A method for in situ remediation of uranium-contaminated groundwater using indigenous functional microbial communities
A functional microorganism, in-situ remediation technology, applied in the field of in-situ remediation of uranium-contaminated groundwater, can solve problems such as large chemical composition interference, difficulty in secondary treatment, secondary environmental pollution, etc., achieving low operating costs, easy control of the treatment process, No secondary pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
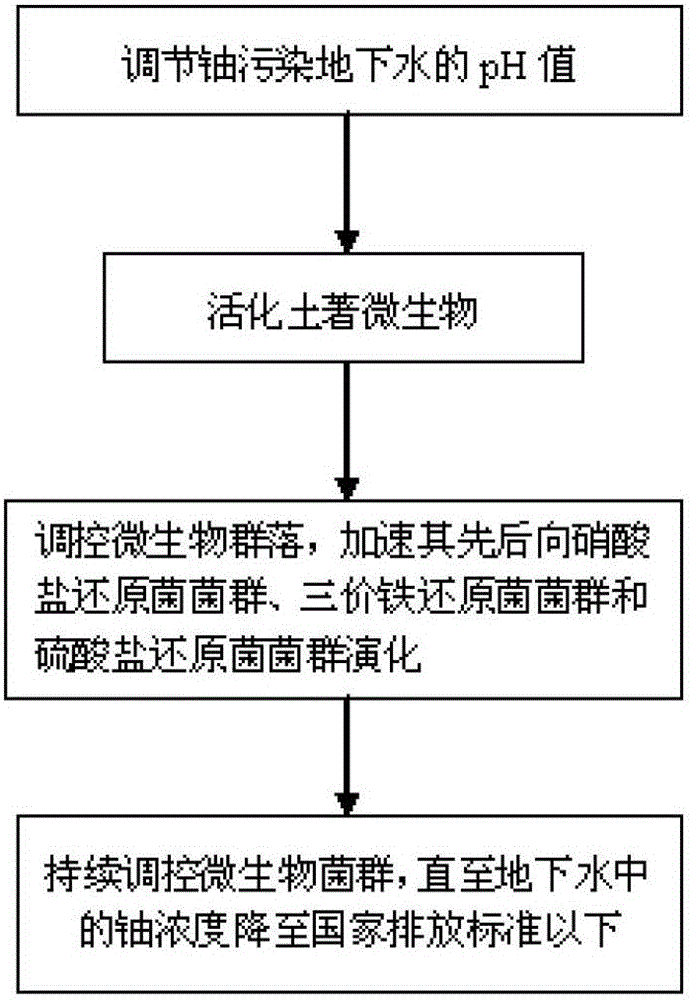
[0045] A method for in-situ remediation of uranium-contaminated groundwater using indigenous functional microbial communities, the specific steps of which are:
[0046] (1) Uranium-contaminated groundwater samples and soil collection
[0047] The uranium-contaminated groundwater is collected in the monitoring well of the uranium tailings pond, and the soil is collected next to the monitoring well for anaerobic preservation.
[0048] (2) Activation of indigenous functional microorganisms
[0049] with 30mM NaHCO 3 The solution adjusts the pH of the uranium-contaminated groundwater to a range of 6.5-7.5, and then mixes the soil and the uranium-contaminated groundwater after the pH adjustment in a jar, adds carbon source materials, and passes through nitrogen to exhaust oxygen. A rubber stopper and a sealing film are used to seal the mouth of the jar, and then the jar is left to stand anaerobically, in the dark and at a constant temperature to activate the indigenous functional...
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1, in the anaerobic bioreactor, adding 1L uranium concentration is 0.462mg / L uranium-contaminated groundwater and 50g fresh soil (moisture content 42%), adding 4.5g glucose as carbon source, and the native functional microbial community After continuous regulation, the uranium concentration in the uranium-contaminated groundwater in the anaerobic bioreactor decreased to 0.040 mg / L after 75 days.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2, in the anaerobic bioreactor, add 1L of uranium-contaminated groundwater with a uranium concentration of 0.462mg / L and 50g of fresh soil (moisture content 42%), add 5g of glucose as a carbon source, and carry out the indigenous functional microbial community After continuous regulation, the uranium concentration in the uranium-contaminated groundwater in the anaerobic bioreactor decreased to 0.037 mg / L after 105 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com