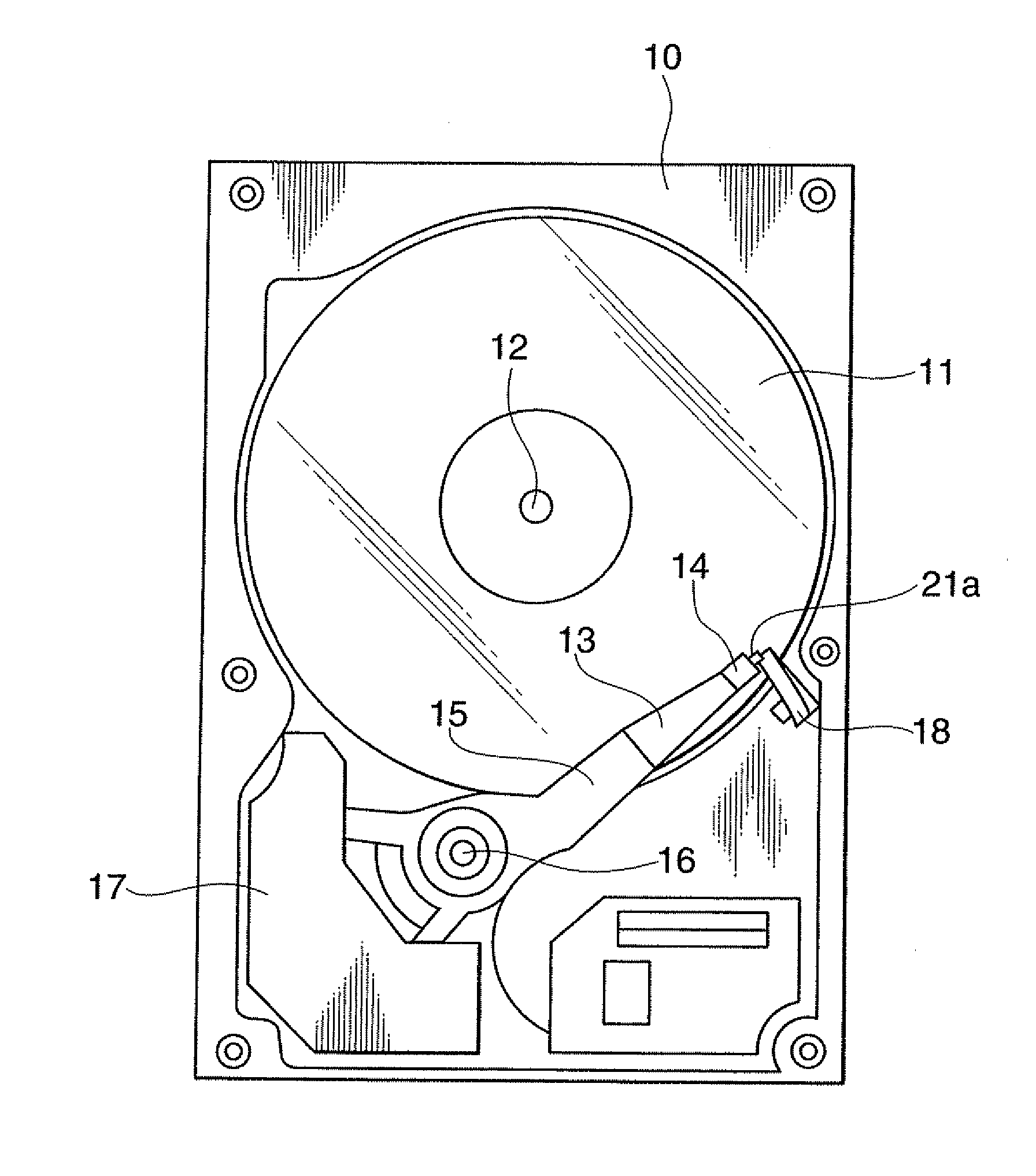
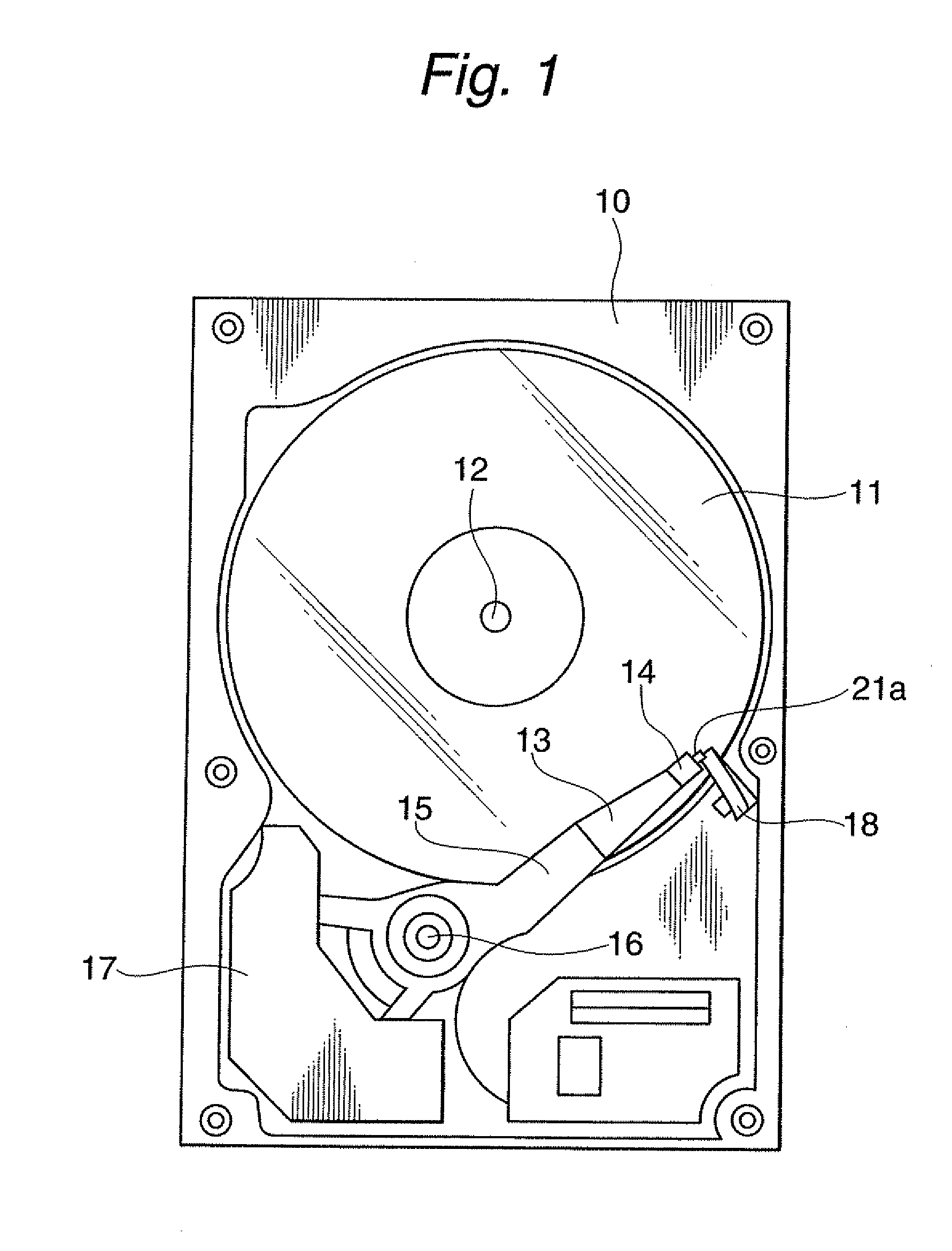
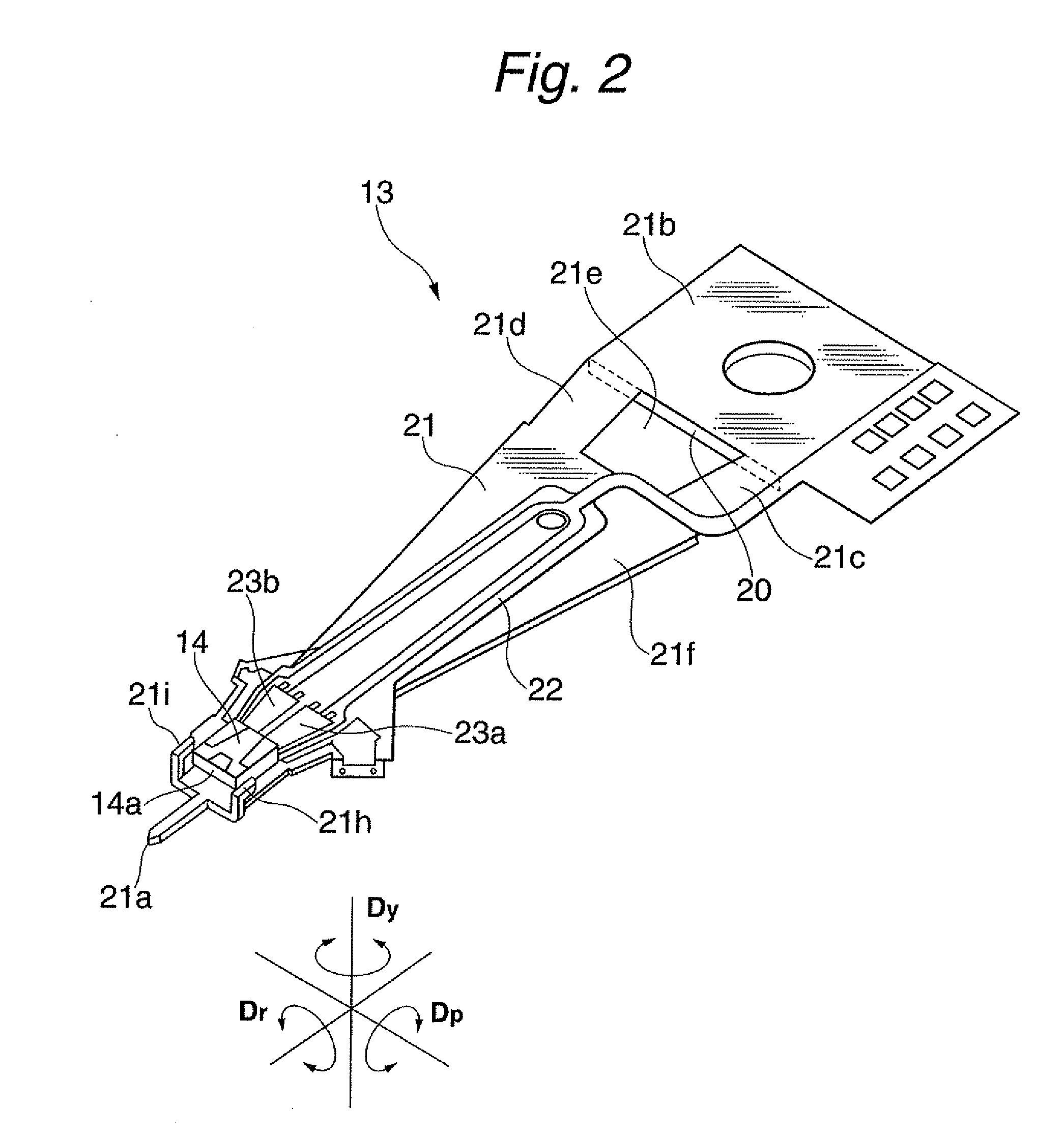
Head assembly, magnetic disk drive apparatus and rotation mechanism
ActiveUS20110211274A1High recording densityGuaranteed adjustment stabilityDriving/moving recording headsArm with actuatorsMagnetic disksDriven element
A head assembly includes a slider having a head element, a load beam, a fulcrum formed at a top end section of the load beam, a slider support plate for supporting the slider to freely turn around the fulcrum, at least one drive element for applying a turning force to the slider support plate in a plane thereof, a first linear link part having at both ends a first top end joint part mechanically connected to the slider support plate, and a first base end joint part mechanically connected to the load beam, and a second linear link part having at both ends a second top end joint part mechanically connected to the slider support plate, and a second base end joint part mechanically connected to the load beam. Both of an extended line of the first linear link part and an extended line of the second linear link part travel toward a position of the fulcrum and intersect with each other.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
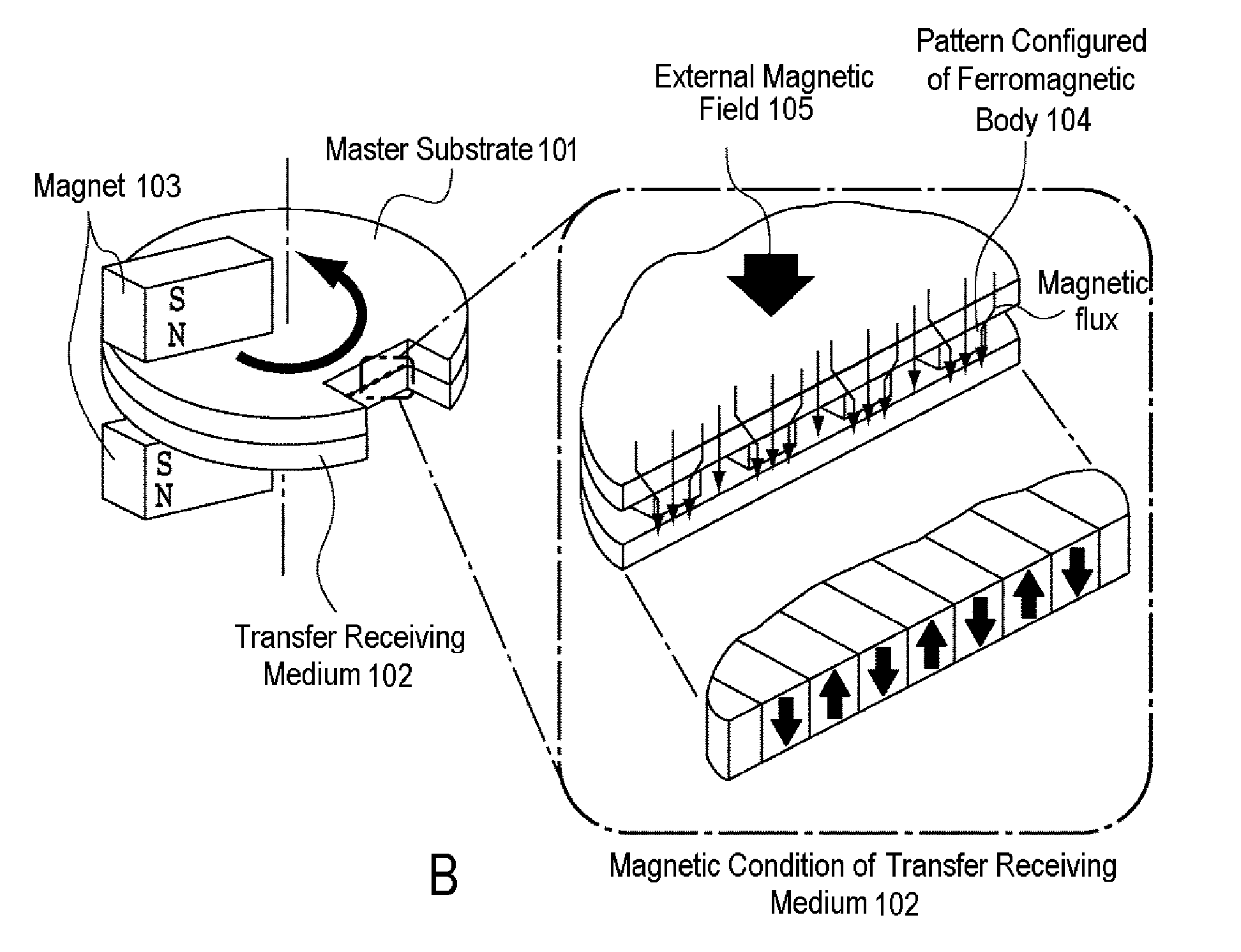
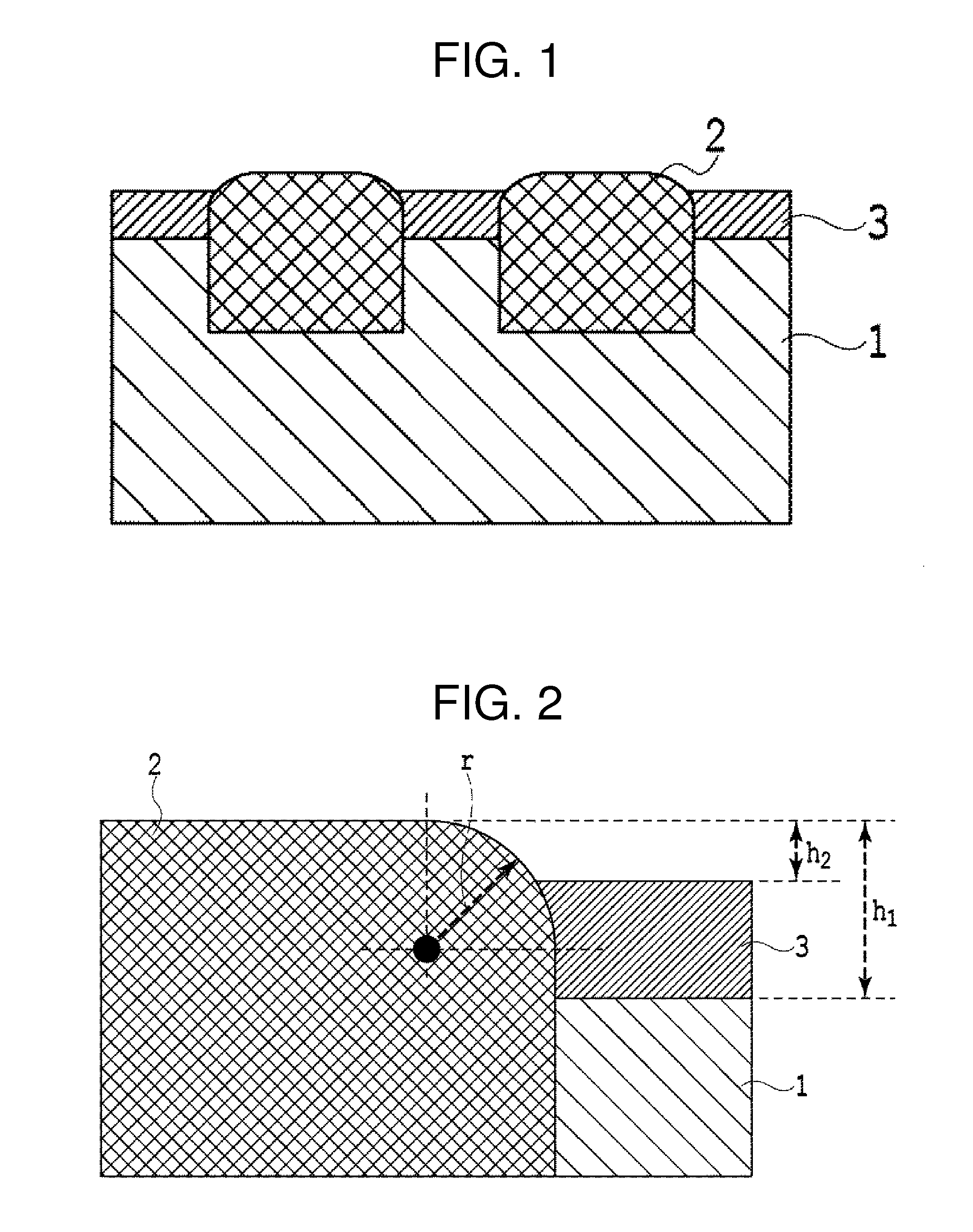
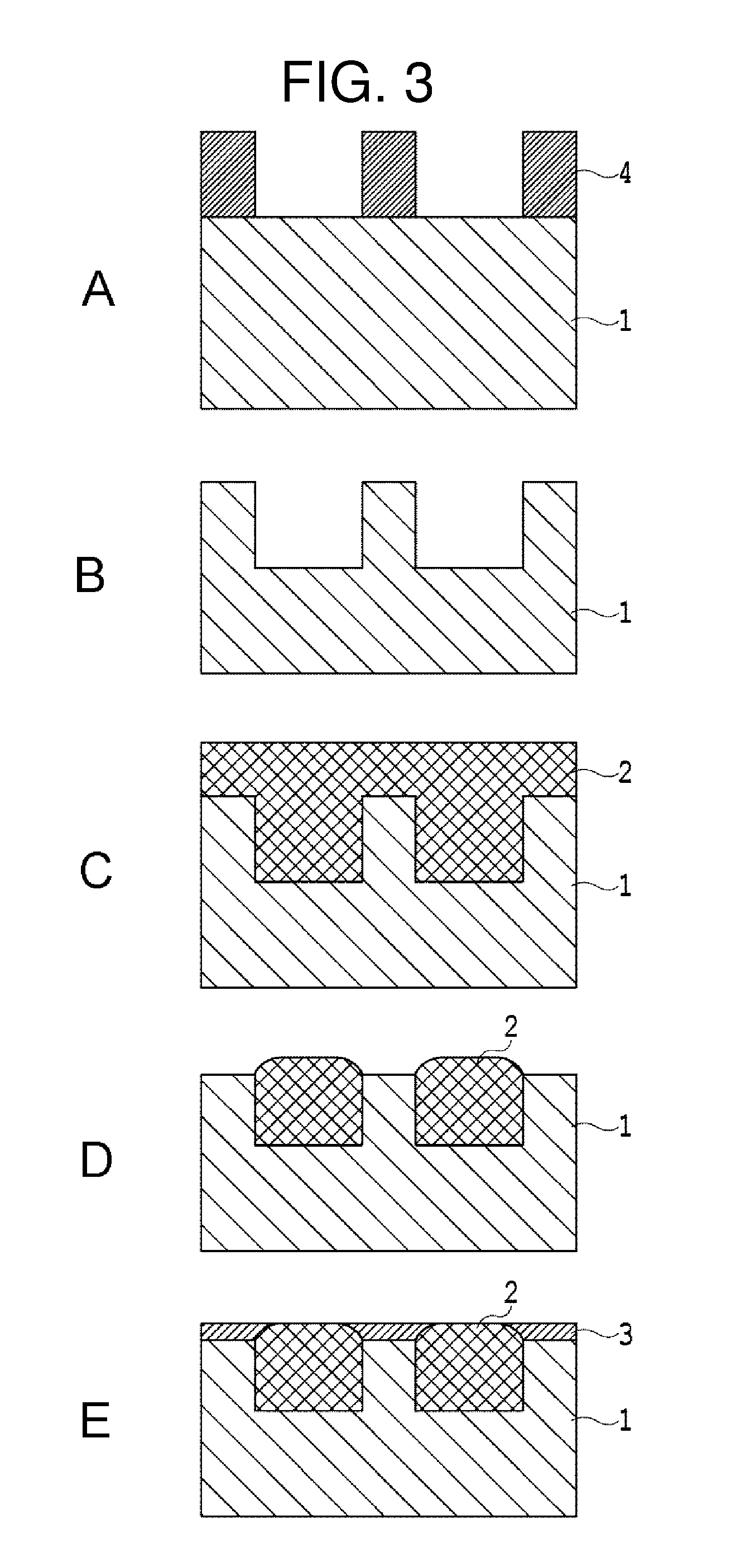
Magnetic transfer master substrate, magnetic transfer method using the substrate, and magnetic transfer medium
InactiveUS20120008224A1Improve durability and magnetic transfer performanceHigh recording densityDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsRADIUSEngineering
A magnetic transfer master substrate includes a non-magnetic base having depressed portions formed on a surface thereof corresponding to an information signal array, a ferromagnetic body formed in the depressed portions and having a top portion thereof protruding above the surface of the non-magnetic base, and a non-magnetic protective film covering the surface of the non-magnetic base, except for the depressed portion thereof, and also covering a side portion of the ferromagnetic body. A section through the ferromagnetic body, taken perpendicularly to the substrate, includes a round corner, a curvature of which has a radius of no less than 1 nm and no more than 10 nm. The apex of the top portion of the ferromagnetic body protrudes above the surface of the non-magnetic base by 2 nm or more, and protrudes above the surface of the non-magnetic protective film by a distance less than the radius of the curvature.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for fabricating a high coercivity hard bias structure for magnetoresistive sensor
ActiveUS20100276272A1High recording densityGreat coercivityMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingCrystalliteHigh concentration
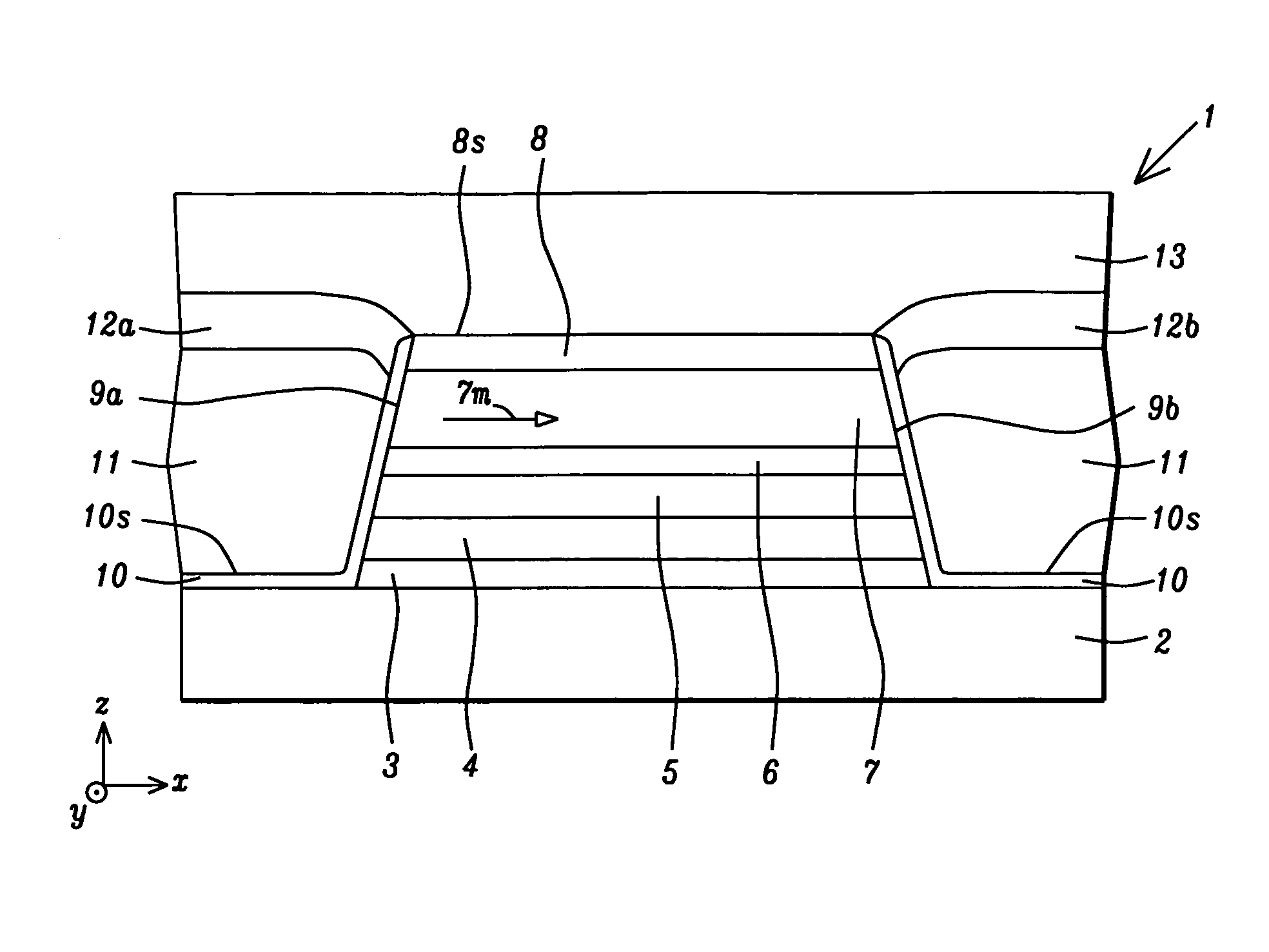
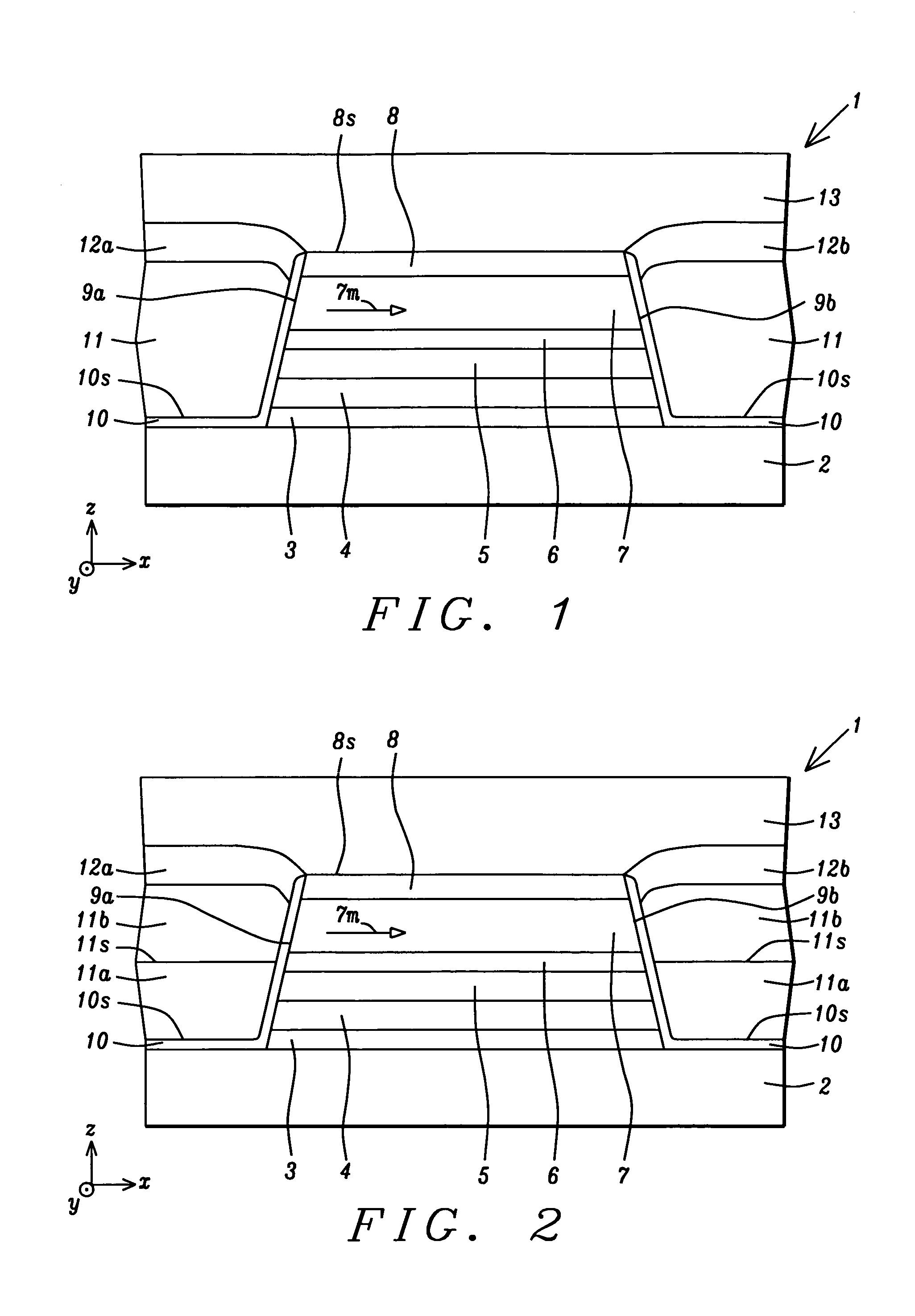
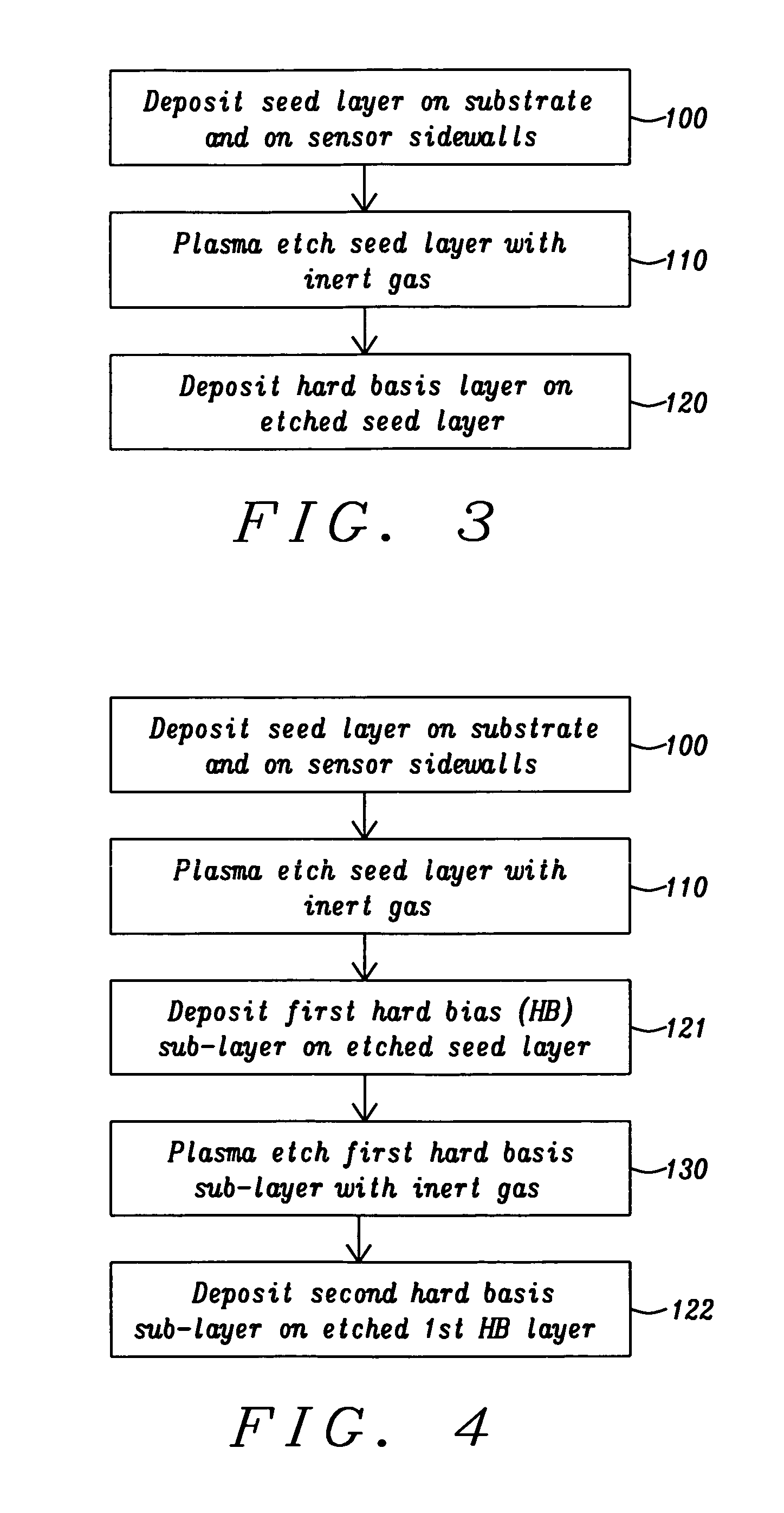
