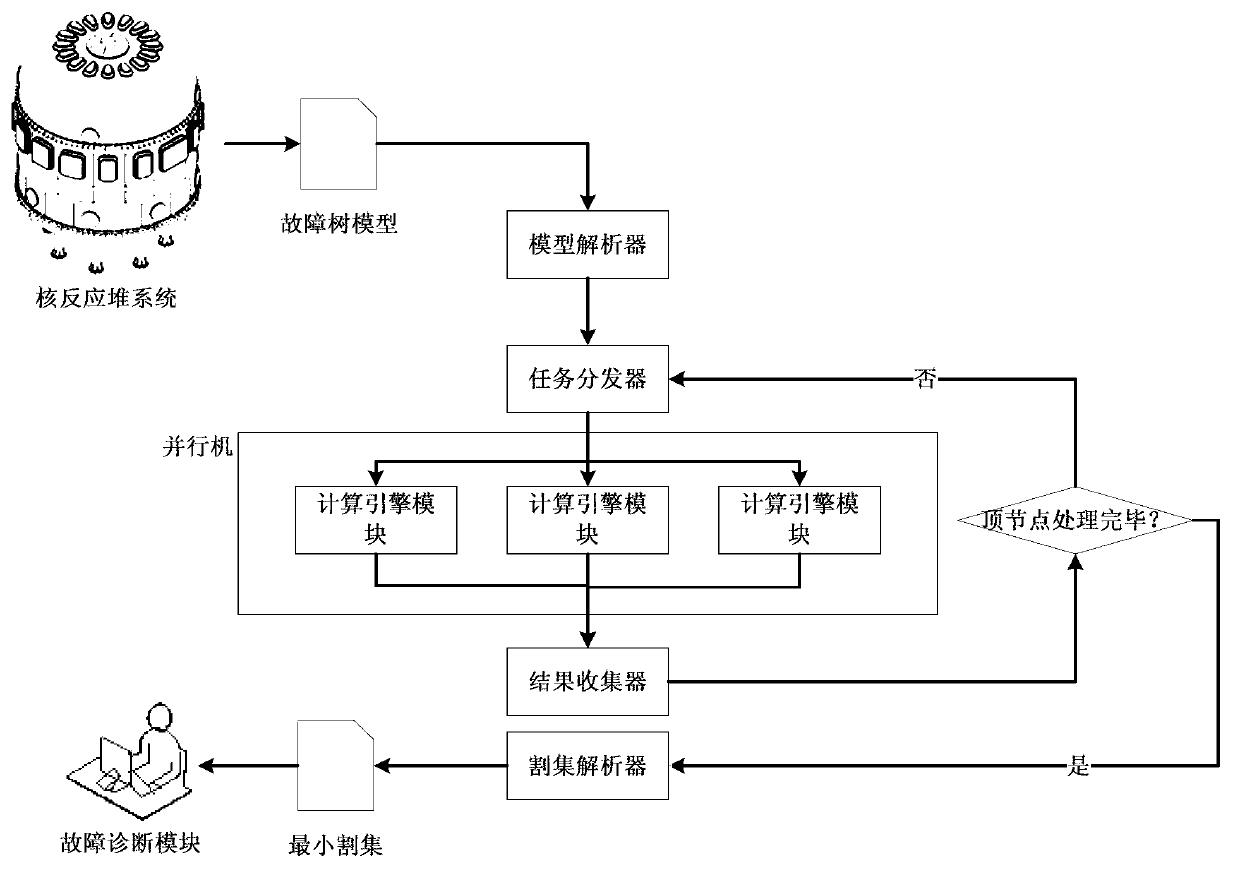
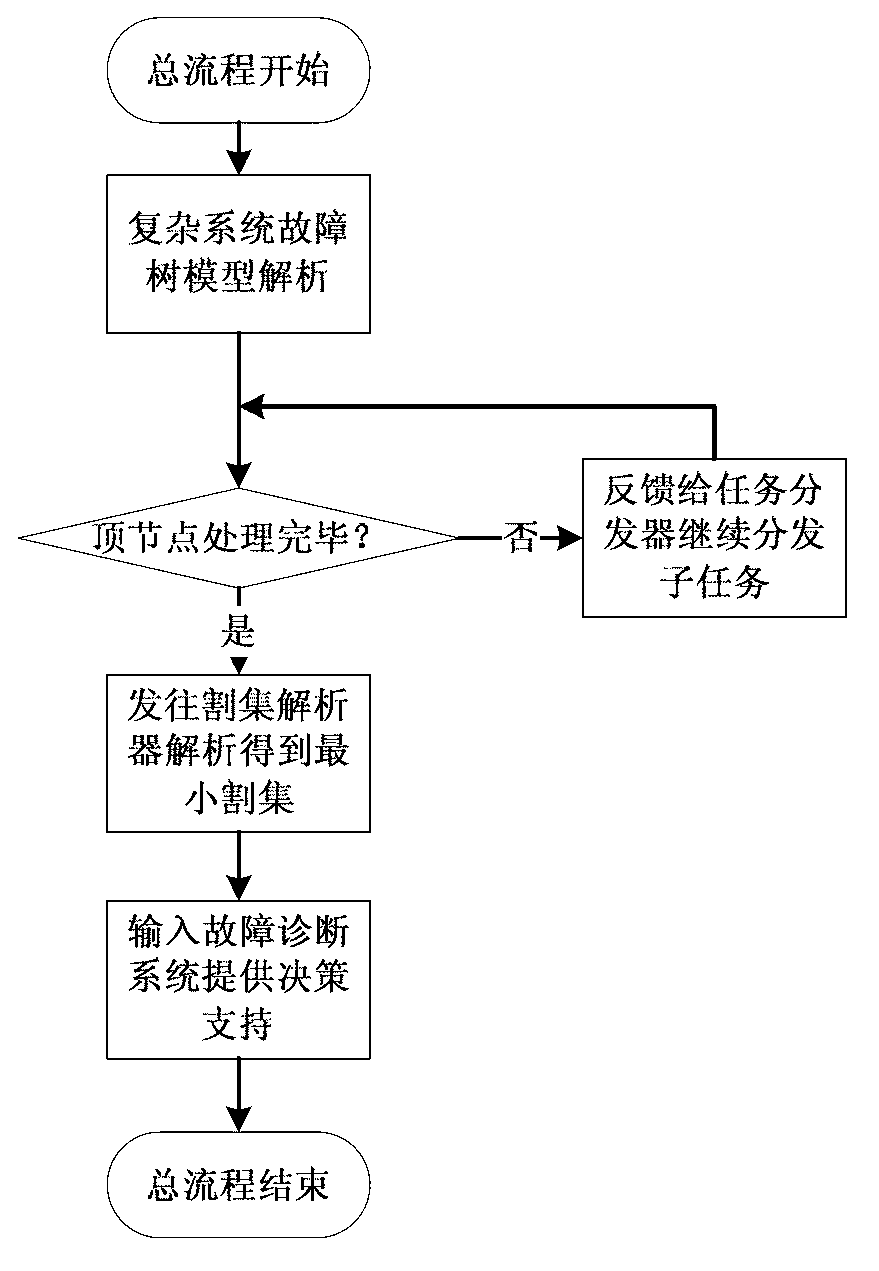
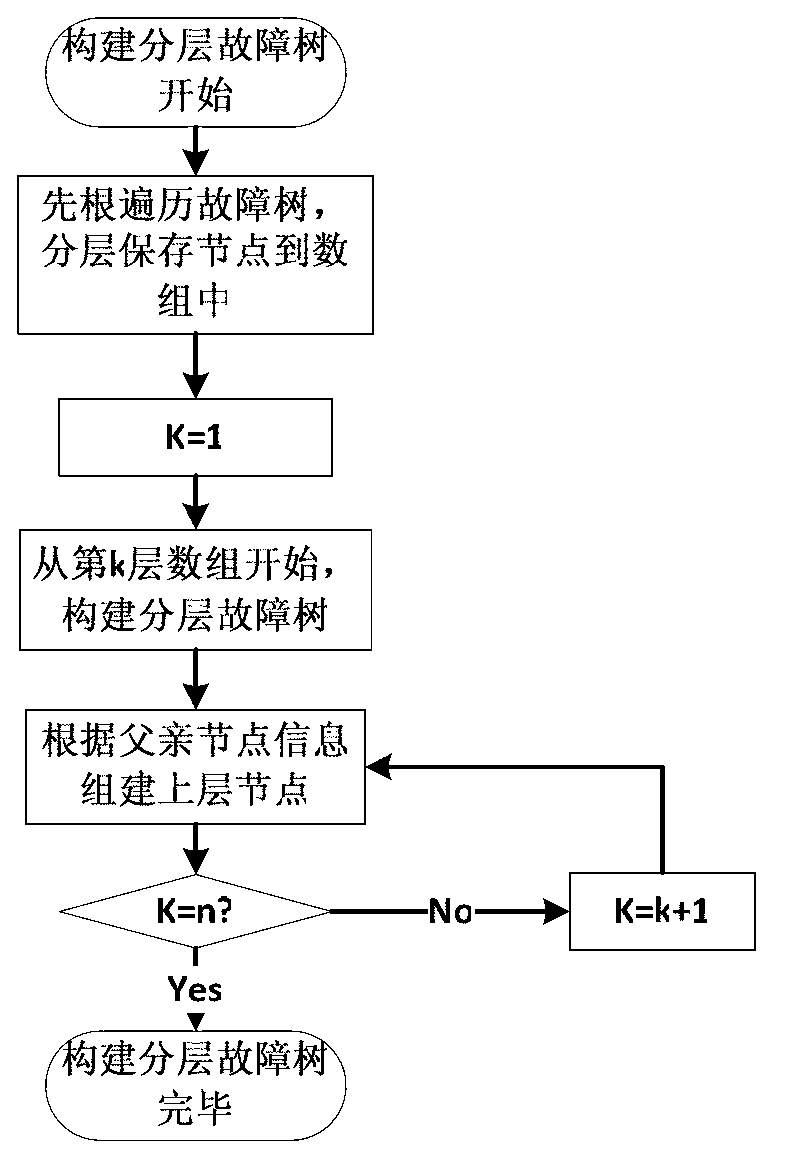
Minimal cut set based system for monitoring faults of nuclear reactors
A technology for nuclear reactor and fault monitoring, applied in the fields of nuclear reactor monitoring, reactors, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of surprisingly large number of judgments, excessive calculation amount, slow calculation speed, etc., to achieve high reliability and easy maintenance, Make full use of computing resources and improve the effect of processing scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] In order to better understand the present invention, some basic concepts are firstly explained.
[0038] Fault tree: a tree structure expressing the failure model of the system, through the modeling of the failure mechanism of the system layer by layer until the basic components that are unnecessary or unable to continue to expand;
[0039] Minimum cut set: the failure mode of the system, which represents the failure combination of several basic components that can cause the system to fail, and if any one of the components does not fail, the system will not fail;
[0040] Intermediate event: the output of the logic gate in the fault tree is the intermediate event;
[0041] Top event: the top node of the fault tree, usually a system failure, is a special intermediate event;
[0042] Bottom event: the leaf node of the fault tree, that is, the basic components in the system fault tree that do not need or cannot continue to expand;
[0043] ITE structure: a logical expres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com