Light-emitting diode (LED) driving power supply
A LED drive and circuit technology, applied in the direction of electric light source, light source, lamp circuit layout, etc., can solve the problems of high-power LED drive power supply complexity, lack of stability and reliability, and low work efficiency, so as to suppress adverse effects and avoid adverse consequences , the effect of cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
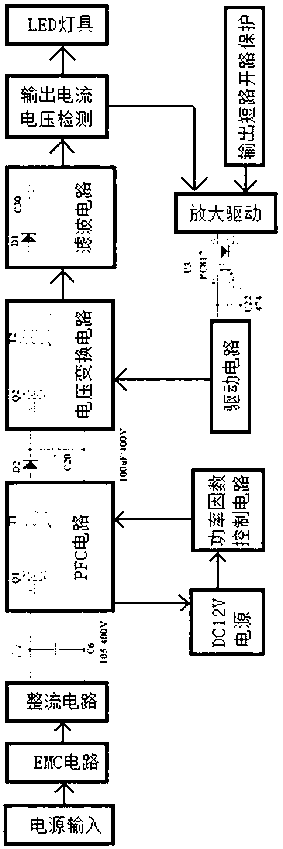
[0025] Such as figure 2 As shown, a LED drive power supply of the present invention includes a power input terminal 101, an EMC circuit 102, a rectifier circuit 103, a voltage conversion circuit 104, a filter circuit 105, an output current and voltage detection circuit 106, and an LED lamp 107 connected in sequence. . It also includes a constant current and constant voltage control circuit, including an amplifying drive 108 and a power factor control circuit 109, the input end of the amplifying drive 108 is connected to the output end of the output current voltage detection circuit 106, and the output end of the amplifying drive 108 is connected to the power factor control circuit 109 The input end of the power factor control circuit 109 is connected to the input end of the voltage conversion circuit 104 . At the same time, an inductor L3 and a piezoresistor YM3 are connected in series between the rectifier circuit 103 and the voltage conversion circuit 104, and the input te...
Embodiment 2
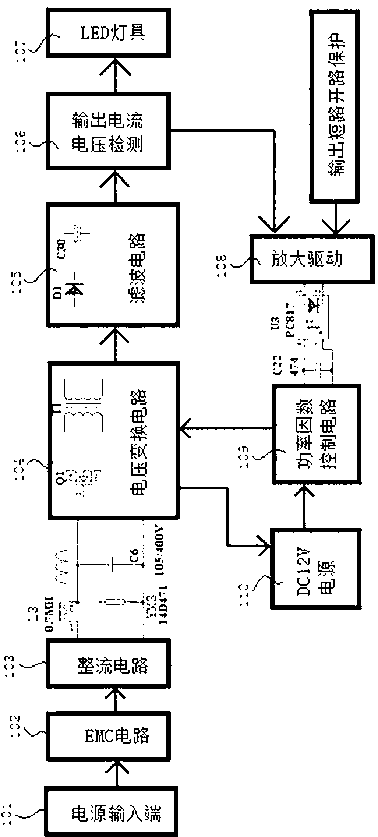
[0031] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: in this embodiment, an overvoltage protection circuit 111 is connected between the rectification circuit 103 and the power factor control circuit 109, and the input terminal of the overvoltage protection circuit 111 It is connected with the output end of the rectification circuit 103 , and the output end of the overvoltage protection circuit 111 is connected with the input end of the power factor control circuit 109 . When the voltage of the rectifier circuit 103 is higher than a certain value, the overvoltage protection circuit 111 sends the signal to the power factor control circuit 109 to control and cut off the voltage conversion circuit 104; when the voltage returns to the normal range, the overvoltage protection circuit 111 sends the signal The output is sent to the power factor control circuit 109, and the voltage conversion circuit 104 is controlled to be turned on.
[0032] ...
Embodiment 3
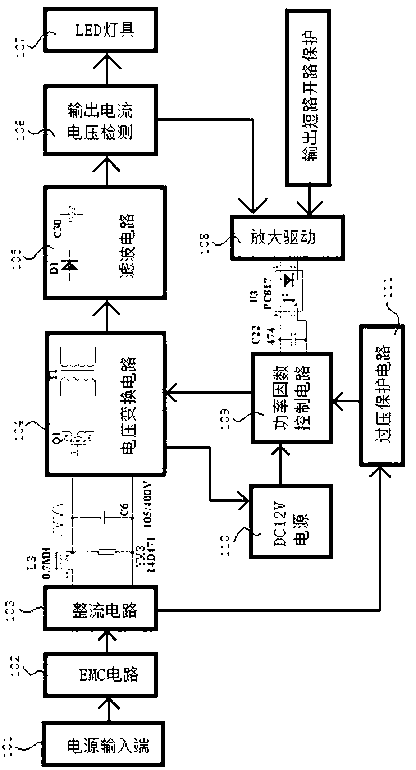
[0034] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in that: in this embodiment, the input end of the amplifying driver 108 is connected with an over-temperature protection circuit 112 . When the temperature of the LED lamp 107 is too high, the over-temperature protection circuit 112 sends the signal to the amplifying driver 108, and the voltage fed back from the amplifying driver 108 to the power factor control circuit 109 increases, and then the power factor control circuit 109 makes the output control signal The duty cycle is reduced, and then the conduction time of the MOS transistor Q1 in the voltage conversion circuit 104 is controlled to be shortened, thereby forcibly reducing the output current, avoiding damage to the LED lamp due to excessive temperature, and further improving the stability and reliability of use.
[0035] Other structures are the same as in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com