A hard bias (HB) structure for longitudinally biasing a free layer in a MR sensor is disclosed that includes a mildly etched seed layer and a hard bias (HB) layer on the etched seed layer. The HB layer may contain one or more HB sub-layers stacked on a lower sub-layer which contacts the etched seed layer. Each HB sub-layer is mildly etched before depositing another HB sub-layer thereon. The etch may be performed in an IBD chamber and creates a higher concentration of nucleation sites on the etched surface thereby promoting a smaller HB average grain size than would be realized with no etch treatments. A smaller HB average grain size is responsible for increasing Hcr in a CoPt HB layer to as high as 2500 to 3000 Oe. Higher Hcr is achieved without changing the seed layer or HB material and without changing the thickness of the aforementioned layers.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Information recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20100142262A1High recording densityLow power consumptionVariable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsOs elementVoltage
An information recording and reproducing apparatus, includes: a recording layer including a first layer including a first compound, the first compound being a conjugated compound including at least two types of cation elements, at least one selected from the cation elements being a transition element having a d orbit incompletely filled by electrons, a shortest distance between adjacent cation elements being not more than 0.32 nm; a voltage application unit that applies a voltage to the recording layer, produces a phase change in the recording layer, and records information; an electrode layer that applies a voltage to the recording layer; and an orientation control layer provided between the recording layer and the electrode layer to control an orientation of the recording layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
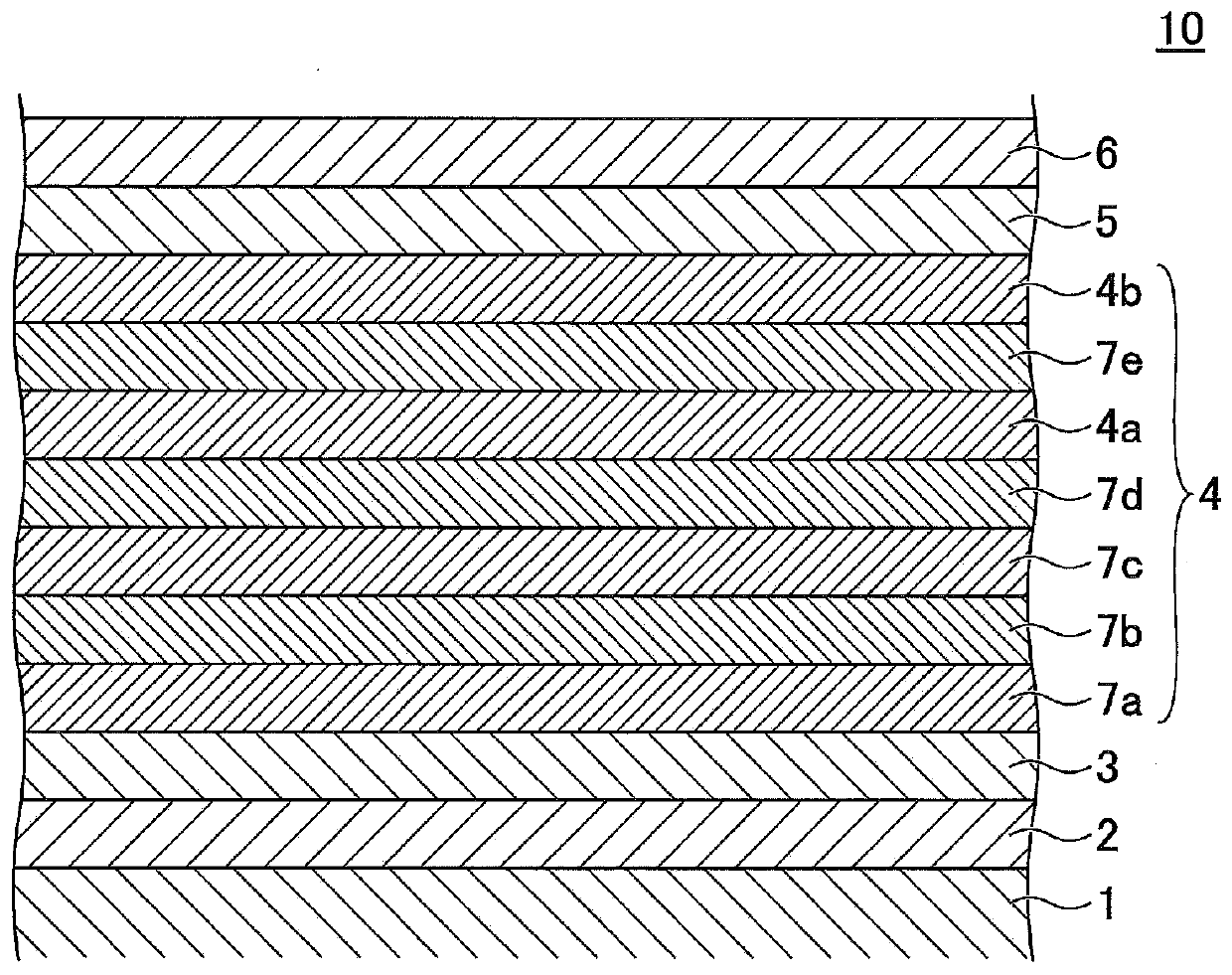
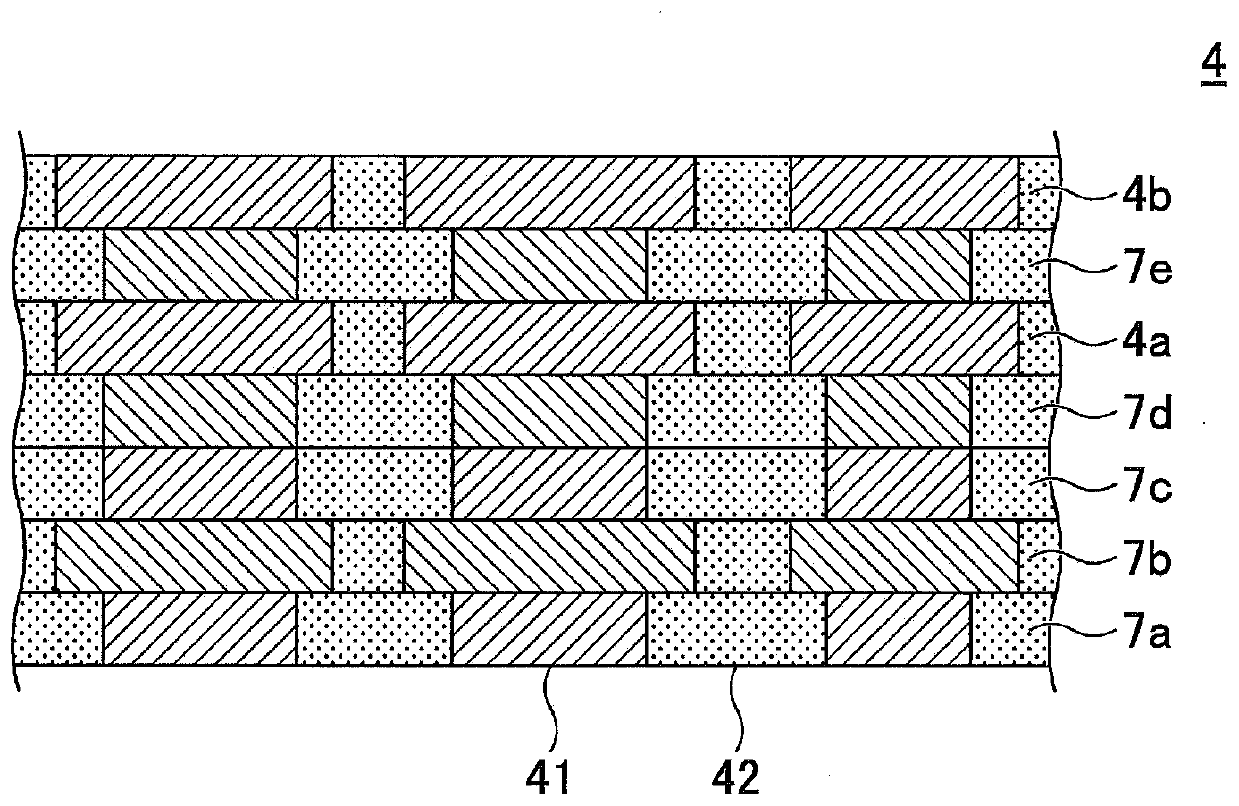
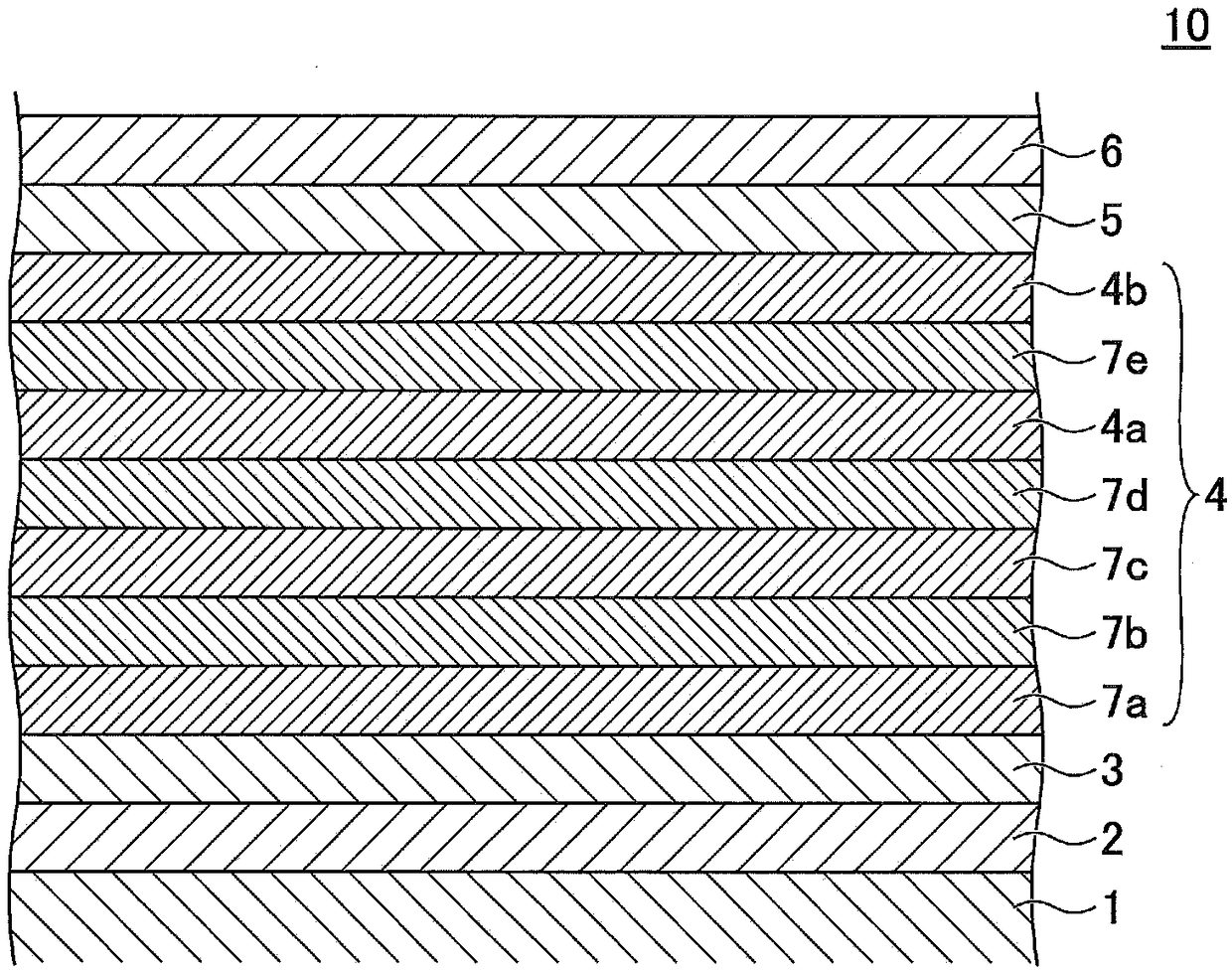
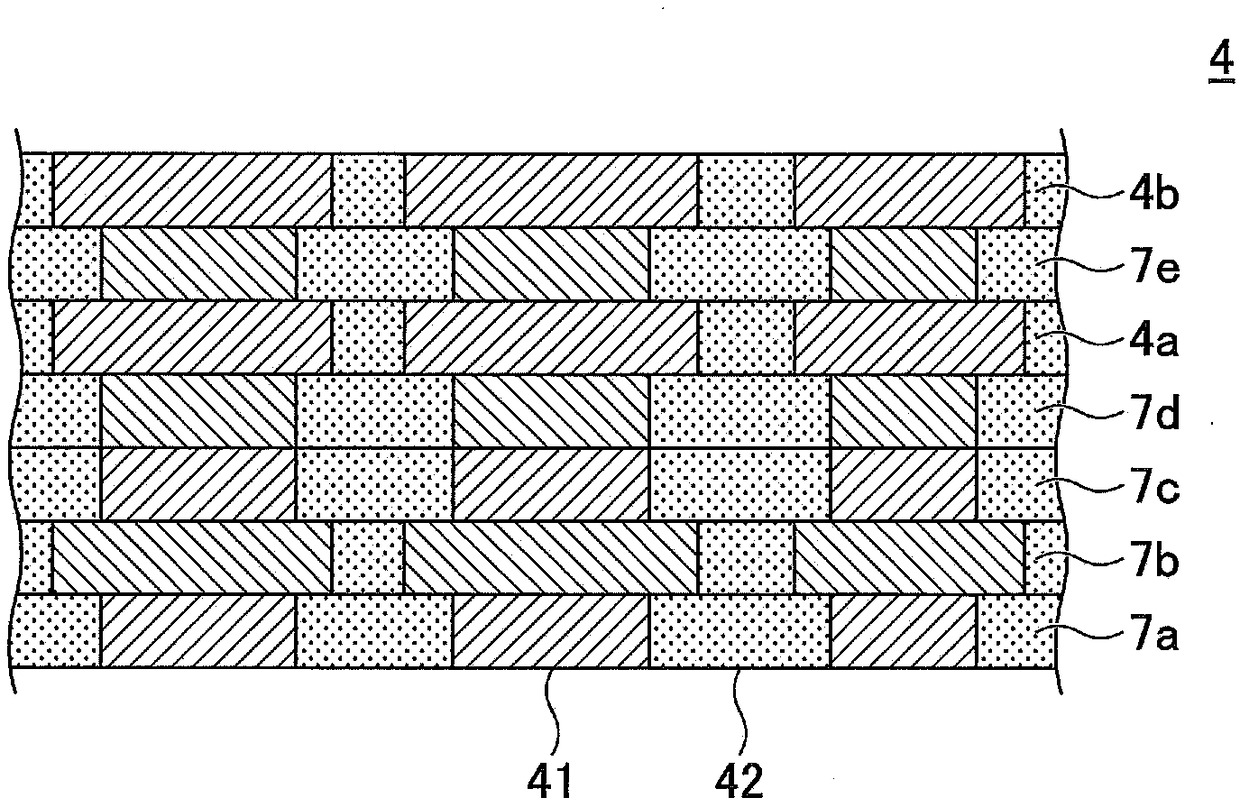
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium, method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic storage unit
InactiveUS20070231608A1Good crystallinity and crystal orientationHigh recording densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCrystalliteMagnetic storage
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium is disclosed that includes a substrate; a soft magnetic underlayer formed on the substrate; a seed layer of an amorphous material formed on the soft magnetic underlayer; an oxidation prevention layer formed on the seed layer; an underlayer formed on the oxidation prevention layer, the underlayer including multiple crystal grains formed of Ru or a Ru alloy having an hcp crystal structure, and a first air gap part configured to separate the crystal grains from each other; and a recording layer formed on the underlayer, the recording layer including multiple magnetic particles having a magnetocrystalline easy axis in a direction substantially perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, and one of a second air gap part and a non-magnetic non-solid-solution phase, the one being configured to separate the magnetic particles from each other. The oxidation prevention layer includes a noble metal element other than R.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
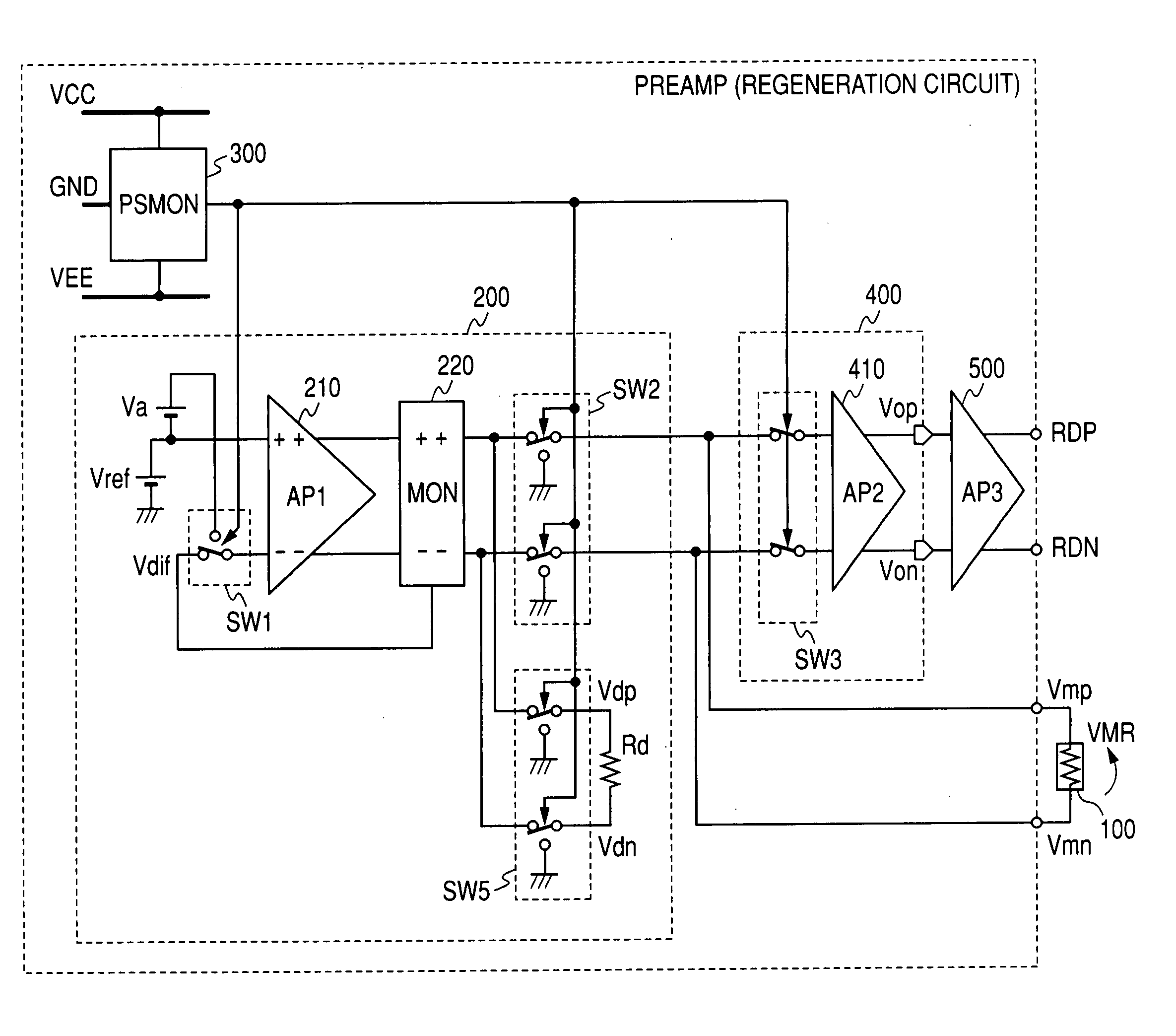
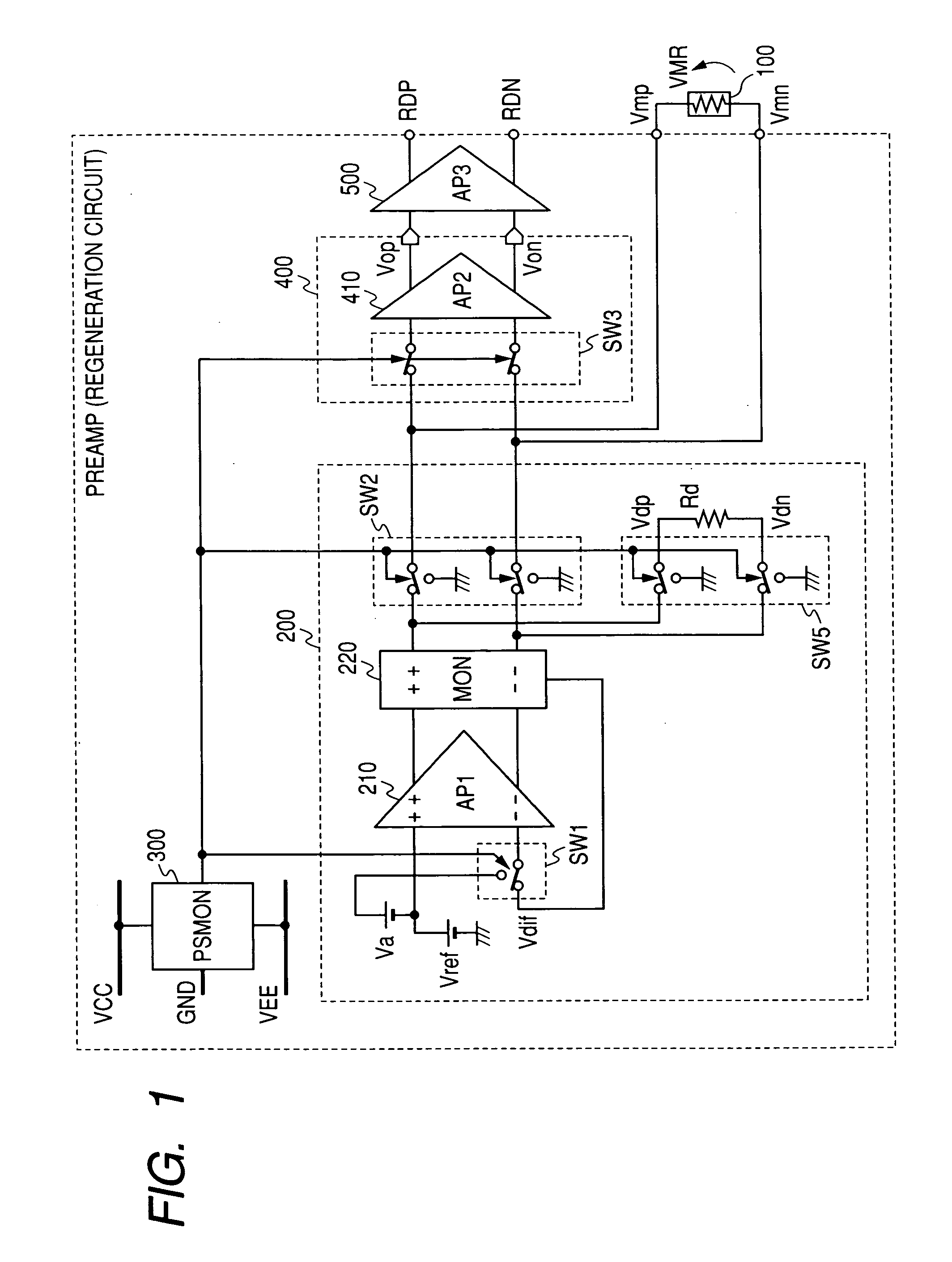
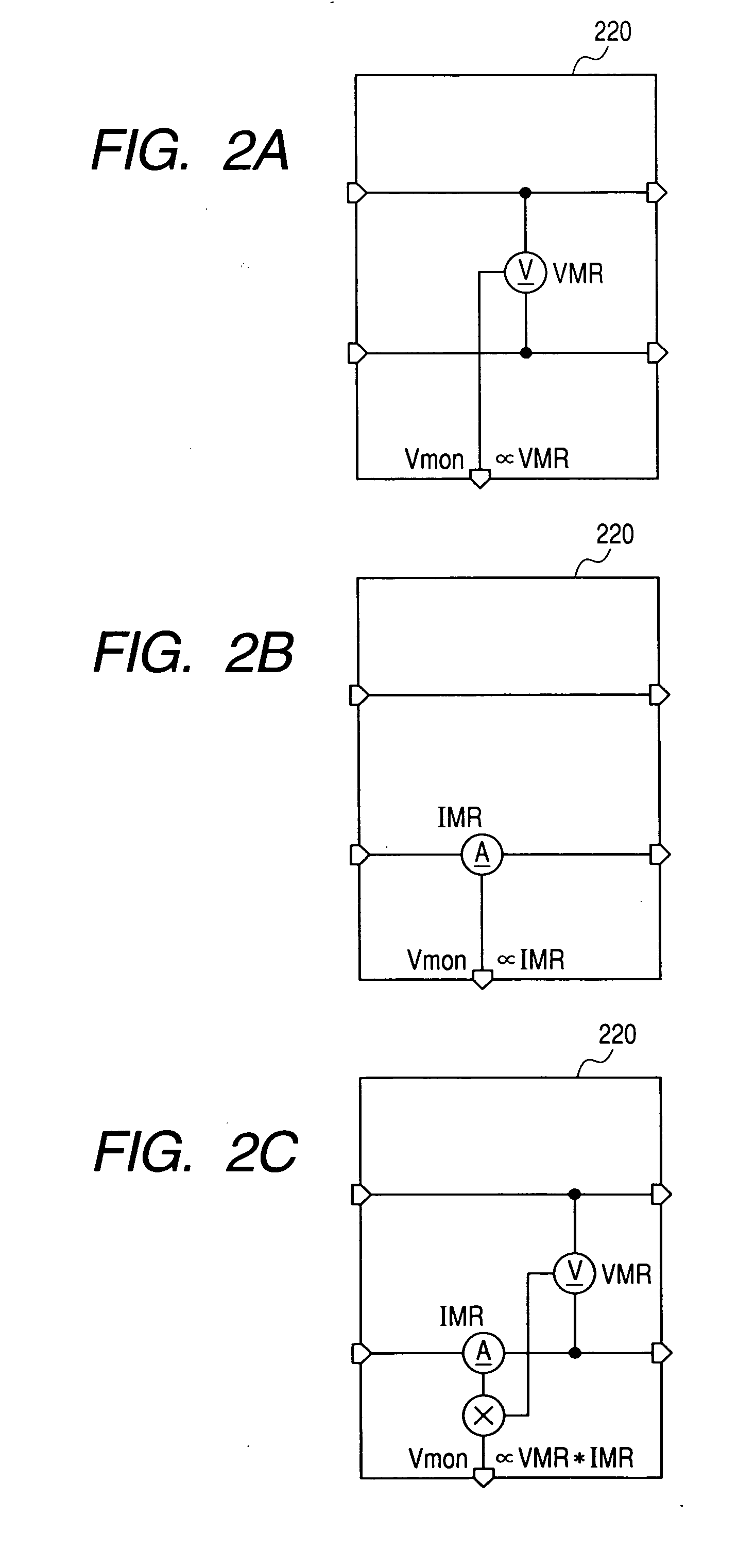
Reproducing circuit and a magnetic disk apparatus using same
InactiveUS20070230008A1High speedHigh recording densityRecord information storageAnalogue recordingMagnetic disksControl circuit
