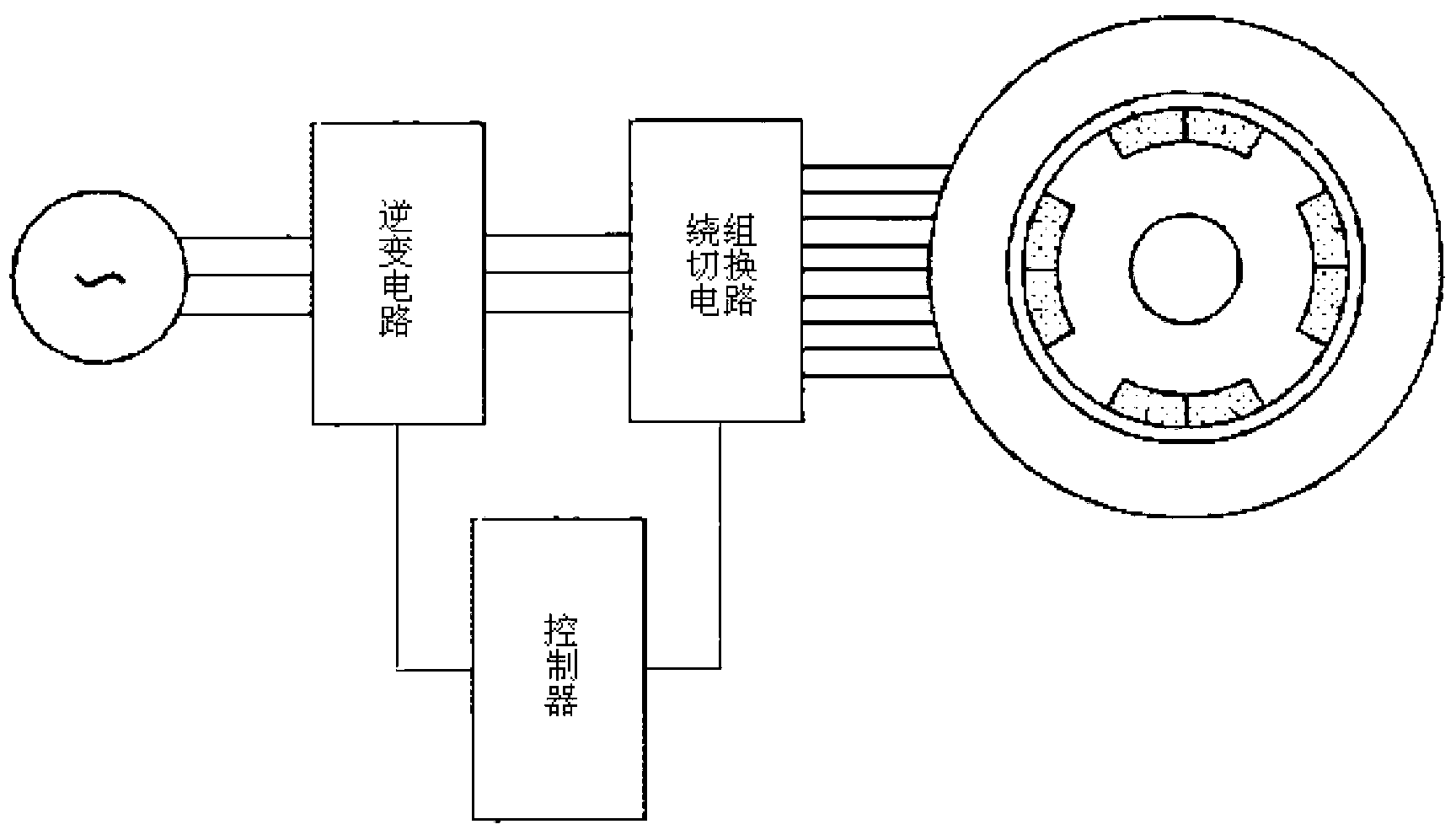
Pole-changing control permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, pole-changing speed regulation technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., can solve the problem of increasing armature current, limiting the application range of permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotor magnetic pole It is difficult to change the number of polar pole pairs to achieve the effect of reducing loss, realizing high-speed constant power characteristics, and widening the speed regulation range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
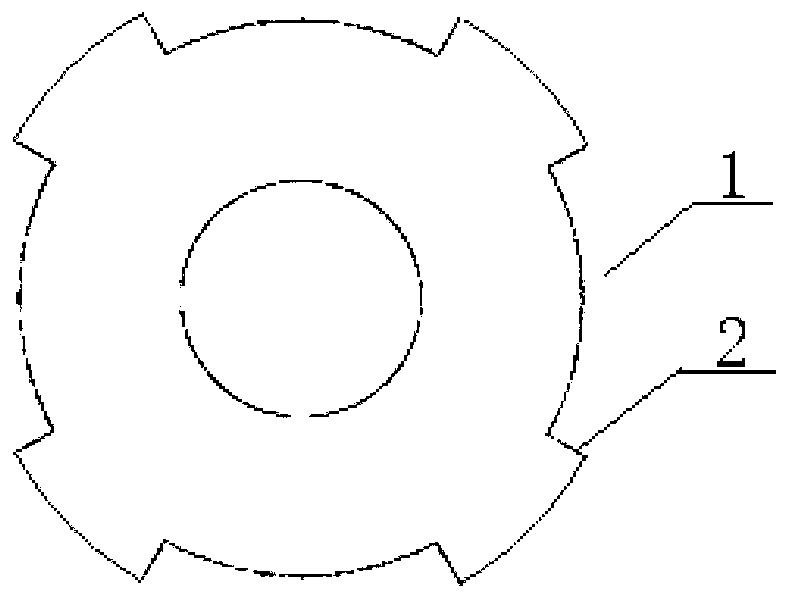
[0018] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 2 , 3 and 4 describe this embodiment. In this embodiment, the pole-changing speed-regulating permanent magnet synchronous motor includes a stator and a rotor, and an air gap is formed between the stator and the rotor; the stator includes a stator core and a stator winding, and the rotor includes a rotor core and a plurality of permanent magnets, and the permanent magnets are tile shape, the multi-piece permanent magnets are divided into two types: strong magnetic permanent magnet 4 and weak magnetic permanent magnet 3; the rotor core is cylindrical, and the air gap side surface of the rotor core has 4 salient poles 2 and 4 grooves 1 structure arranged alternately along the circumferential direction, the cross section of the groove 1 is fan-shaped, the width of each groove 1 along the circumferential direction is twice the width of the salient pole 2 along the circumferential direction, in each groove 1 Embed two tile-shape...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Specific implementation mode two: see Figure 5 This embodiment will be described. The pole-changing speed-regulating permanent magnet synchronous motor described in this embodiment includes a stator and a rotor, and there is an air gap between the stator and the rotor; the stator includes a stator core and a stator winding, and the rotor includes a rotor core and a plurality of permanent magnets. The permanent magnets are tile-shaped, and the multi-piece permanent magnets are divided into two types: strong magnetic permanent magnets 4 and weak magnetic permanent magnets 3; the rotor core is cylindrical, and the air gap side surface of the rotor core is four salient poles 2 and 4 A structure in which four grooves 1 are arranged alternately along the circumferential direction, the cross section of the grooves 1 is fan-shaped, there are 2 wide grooves and 2 narrow grooves in the 4 grooves 1, and the wide grooves and narrow grooves are alternated Arranged, the width of th...
