Nano bacterial cellulose superfine fiber processing method
A bacterial cellulose and microfiber technology, applied in fiber processing, complete sets of equipment for producing artificial threads, filament/thread forming, etc., can solve the problem of single product structure, low added value of products, insufficient investment in deep processing and application research, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of clean processing method, wide range of application fields and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
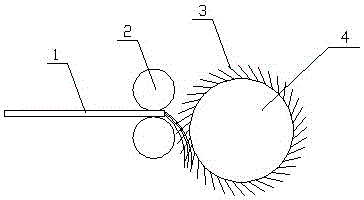
[0022] The bacterial cellulose wet film 1 is gripped and fed by a gripping roller 2 with a diameter of 20 mm, and the feeding speed is 10 mm / min.
[0023] At a diameter of 300mm, a rotational speed of 400 rpm, and a planting density of 2 roots / cm 2 Under the action of needle-punched licker-in rollers, the bacterial cellulose wet film is carded and divided to obtain ultrafine bacterial cellulose fibers with a fiber diameter of 450nm and a length of 5-100mm. The acupuncture length is 0.1cm, the diameter of the acupuncture shaft is 0.001mm, the diameter of the acupuncture tip is 1um, and the length of the acupuncture tip is 1mm.
[0024] Put the obtained bacterial cellulose fibers in a refiner to refine pulp to form bacterial cellulose superfine fibers, and then filter them through a filter press to prepare bacterial cellulose superfine fibers with a moisture content of 20,000%. The fiber diameter is 450nm, and the ultrafine fiber length is 5~100mm.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Use a holding roller with a diameter of 30mm to hold and feed the bacterial cellulose wet film, and the feeding speed is 20mm / min.
[0027] At a diameter of 300mm, a rotational speed of 400 rpm, and a planting density of 20 roots / cm 2 Under the action of needle-punched licker-in rollers, the bacterial cellulose wet film is carded and divided to obtain ultrafine bacterial cellulose fibers with a fiber diameter of 450nm and a length of 5-100mm. The acupuncture length is 1cm, the diameter of the acupuncture shaft is 0.1mm, the diameter of the acupuncture tip is 10um, and the length of the acupuncture tip is 2mm.
[0028] Put the obtained bacterial cellulose fibers in a refiner to refine the pulp to form bacterial cellulose ultrafine fibers, and then filter them through a filter press to prepare bacterial cellulose ultrafine fibers with a moisture content of 20,000%. The fiber diameter is 350nm, and the ultrafine fiber length is 5~100mm.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Use a holding roller with a diameter of 40mm to hold and feed the bacterial cellulose wet film, and the feeding speed is 40mm / min.
[0031] At a diameter of 300mm, a rotational speed of 400 rpm, and a planting density of 100 roots / cm 2 Under the action of needle-punched licker-in rollers, the bacterial cellulose wet film is carded and divided to obtain ultrafine bacterial cellulose fibers with a fiber diameter of 450nm and a length of 5-100mm. The acupuncture length is 2cm, the diameter of the acupuncture shaft is 2mm, the diameter of the acupuncture tip is 20um, and the length of the acupuncture tip is 5mm.
[0032] Put the obtained bacterial cellulose fibers in a refiner to refine the pulp to form bacterial cellulose ultrafine fibers, and then filter them through a filter press to prepare bacterial cellulose ultrafine fibers with a moisture content of 20,000%. The fiber diameter is 250nm, and the ultrafine fiber length is 5~100mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com