A reproducing circuit for magnetic disks wherein a MR head bias voltage does not exceed the specified value during any malfunction of the power supply voltage including the cases of power supply ON / OFF, and the central voltage of the MR head is controlled to the ground. The reproducing circuit for magnetic disk apparatus is composed of a MR head, a bias circuit that provides bias voltage specified relative to the MR head, an amplifying circuit for amplifying the output signals of the MR head, a power supply voltage monitor circuit that monitors the changes in the power supply voltage, and a control circuit that is controlled by the power supply voltage monitor circuit. MR bias voltage does not exceed the specified value during any malfunction of the power supply voltage including the cases of power supply ON / OFF, and the central voltage of the MR head is controlled to the ground such that the MR head is protected.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Soft magnetic film having high saturation magnetic flux density, thin-film magnetic head using the same, and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20050029108A1Increase magnetic flux densityHigh recording densityHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageRecording densityHead parts
A soft magnetic film is formed of a CoFe alloy having an Fe content in the range of 68 to 80 mass %, thereby having a saturation magnetic flux density of 2.0 T or more. The center lain average roughness of the film surface is 9 nm or less. The soft magnetic film can achieve a corrosive resistant magnetic head with a high recording density.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Data recording/readback method and data recording/readback device for the same
InactiveUS7076721B2Accurately decodeHigh recording densityModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceData recording
The present invention discloses an information processing method including the following steps:(1) a first step receiving an encoded information data series as input;(2) a second step selecting a candidate decoded data code series from a first candidate decoded data code series group, decoding the encoded information data series, and generating a first decoded data code series;(3) a third step detecting a position and contents of erroneous decoded data codes in the first decoded data code series that cannot exist in the information data code;(4) a fourth step correcting the erroneous decoded data code and generating a corrected data code;(5) a fifth step selecting a single decoded data code series out of a second candidate decoded data code series group, decoding the encoded information data code series again, and generating a second decoded data code series;(6) The second candidate decode data code series group includes candidate decoded data code series from the first candidate decoded data code series group that fulfills at least one of the following conditions:1. A candidate decoded data code series that does not contain erroneous decoded data codes that were detected at the third step and that could not be corrected at the fourth step.2. A candidate data code series that contains: data codes that were determined at the third step to not contain erroneous decoded data codes; and corrected data codes corrected at the fourth step.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD +1
Thermal transfer ink, thermal transfer sheet and method of thermal transfer recording therewith