specific Embodiment approach 3
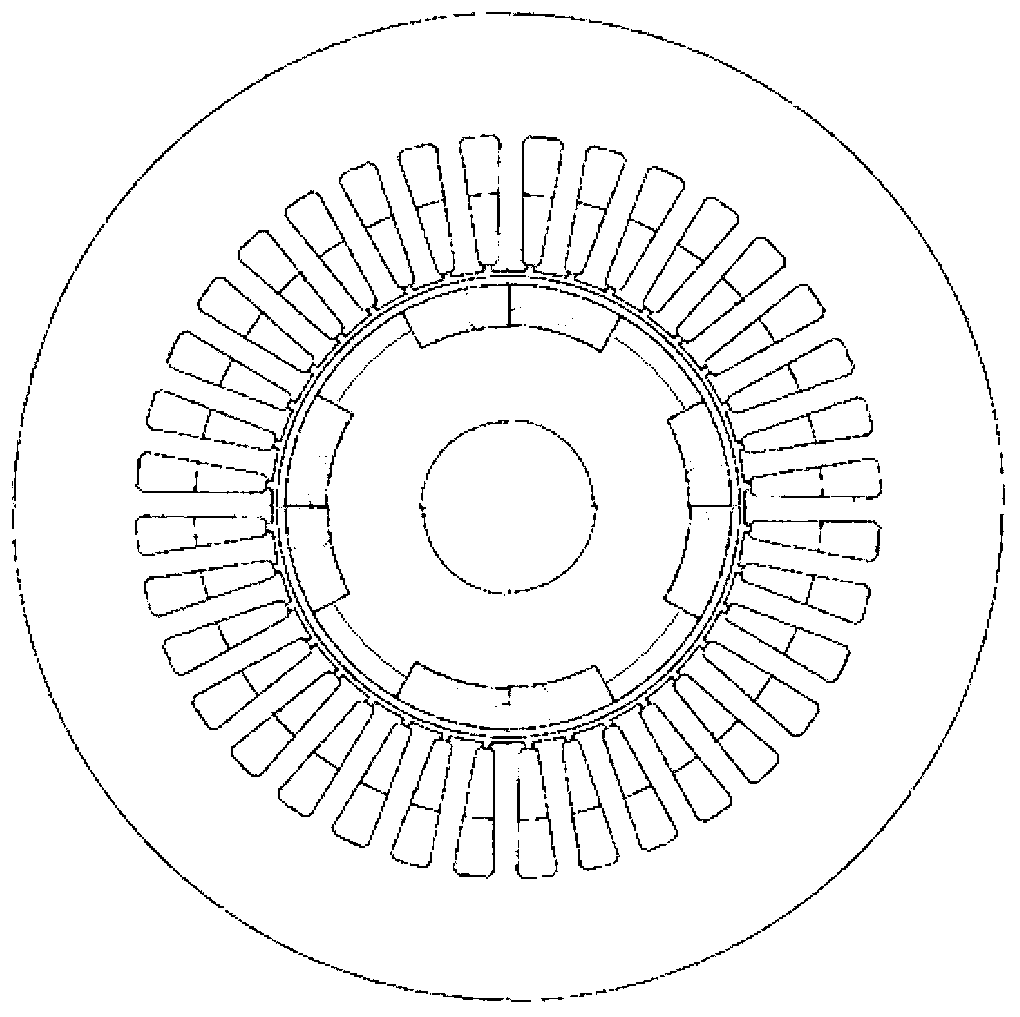
[0020] Specific implementation mode three: see Figure 6 This embodiment will be described. The pole-changing speed-regulating permanent magnet synchronous motor described in this embodiment includes a stator and a rotor, and there is an air gap between the stator and the rotor; the stator includes a stator core and a stator winding, and the rotor includes a rotor core and a plurality of permanent magnets. The permanent magnet is in the shape of a flat plate, and the multi-piece permanent magnets are divided into two types: strong magnetic permanent magnet 4 and weak magnetic permanent magnet 3; the rotor core is cylindrical, and 12 pieces are axially opened inside the rotor core near the side surface of the air gap. Trapezoidal grooves, the 12 trapezoidal grooves are evenly distributed along the circumferential direction, a permanent magnet is embedded in each trapezoidal groove, and every two strong magnetic permanent magnets 4 and a weak magnetic permanent magnet 3 are arra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com