Self-starting mode-locked fiber laser for polarization state stability control
A technology of fiber lasers and polarization controllers, applied in lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of high price of polarization-maintaining doped fibers, affecting long-term stability of mode-locking, difficulties in starting and maintaining mode-locking, etc. problems, to achieve increased long-term stability and service life, easy compression, and high pulse contrast
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
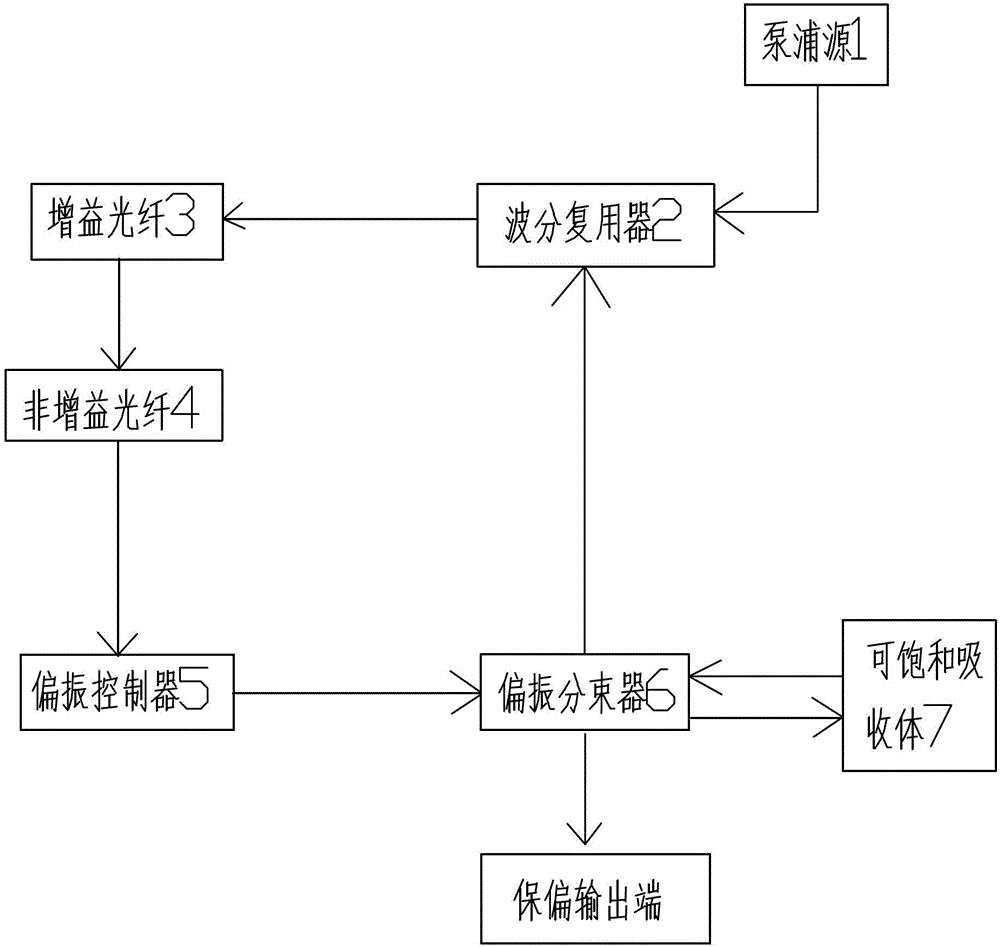
[0029] Such as figure 2 As shown, between the polarizing beam splitter 6 and the saturable absorber 7, a λ / 4 wave plate and a microlens are sequentially arranged.
[0030] A light collimator is provided between the polarization controller 5 and the polarization beam splitter 6 .
[0031] An optical isolator is provided between the polarization controller 5 and the optical collimator.
[0032] An optical collimator is provided between the polarization beam splitter 6 and the wavelength division multiplexer 2 .
[0033] As mentioned above, this embodiment is a half-space half-fiber laser structure, using figure 2 The σ-cavity structure shown uses saturable absorbing mirrors and polarization rotation to achieve mode-locking.
[0034] In this embodiment, a semiconductor laser with a wavelength of 980nm is used for forward pumping, and is coupled into the optical path through a wavelength division multiplexer. In order to fully absorb, a highly doped ytterbium-doped fiber is u...