InactiveCN1906252AGood light fastnessBright yellowMethine/polymethine dyesDuplicating/marking methodsLightfastnessPhotochemistry
A thermal transfer sheet and yellow ink for use in thermal transfer, with which highly dense clear yellow color can be exhibited with low energy, with which a thermal transfer record excelling in color tone and light fastness can be obtained, and with which a highly dense preferable green tone can be exhibited when mixed with cyan, and to provide a thermal transfer sheet. There is provided a dye composition characterized by containing a dye having an arylidene pyrazolone skeleton and a dye having a bispyrazolone methine skeleton. There is further provided a thermal transfer ink characterized by containing a dye having an arylidene pyrazolone skeleton, a dye having a bispyrazolone methine skeleton and a medium. There is still further provided a thermal transfer sheet comprising a base material and, superimposed thereon, a color material layer containing a dye having an arylidene pyrazolone skeleton and a dye having a bispyrazolone methine skeleton.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Information storage medium using nanocrystal particles, method of manufacturing the information storage medium, and information storage apparatus including the information storage medium
ActiveUS20080186837A1High recording densityElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingLayered productsInformation storageNanocrystal
Provided is an information storage medium using nanocrystal particles, a method of manufacturing the information storage medium, and an information storage apparatus including the information storage medium. The information storage medium includes a conductive layer, a first insulating layer formed on the conductive layer, a nanocrystal layer that is formed on the first insulating layer and includes conductive nanocrystal particles that can trap charges, and a second insulating layer formed on the nanocrystal layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH INT
Method and apparatus for data reproducing in disk storage system
InactiveUS6104560AHigh recording densityImprove recording densityModification of read/write signalsDisc-shaped record carriersOperation modeDisk storage
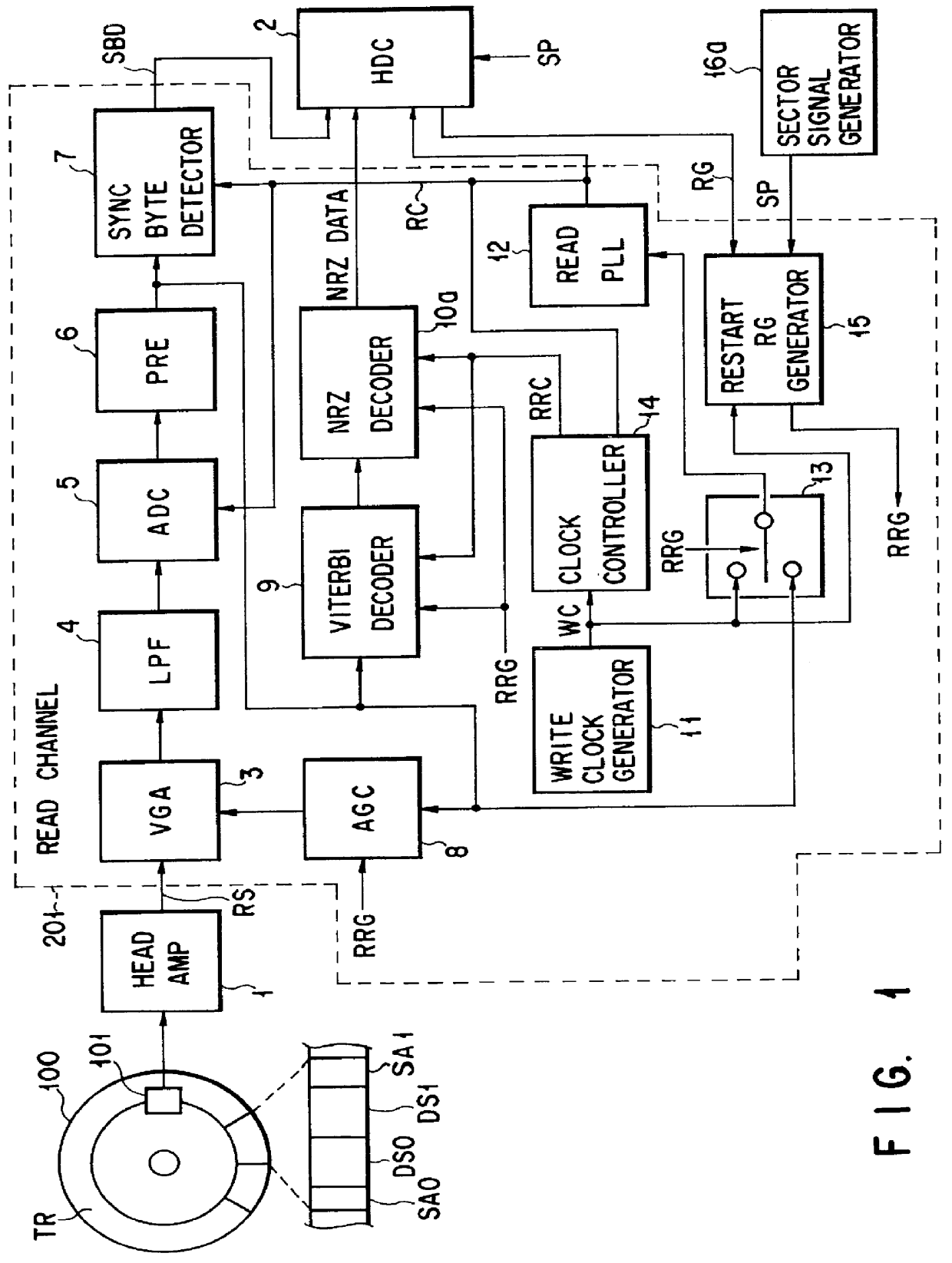
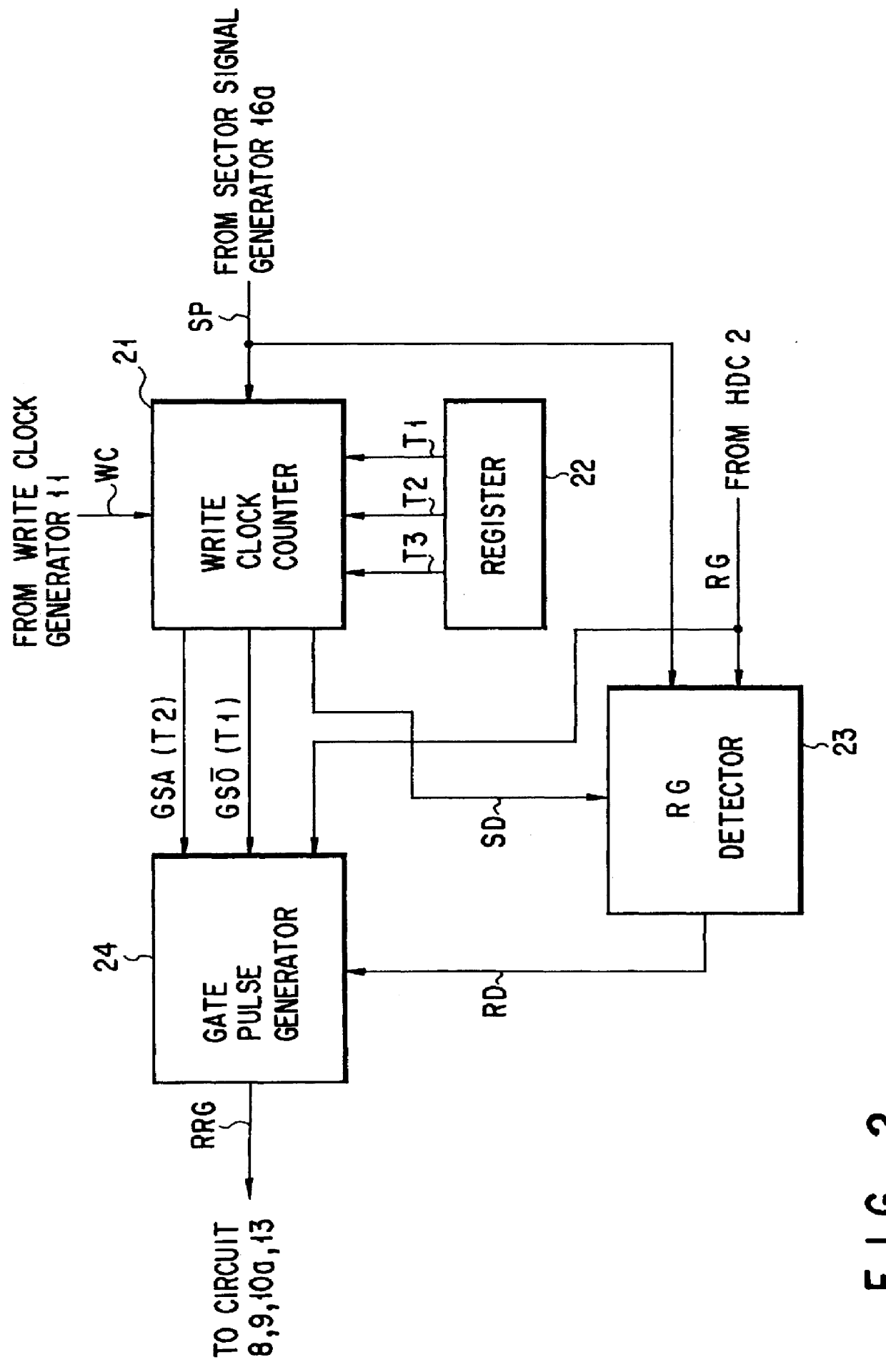
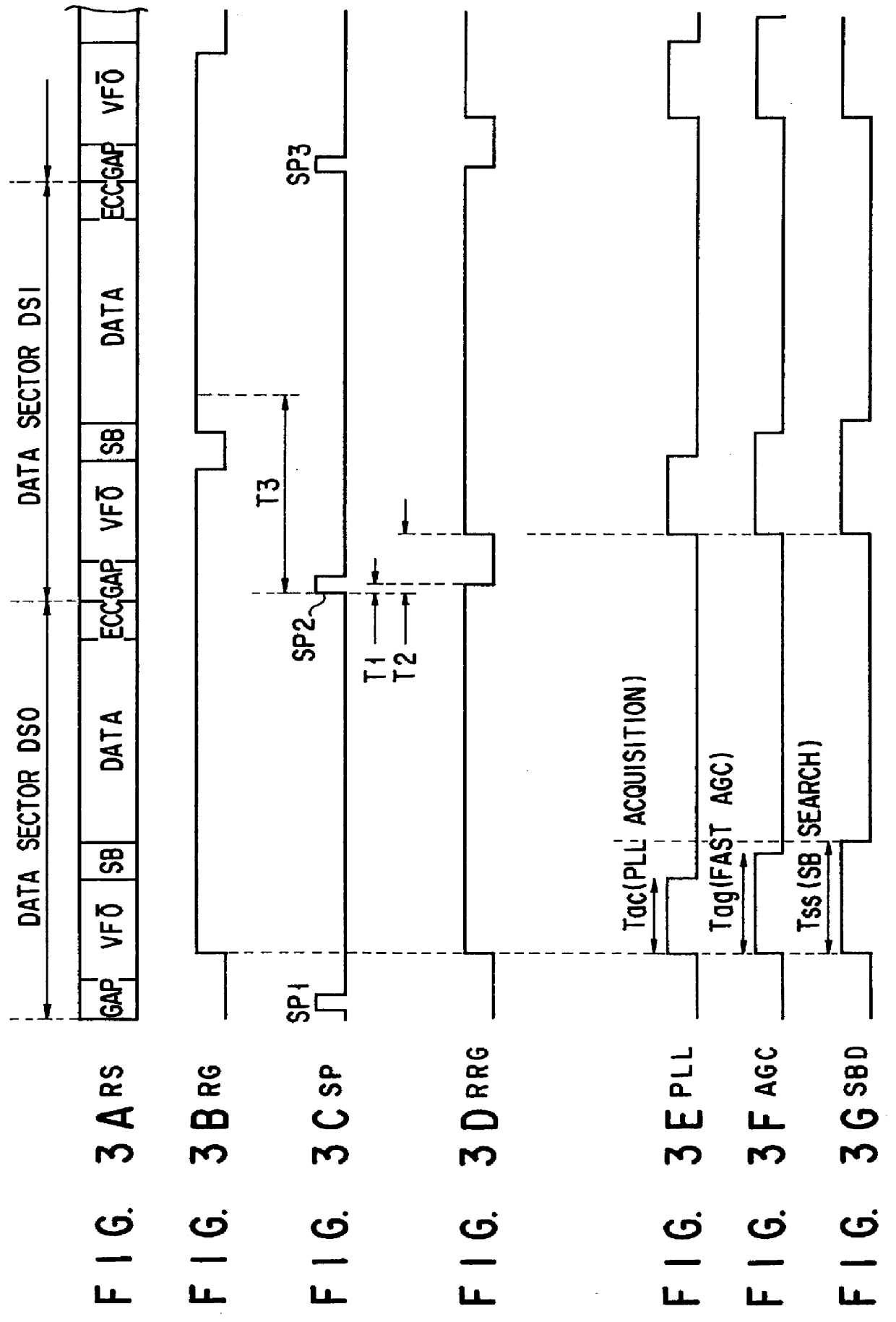
In a data reproducing device using a read channel of a PRML system, during a period of a continuous reproducing operation mode for continuous reproduction processing of adjacent data sectors, a restart RG generator switches a restart read gate signal RRG ON in synchronization with switching ON of a reference read gate signal RG. Therefore, when data is reproduced from a data sector before continuous data sectors, data reproduction processing is started by means of the restart read gate signal RRG equivalent to the reference read gate signal RG. When data is continuously reproduced from a next data sector adjacent to the previous data sector, the restart RG generator switches the restart read gate signal RRG ON ahead of the reference read gate signal RG by a specified period.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS7163756B2High recording densitySatisfactory thermal fluctuation resistanceBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageUnit recordingMagnetic layer
