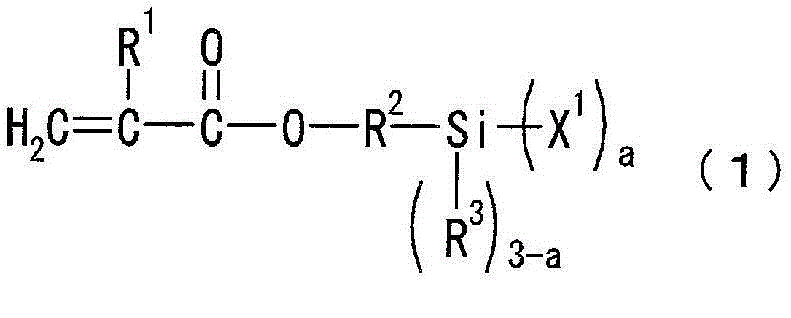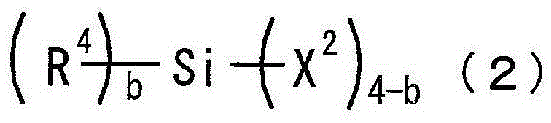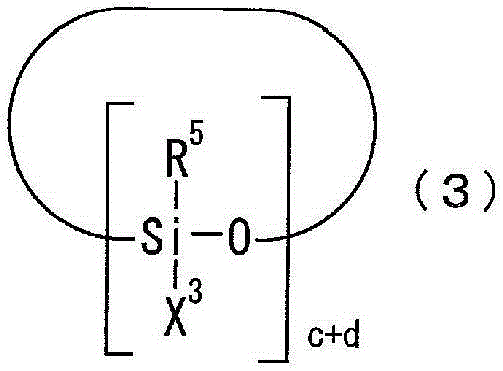Photosensitive resin composition
A technology of photosensitive resin and composition, which is applied in the field of permanent resist) and negative photoresist, and can solve the problems of chemical reagent resistance such as inability to form patterns, acid resistance, alkali resistance, solvent resistance, etc. High transparency, excellent heat resistance, excellent resistance to change over time, and excellent alkali developability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
manufacture example 1
[0095] [Production Example 1: Production of the polysiloxane compound A-1 of the present invention]
[0096]
[0097] 300 g of toluene as a solvent and 120 g of 2,4,6,8-tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane as a compound represented by the above general formula (3a) were placed in a reaction vessel equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, and a reflux device. (0.5 mol), and 0.0001 g of a platinum-divinyltetramethyldisiloxane complex (Karstedt catalyst) as a catalyst. While stirring, 213 g (1.5 mol) of tert-butyl methacrylate, which is a compound represented by the above general formula (4b), was added at 60° C. over 1 hour, followed by stirring for 4 hours and aging. Next, after adding 77 g (0.52 mol) of vinyltrimethoxysilane as a compound represented by the general formula (5a) over 1 hour, it stirred at 70 degreeC for 5 hours, and it aged. The solvent was distilled off from the reaction solution under reduced pressure at 60°C to obtain a cyclic siloxane compound a (the ring repres...
manufacture example 2 and 3
[0100] [Production Examples 2 and 3: Production of Polysiloxane Compounds A-2 and A-3 of the Present Invention]
[0101] The polysiloxane compound A of the present invention was obtained in the same manner as in Production Example 1, except that the amount of the compound represented by the above general formulas (1) to (3) was changed to the number of moles shown in Table 1 below. 50% PGMEA solution of -2 and A-3. The mass average molecular weights of the obtained polysiloxane compounds A-2 and A-3 of the present invention were determined by GPC analysis.
manufacture example 4
[0102] [Production Example 4: Production of the polysiloxane compound A-4 of the present invention]
[0103] Using trimethylchlorosilane, the silanol group of the polysiloxane compound A-1 of the present invention obtained in Production Example 1 was protected with a trimethylsilyl group by a conventional method to obtain the polysiloxane of the present invention Compound A-4 in 50% PGMEA solution. The mass average molecular weight of the obtained polysiloxane compound A-4 of this invention was calculated|required by GPC analysis.
[0104] The number of moles of each compound used in the reaction of the polysiloxane compounds A-1 to A-4 of the present invention obtained in Production Examples 1 to 4 in Table 1 (numbers in () in Table 1), by The mass average molecular weight obtained by GPC analysis and the state of the terminal group are described.
[0105] Table 1
[0106]
[0107] MCSi(OMe) 3 :3-Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane
[0108] Ph 2 Si(OMe) 2 :Diphenyldi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com