Embodiment 2
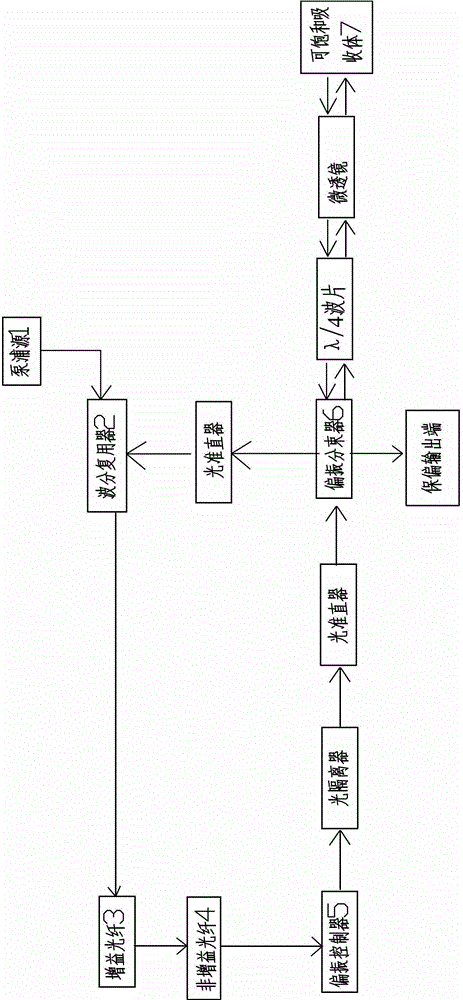
[0036] Such as image 3 As shown, a polarization controller is provided between the polarization beam splitter 6 and the saturable absorber 7 .
[0037] An optical isolator is provided between the polarization controller 5 and the polarization beam splitter 6.
[0038] As mentioned above, this embodiment is an all-fiber laser structure, using image 3 The σ-cavity structure shown uses saturable absorbing mirrors and polarization rotation to achieve mode-locking.
[0039]In this embodiment, a semiconductor laser with a wavelength of 980nm is used for forward pumping, and is coupled into the optical path through a wavelength division multiplexer. In order to fully absorb, a highly doped ytterbium-doped fiber is used as the gain medium. Single-mode fiber is used to control the repetition rate, and its length depends on the actual required pulse repetition rate. A polarization controller is used to change the polarization state of the laser. The light then passes through an op...
Embodiment 3
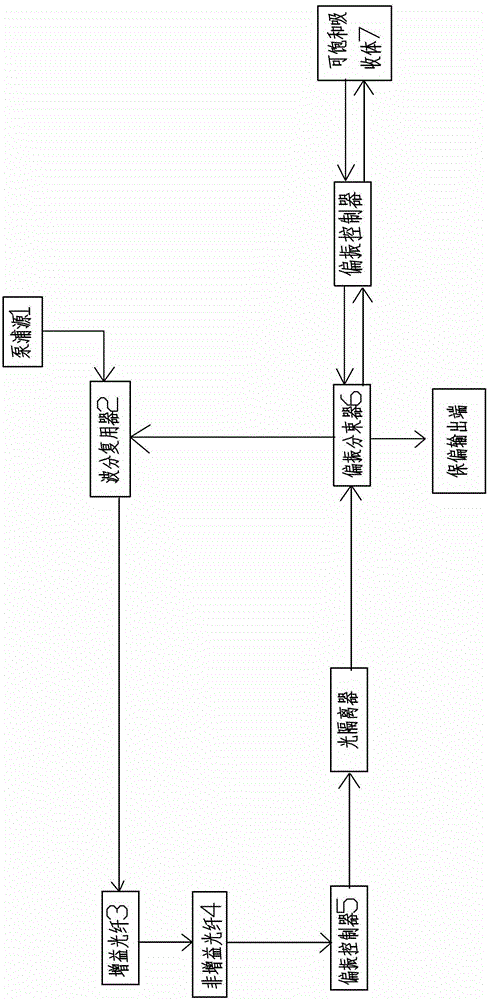
[0041] This embodiment is the control of the center wavelength, in figure 2 with image 3 In this method, the laser cavity structure is kept unchanged, and the saturable absorbing mirror and polarization rotation are used to achieve mode locking.
[0042] In this embodiment, a semiconductor laser with a wavelength of 980nm is used for forward pumping, a wavelength division multiplexer is used to couple the pump light into the optical path, a highly doped erbium-doped fiber is used as the gain medium, and a single-mode fiber with a center wavelength of 1550nm is used. Controls the repetition rate of the pulses. After passing through the single-mode fiber, the light enters the polarization controller to change the polarization state of the laser. Then the light passes through an optical isolator with a wavelength of 1550nm to ensure the unidirectional operation of the light, figure 2 In the process, the central wavelength of the optical collimator, λ / 4 glass slide, spatial ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com