A large-capacity, low-cost, longitudinal magnetic recording medium capable of ultra-high-density recording of 70 Gigabits or more per square inch is disclosed. The longitudinal magnetic recording medium of the present invention comprises a first seed layer, a second seed layer, a first underlayer, a second underlayer, and a magnetic layer, which are formed on a nonmagnetic substrate in this order. A material containing at least Al and any one of Ru and Re is used to form the second seed layer, and a material containing at least any one of Co and Ni and one or both of Al and Ti is used to form the first underlayer. It is also possible to use Cr or a Cr alloy containing Cr and at least one element selected from the constituent element group A consisting of Ti, Mo, and W for forming the second seed layer.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
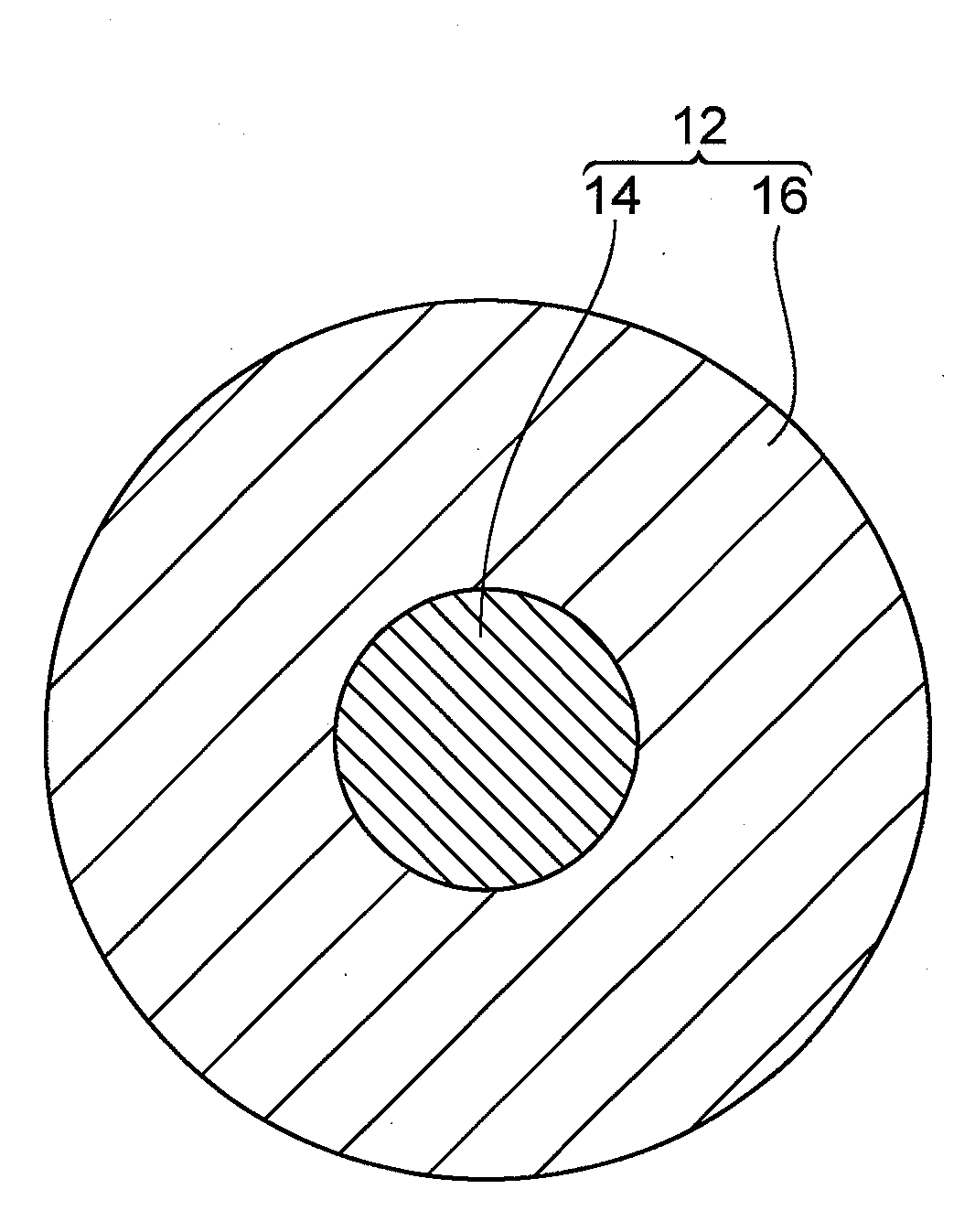
Magnetic recording medium and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20090142623A1High recording densityNot easy to layerMaterials with cobaltRecord information storageRecording densityNanometre
The present invention provides a magnetic recording medium capable of obtaining high recording density and also having a hardly charged magnetic layer. The magnetic recording tape 2 (magnetic recording medium) of a preferable embodiment has a magnetic layer 6 containing a SmCo magnetic fine particle 12 and a hydrophilic binder, wherein the SmCo magnetic fine particle 12 has a core 14 made of a SmCo nano particle and a coating layer 16 made of a hydrophilic polymer and coating at least a part of a surface of the core 14.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Spin valve element, method of driving the same, and storage device using the same
ActiveUS20110102939A1High recording densityImprove recording densityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMulti valuedMagnetic layer
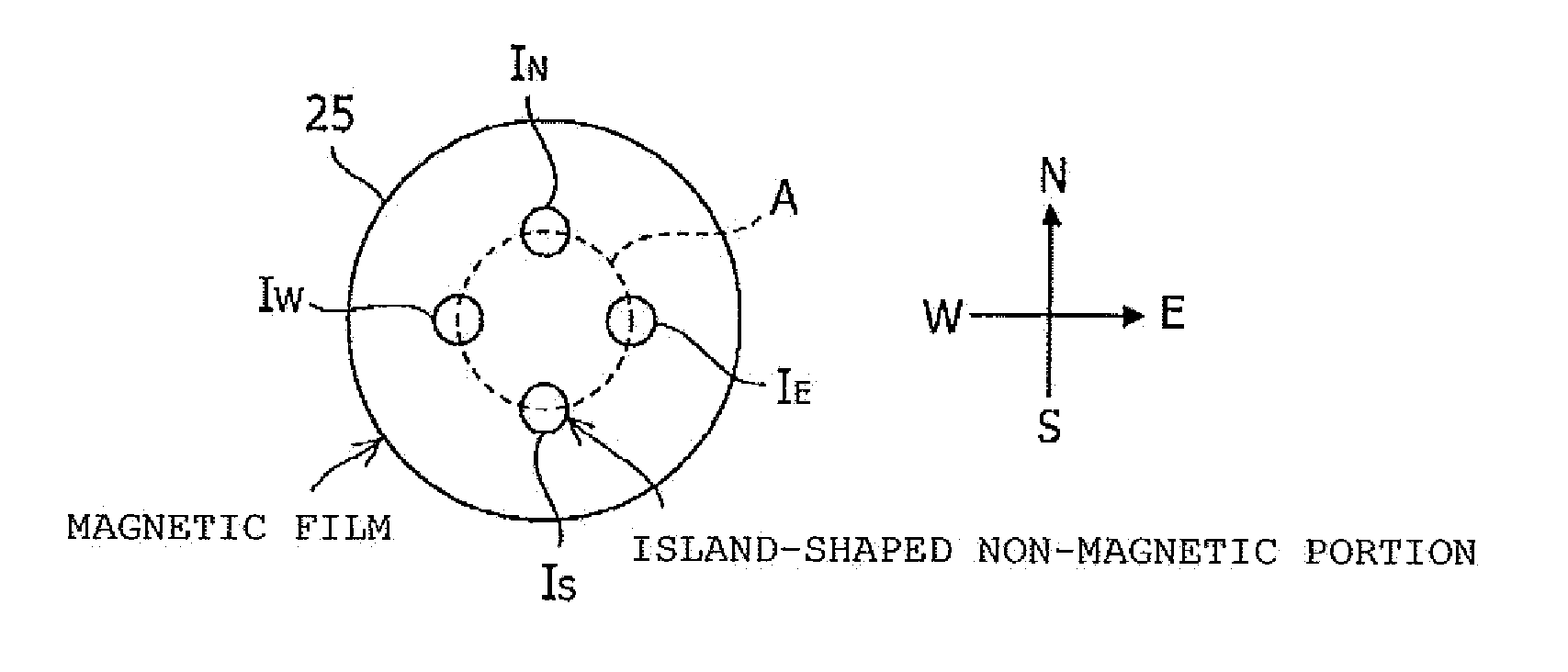
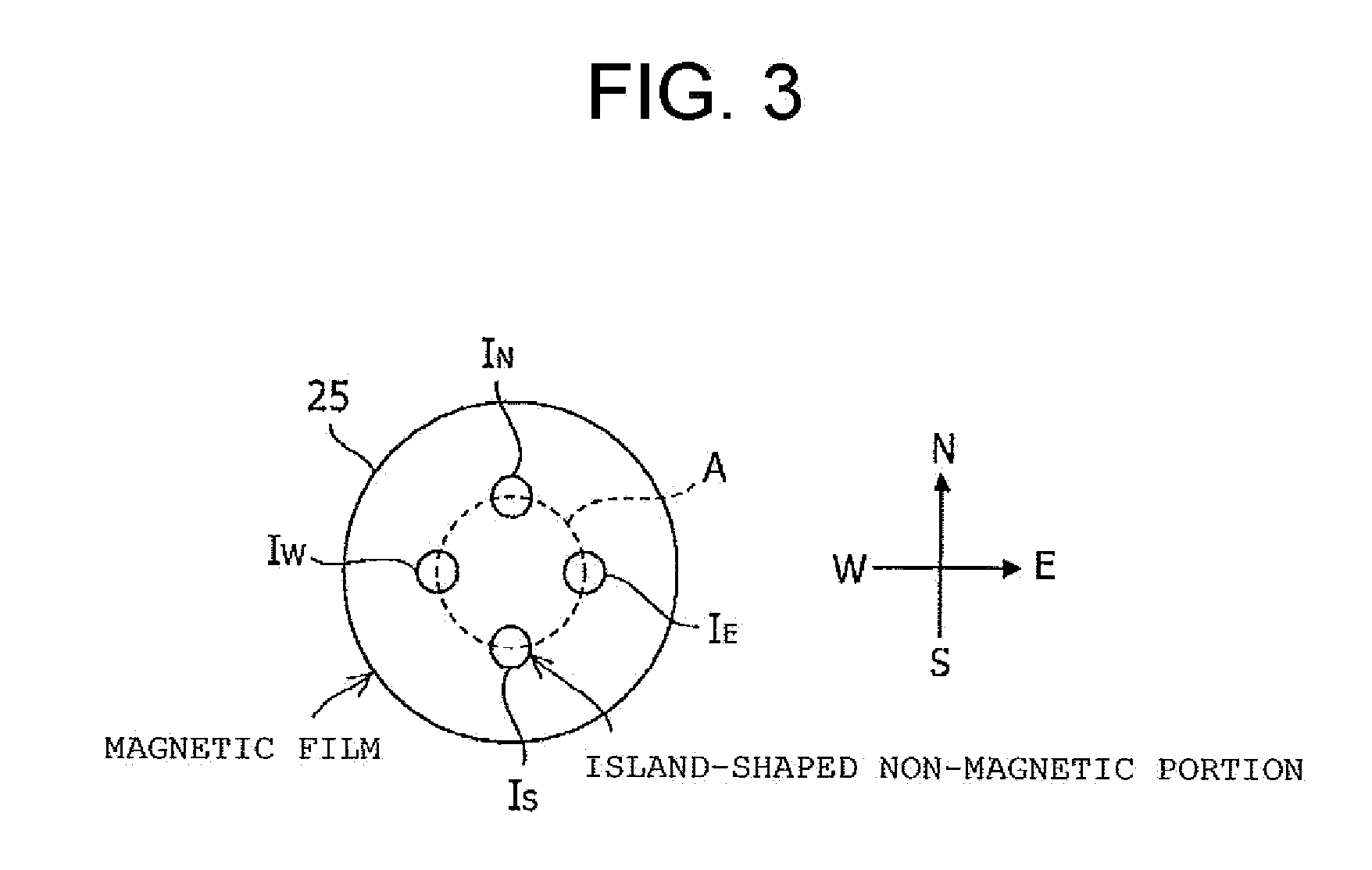
Provided is a spin valve element capable of performing multi-value recording, which includes a pair of ferromagnetic layers having different coercivities from each other, and sandwiching an insulating layer or a non-magnetic layer. The ferromagnetic layer having the smaller coercivity has a substantially circular in-plane profile, and a plurality of island-shaped non-magnetic portions IN, IE, IW, and IS are included. In addition, a storage device is manufactured by using such a spin valve element.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS20070009701A1High recording densityHigh transmittance velocityLayered productsRecord information storageRecording densityTransmittance
The present invention relates to an optical recording medium. The optical recording medium according to one embodiment of the present invention includes a substrate, a reflective layer located on the upper side of the substrate and reflecting an incident laser beam, and an information recording layer located on the reflective layer. The information recording layer includes a first recording layer containing Au and a second recording layer containing at least one element selected from the group consisting of Si, Ge, C, Sn and Zn. Therefore, the optical recording medium of the present invention may provide high recording density and transmittance velocity suitable for BD system by combining the recording layer materials.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Glass substrate for information recording media and information recording medium
