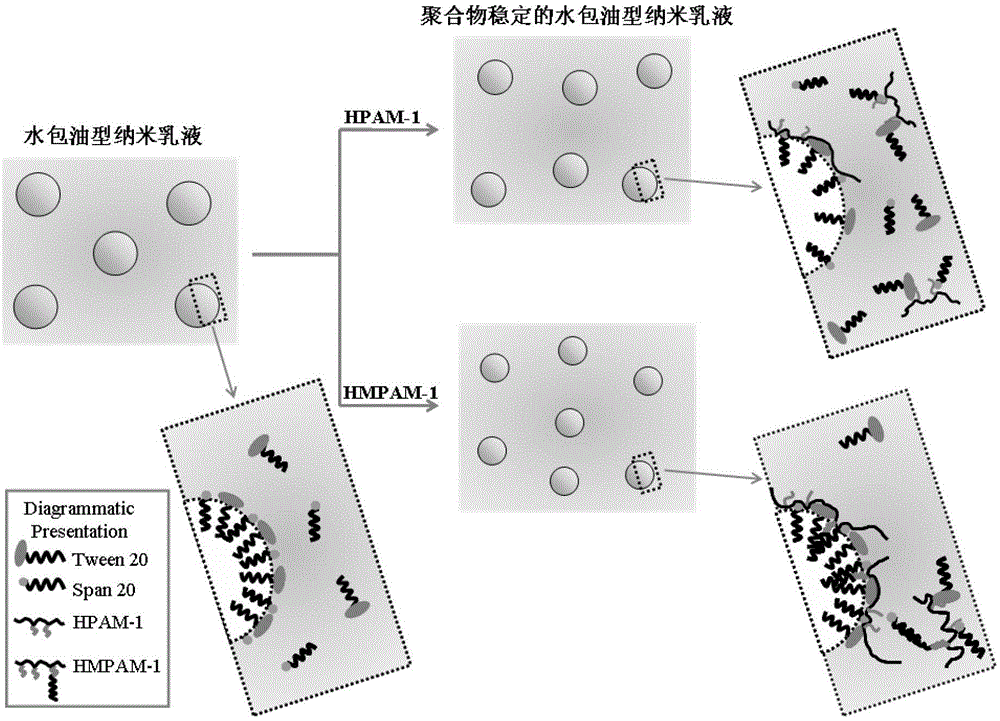
Preparation method for nano-emulsion with stable polymers
A nanoemulsion and polymer technology, applied in drilling compositions, chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of poor nanoemulsion stability, easy contamination of preparations, and high cost, and achieve a simple and easy preparation method. Operation, low energy consumption, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Preparation of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM-1) stabilized nanoemulsion
[0044] The nanoemulsion is based on 100 parts by weight, and the components are as follows: 20 parts of liquid paraffin, 5.12 parts of nonionic surfactant Tween20, 4.88 parts of nonionic surfactant Span20, partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (average molecular weight is 12 million, degree of hydrolysis 18 %, abbreviated as HPAM-1) 7×10 -5 ~1.4×10 -2 parts, and the balance is water.
[0045] The preparation steps are as follows:
[0046] (1) Weigh 1.25g HPAM-1 and dissolve it in 250ml three times of water to prepare 0.5wt% HPAM-1 mother liquor.
[0047] (2) Weigh 1.28g of nonionic surfactant Tween20 and 1.22g of Span20 into a 30ml bottle, then add 5g of oil-phase liquid paraffin respectively, and stir at a temperature of 15-20°C and 1000-2000rpm at high speed for 5-10min. A total of 9 bottles (marked as A~I) of nanoemulsion mixture were prepared.
[0048] (3) Sequentia...