InactiveCN1650353AImprove water resistanceImprove patienceBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageYoung's modulusEngineering
A glass substrate for information recording media in which the ratio (Rab / Raf) of the center line average height Raf of the surface of when the substrate is held in water at 80 DEG C for 24 hours to the center line average height Rab before it is held in water as above described is 0.8 to 1, and the Young's modulus is 90 GPa or more. An information recording medium having an information recording layer on such a glass substrate is also disclosed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Master disk exposure apparatus and master disk exposure method
InactiveUS20050094547A1High-density recordingHigh recording densityInformation arrangementRecord information storageComputational physicsPhotoresist
In Two-dimensional optical Compensation Exposure method, Beam 1, which has an intensity not less than a sensitivity of a photoresist layer and has a predetermined irradiation timing of exposed patterns, is radiated onto a predetermined area of the photoresist, and Beam 2, which has an intensity less than the sensitivity of the photoresist layer and has an irradiation timing of exposed patterns opposite to the predetermined timing, is radiated onto an area different from the predetermined area. Beam 2, which has the intensity less than the sensitivity of the photoresist layer, is radiated onto both sides P / P (2 T) in a disk radial direction of an area in which a shortest mark P22 is formed. The pit width is uniform irrelevant to the pit length. Further, it is possible to form the pit having a width shorter than a pit length. Therefore, it is possible to realize a high density.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
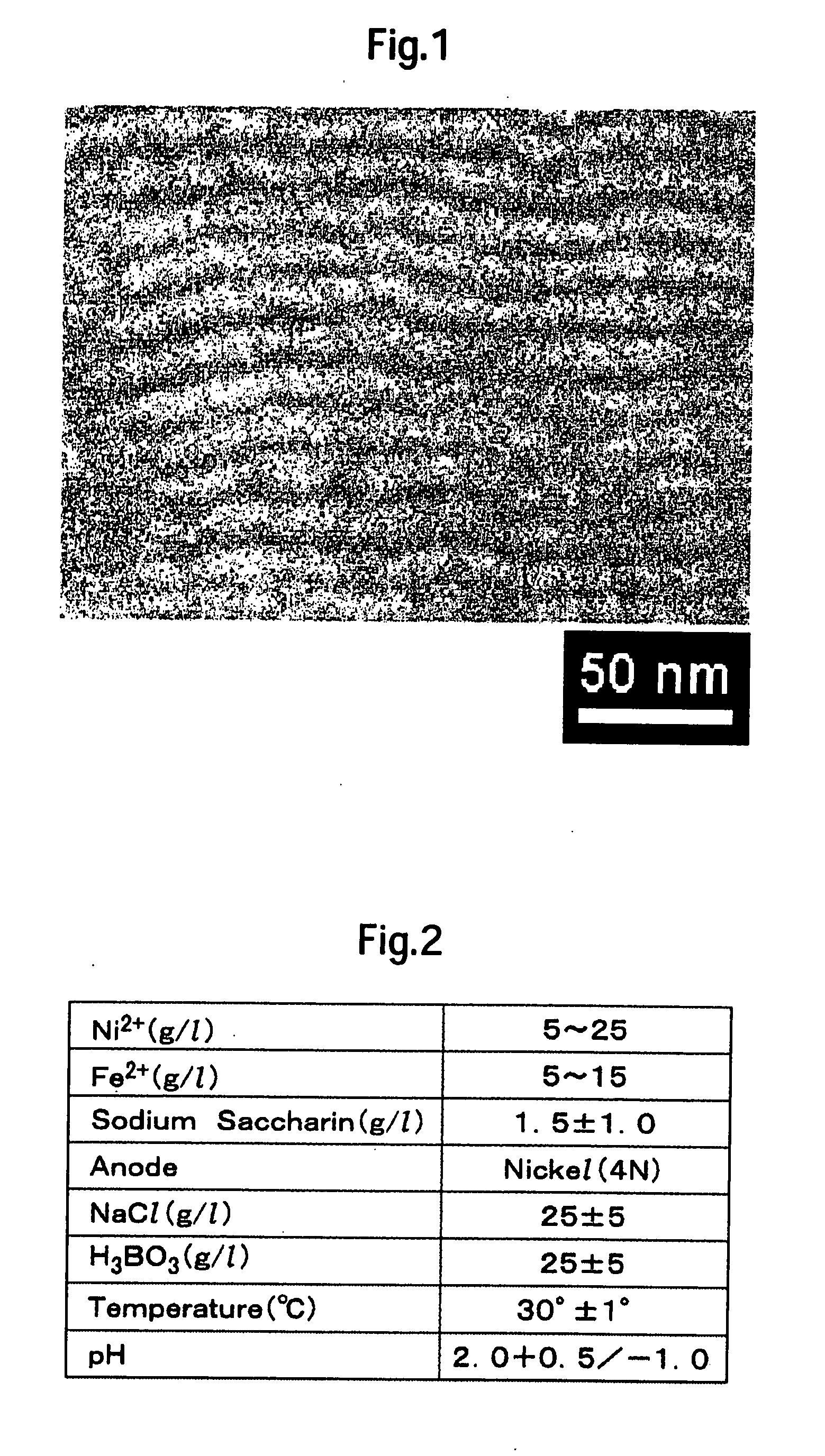
Magnetic film, manufacturing method thereof and thin film magnetic head
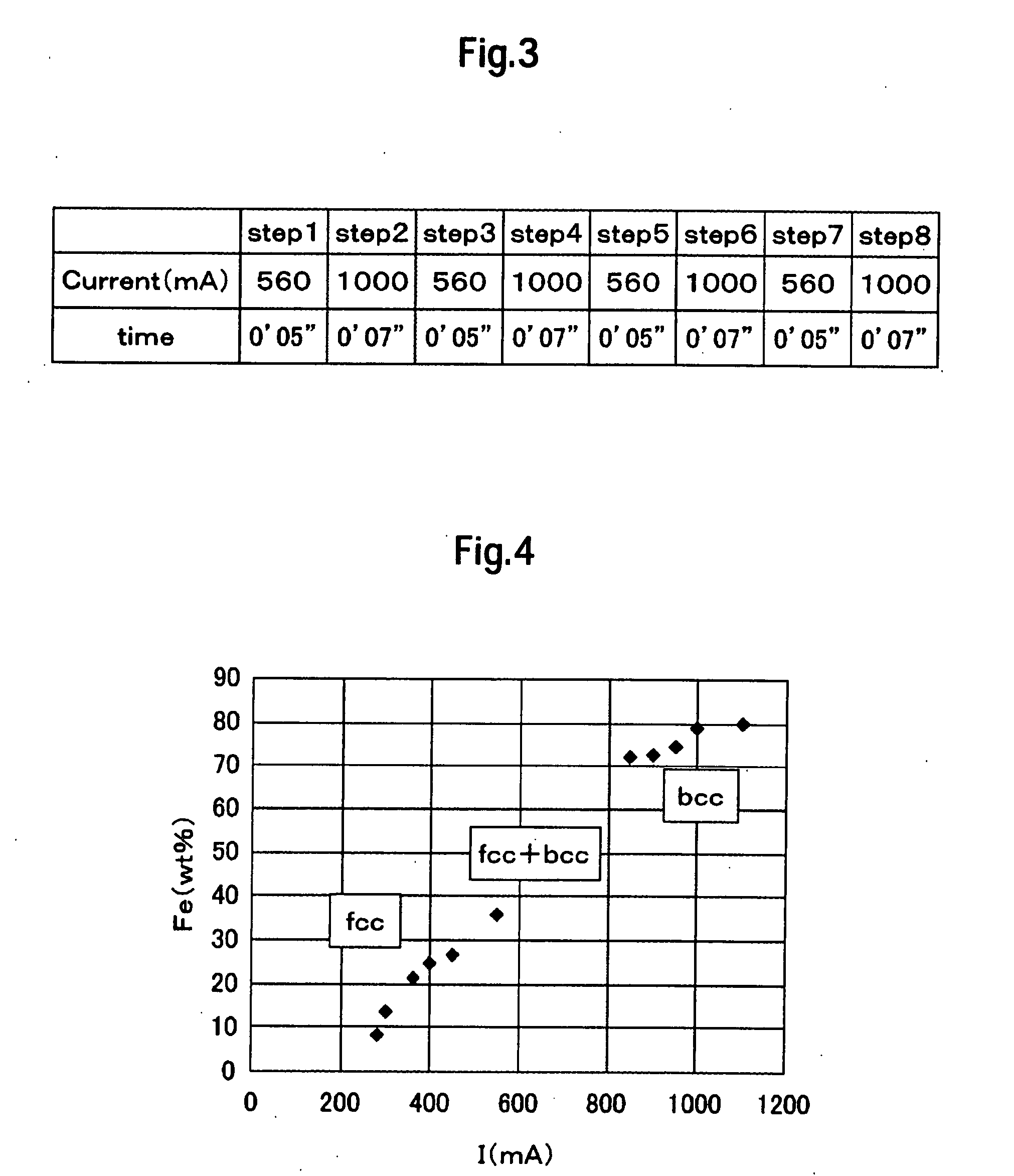
InactiveUS20080075977A1High data transfer rateHigh recording densityElectrical transducersRecord information storageMagnetic disksData transmission
Embodiments of the present invention provide a magnetic disk drive capable of allowing higher data transfer rates and higher recording densities. According to one embodiment, an upper magnetic core and lower magnetic core comprise a multi-layered magnetic film formed by alternately stacking a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystalline magnetic thin layer and a body-centered cubic (bcc) crystalline magnetic thin layer by plating. The plating bath is such that the temperature is about 30±1° C., pH is about 2.0−1.0 to 2.0+0.5, metal ion concentrations are about 5 to 25 (g / l) for Ni2+ and 5 to 15 (g / l) for Fe2+, saccharin sodium concentration is about 1.5±1.0 (g / l), sodium chloride concentration is about 25±5 (g / l), and boric acid concentration is about 25±5 (g / l). Since each layer's crystal structure is different from that of its adjacent lower layer, epitaxial growth is broken within each layer. Thus, since crystal grains are reduced in size, it is possible to lessen the decrease of the permeability μ at higher frequencies.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of manufacturing a thin film magnetic head comprising an insulating layer provided between a core and coil
InactiveUS7111387B2Decrease in inductanceHigh recording densityConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceVoltageEngineering
A method of manufacturing a thin film magnetic head comprising an insulating layer provided between a core and a coil is provided. Also provided is a method for forming an inorganic insulation underlying layer and an organic insulation underlying layer on a lower core layer behind a recording region. The withstand voltage between the lower core layer and the coil layer can be improved because a coil is formed on the organic insulation underlying layer with an inorganic insulation layer disposed on the organic insulation layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thermal transfer ink, thermal transfer sheet and method of thermal transfer recording therewith
InactiveCN100526393CImprove performanceBright colorMethine/polymethine dyesDuplicating/marking methodsLightfastnessPhotochemistry
A thermal transfer sheet and yellow ink for use in thermal transfer, with which highly dense clear yellow color can be exhibited with low energy, with which a thermal transfer record excelling in color tone and light fastness can be obtained, and with which a highly dense preferable green tone can be exhibited when mixed with cyan, and to provide a thermal transfer sheet. There is provided a dye composition characterized by containing a dye having an arylidene pyrazolone skeleton and a dye having a bispyrazolone methine skeleton. There is further provided a thermal transfer ink characterized by containing a dye having an arylidene pyrazolone skeleton, a dye having a bispyrazolone methine skeleton and a medium. There is still further provided a thermal transfer sheet comprising a base material and, superimposed thereon, a color material layer containing a dye having an arylidene pyrazolone skeleton and a dye having a bispyrazolone methine skeleton.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Aluminum alloy substrate for magnetic disk and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104109783BImprove smoothnessImprove impact resistanceBase layers for recording layers5005 aluminium alloy5052 aluminium alloy
The present invention provides an aluminium alloy substrate used for a magnetic disc, and a method of manufacturing the same. The aluminium alloy substrate is resistant to impact, has great flatness, and has a plated surface with excellent smoothness. The aluminium alloy substrate is characterized by comprising the following aluminium alloys: below 0.03 by mass of Si, below 0.03 by mass of Fe, over 3.5 and below 4.5 by mass of Mg, below 0.2 by mass of Cr, and at least one selected from over 0.01 and below 0.20 by mass of Cu and over 0.01 and below 0.40 by mass of Zn, the balance being Al and unavoidable impurities, wherein the degree of flatness is less than 5 [mu]m, and the area rate of equiaxed grains on the surface of the substrate is less than 30%.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
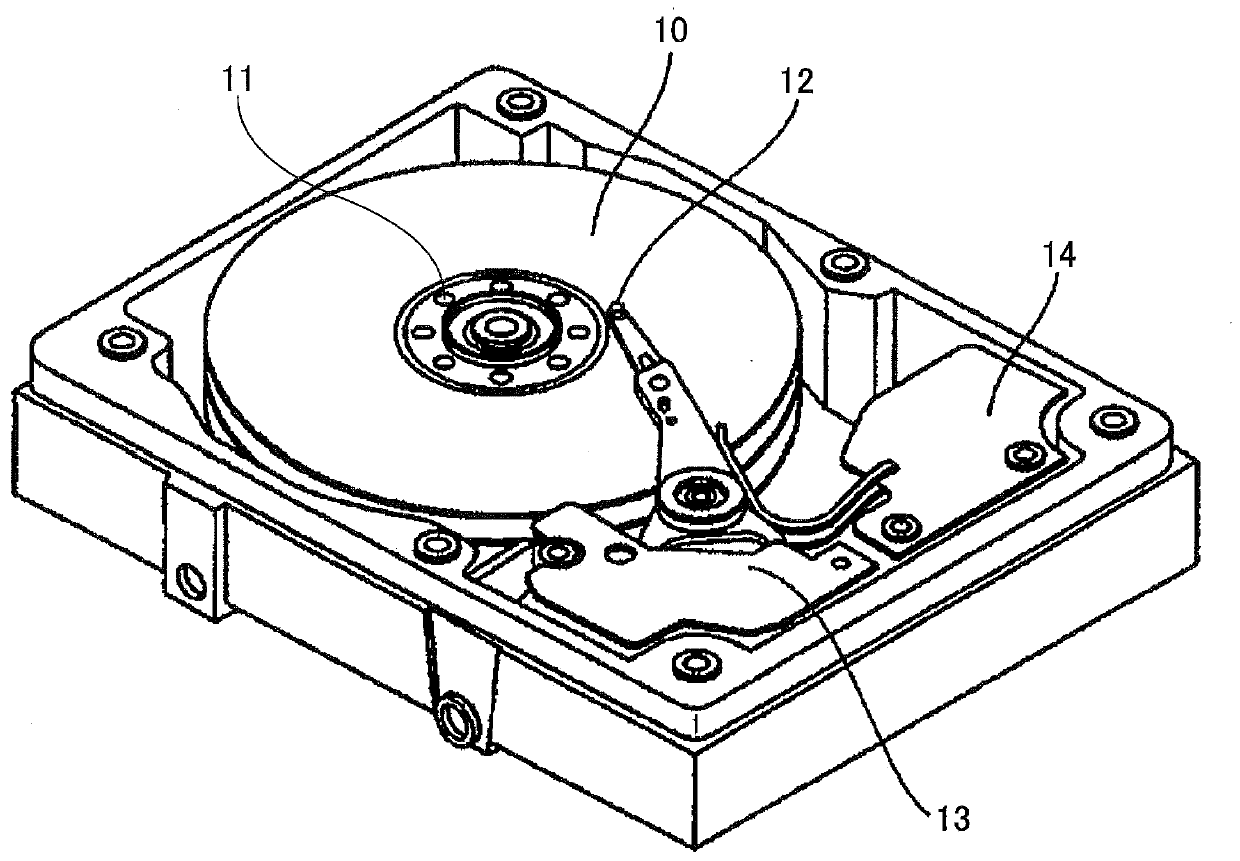
Information storage apparatus
InactiveCN101305426AHigh-speed rotationHigh recording densityCarrier constructional parts dispositionUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecording densityComputer science
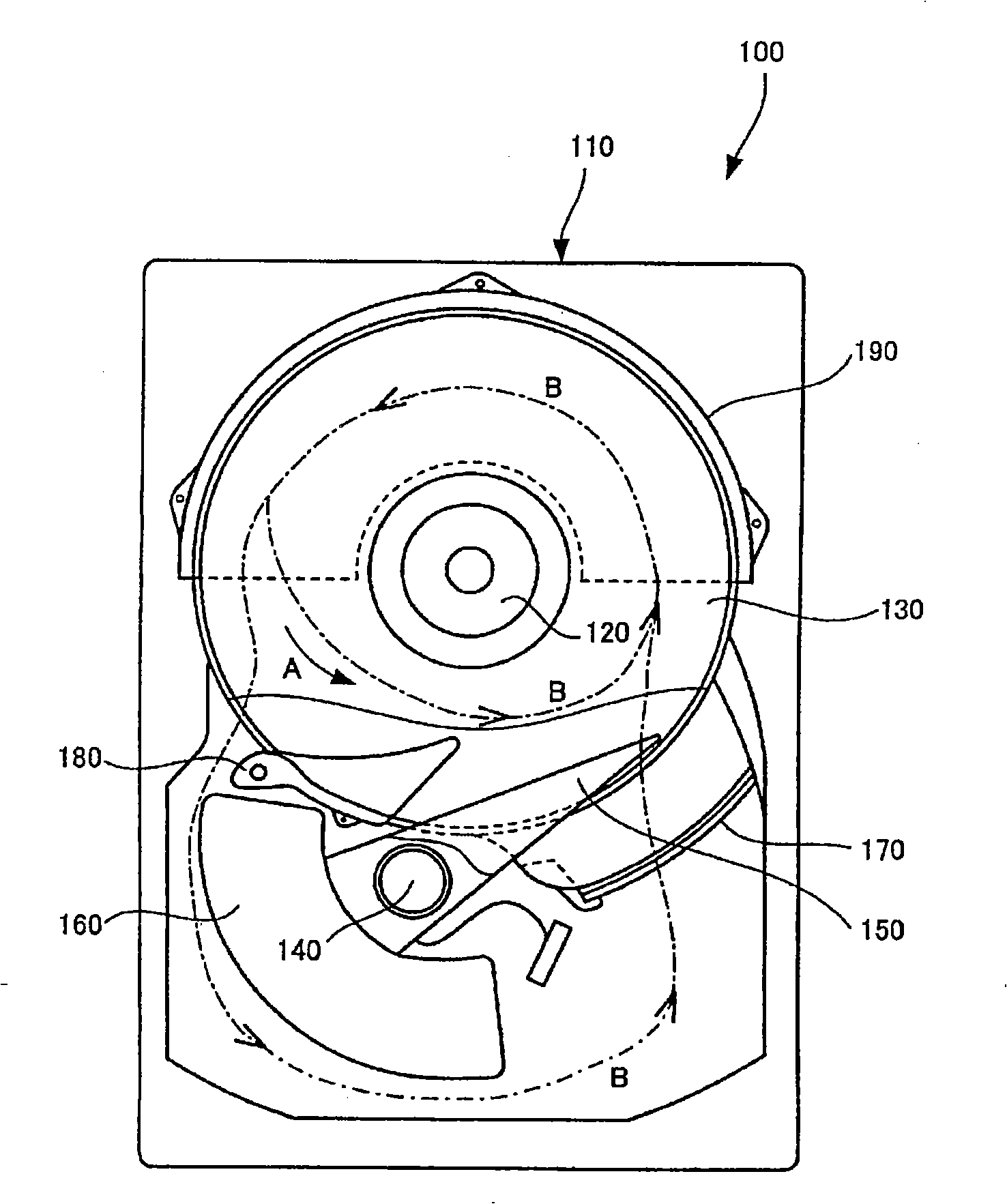