Embodiment 2
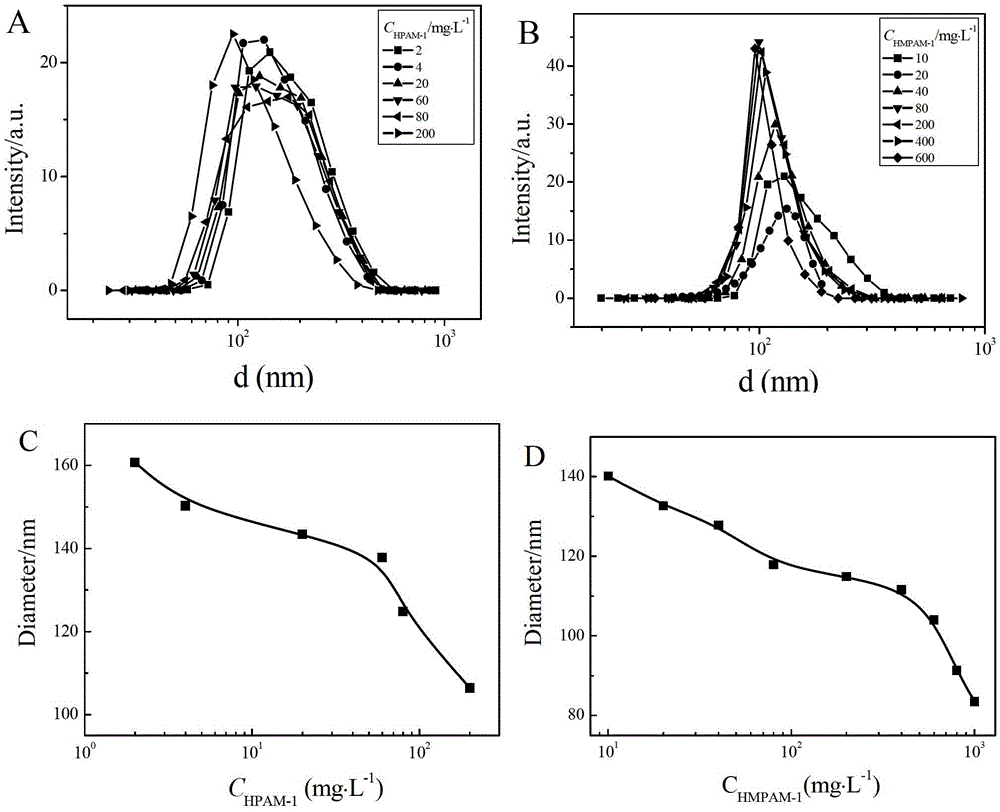
[0050] Gained HPAM-1O / W emulsion changes trend figure and particle size distribution with polymer concentration change as image 3 As shown in (A,C), the surface tension of pure HPAM-1 aqueous solution and the O / W emulsion at the same concentration and the oil-water interfacial tension are as follows: Figure 4 As shown in (A,C), the zeta potential of the emulsion changes with the polymer concentration as Figure 5 As shown in (A), the viscosity of the emulsion changes with the shear rate at different polymer concentrations as follows Image 6 As shown in (A), the zero-shear viscosity of the emulsion changes at different polymer concentrations as Figure 7 Shown in (A). Example 2: Preparation of Hydrophobically Modified Polyacrylamide (HMPAM-1) Stabilized Nanoemulsion
[0051] The nanoemulsion is based on 100 parts by weight, and the components are as follows: 20 parts of liquid paraffin, 5.12 parts of nonionic surfactant Tween20, 4.88 parts of nonionic surfactant Span, hyd...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The trend graph and particle size distribution of HMPAM-1O / W emulsion with the change of polymer concentration are as follows image 3 As shown in (B, D), the surface tension of pure HMPAM-1 aqueous solution and O / W emulsion at the same concentration and the interfacial tension of oil and water are as follows: Figure 4 As shown in (B,D), the zeta potential of the emulsion changes with the polymer concentration as Figure 5 As shown in (B), the viscosity of the emulsion changes with the shear rate at different polymer concentrations as Image 6 As shown in (B), the zero-shear viscosity of the emulsion changes at different polymer concentrations as Figure 7 (B) shown. Example 3: Preparation of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM-2) stabilized nanoemulsion
[0057] The nanoemulsion is based on 100 parts by weight, and the components are as follows: 20 parts of n-heptane, 5.12 parts of nonionic surfactant Tween 60, 4.88 parts of nonionic surfactant Span 60, parti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com