An information storage in which high-speed rotation of an information storage medium and high recording density of storage data are achieved. The information storage has one or more information storage media that each have a disc shape, that rotate while being secured to a common rotating shaft, and on which information is recorded; heads that approaches or in contact with the information storage media to access information; arms that extend along the surfaces of the information storage media, hold the heads on its their side, and pivot about a pivot shaft placed on the root side of the arms, and spoilers that straighten air flows between the information storage media and consist of metallic air flow control boards arranged between the information storage media; ; and a resin bracket that is formed integral with the air flow control boards and hold the air flow control boards between the information storage media.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Magnetic recording medium, manufacturing method of magnetic recording medium, and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
ActiveCN108231092BExcellent noise characteristicsHigh recording densityProtective coatings for layersBase layers for recording layersCarbideNon magnetic
A magnetic recording medium has a soft magnetic underlayer, an alignment control layer, a perpendicular magnetic layer and a protective layer in sequence on a non-magnetic substrate. The perpendicular magnetic layer has a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer in this order from the non-magnetic substrate side. The second magnetic layer is a magnetic layer on the outermost side including magnetic grains. The first magnetic layer is a magnetic layer having a granular structure in which grain boundaries contain oxide. The second magnetic layer is a magnetic layer having a granular structure including carbides at grain boundaries. The carbides are carbides of elements contained in the magnetic particles.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
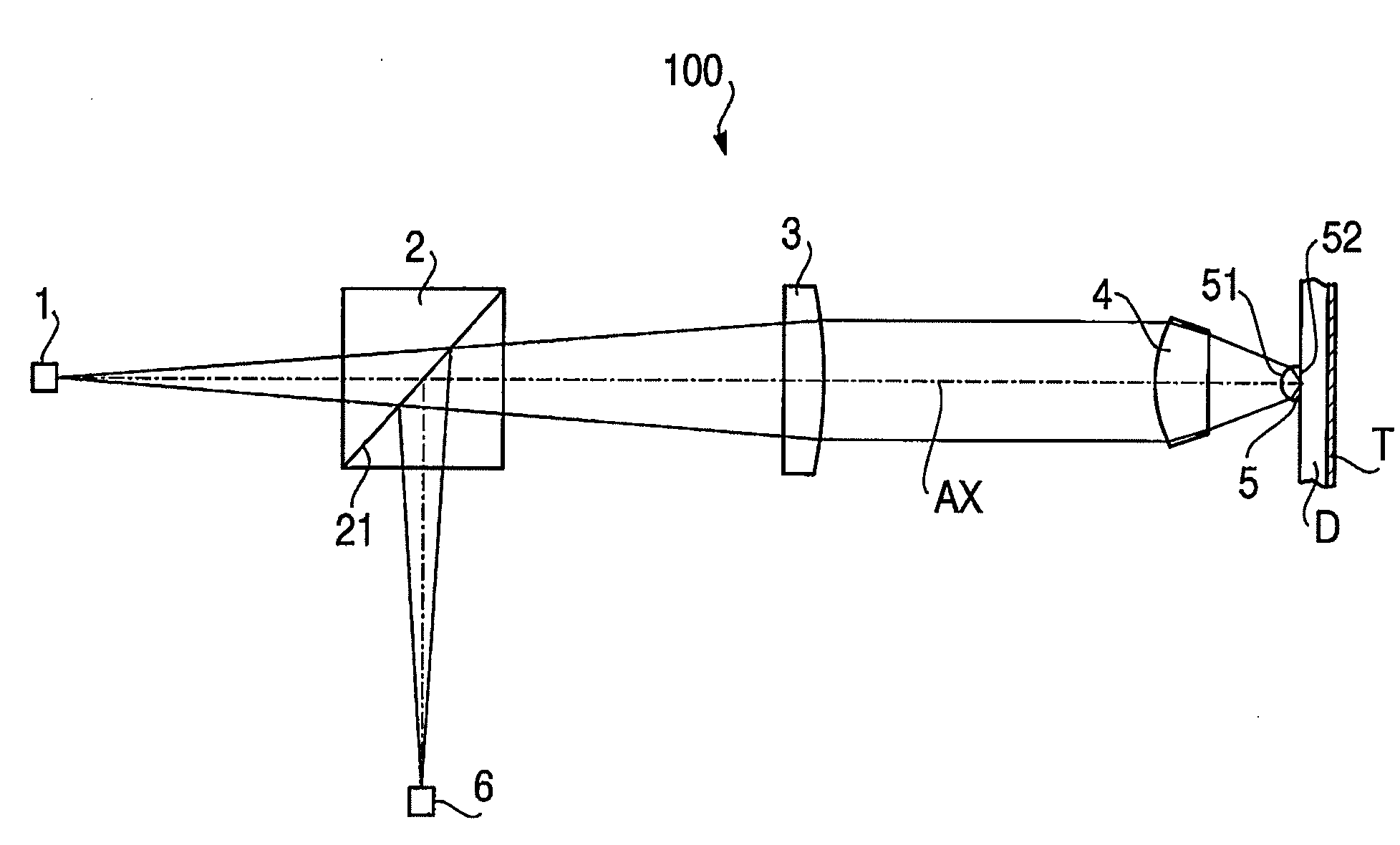
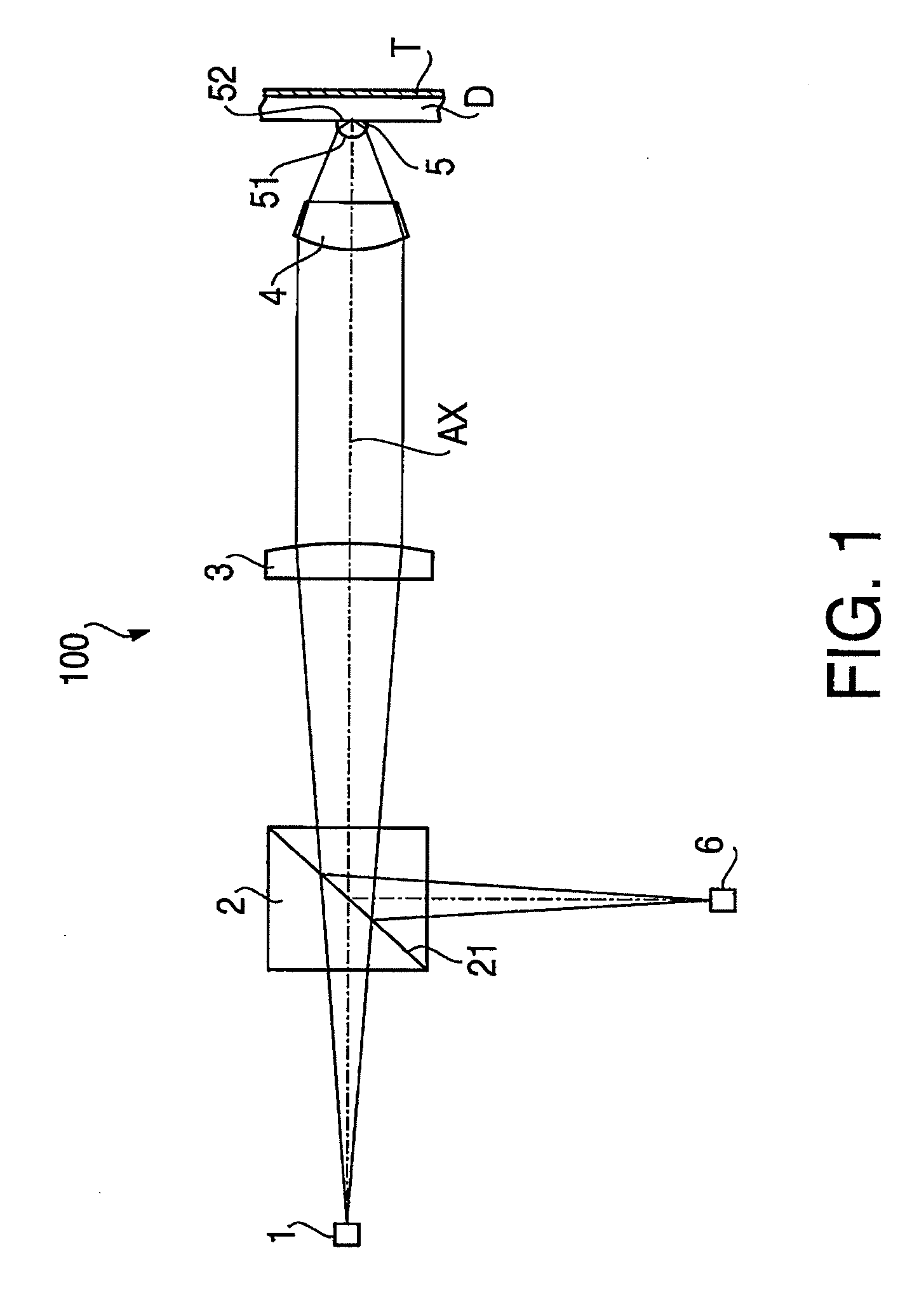
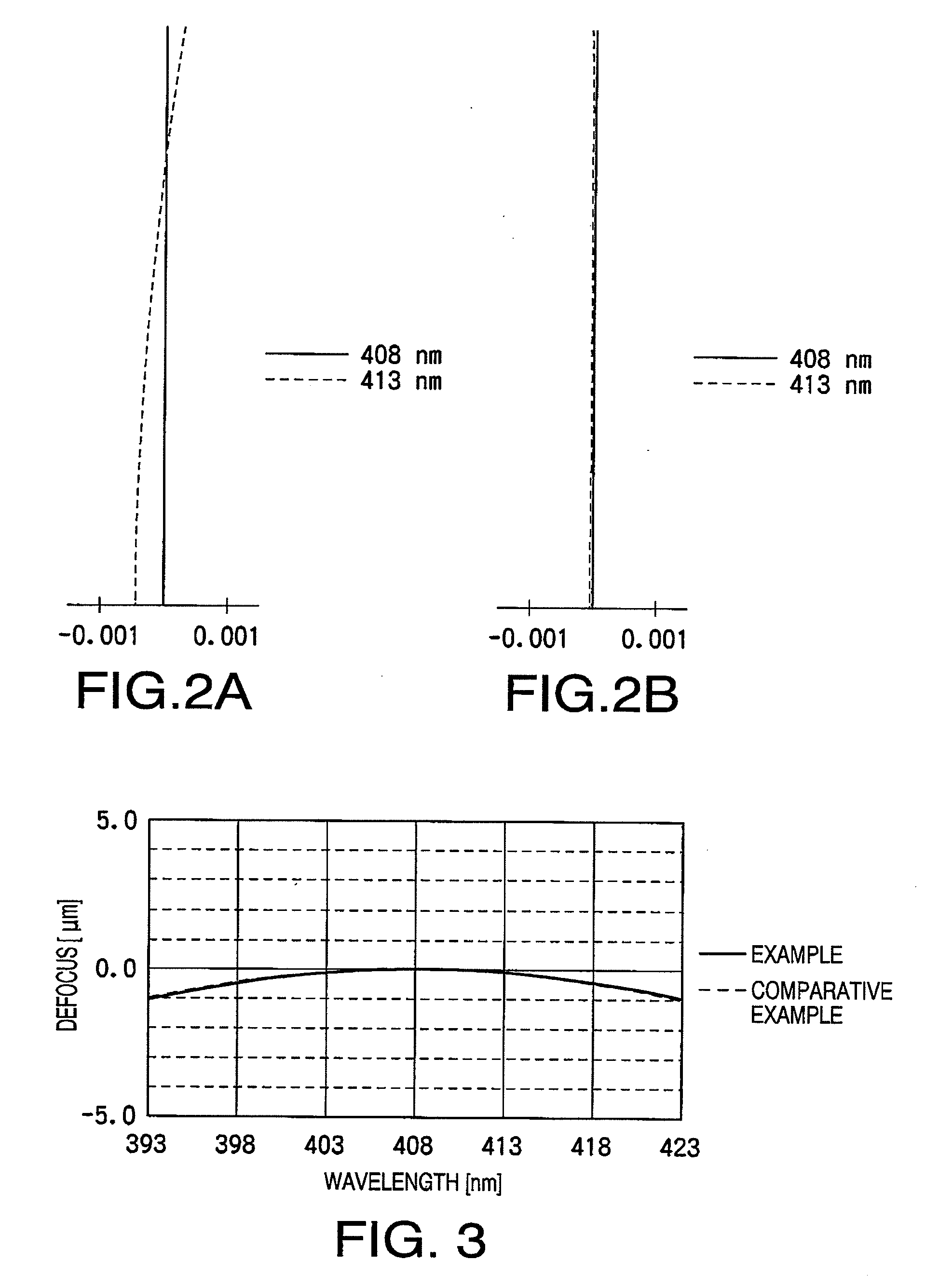
Optical element and objective optical system
InactiveUS20090201786A1High recording densitySuppress longitudinal chromatic aberrationRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansComputational physicsOptical path
There is provided an optical element for an objective optical system of an optical information recording / reproducing device. The objective optical system is configured to satisfy conditions: λ<500; NA≧0.7; and f≦1.0, and at least one of surfaces of the optical element includes a diffraction structure defined by an optical path difference function φ(h):φ(h)=(P2h2+P4h4+P6h6+P8h8+P10h10+P12h12)mλwhere P2, P4, P6 . . . denote coefficients of 2nd order, 4th order, 6th order . . . , respectively, h denotes a height from an optical axis of the optical element, and m denotes a diffraction order at which diffraction efficiency for the laser beam is maximized. The diffraction structure satisfies conditions:P2<0 (4);P2×P4<−100 (5); and−60<P2 / P4<0 (6).
Owner:HOYA CORP
Magnetic recording medium, method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
ActiveCN108231092AExcellent noise characteristicsHigh recording densityProtective coatings for layersBase layers for recording layersCarbideProtection layer
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com