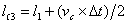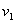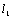Fault location method of power distribution network cable-wire combined circuit based on tested simulation
A technology of mixed line and post-test simulation, applied in the direction of fault location, information technology support system, etc., can solve the problems of large difference in propagation speed, different line wave impedance, and difficult identification of fault traveling wave head, etc., to achieve a simple and robust principle good sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 The cable hybrid model in the PSCAD simulation software model shown, in which the feeder L 1 It is a hybrid cable feeder, the length of the overhead line is 10km, the length of the cable is 5km, and the feeder is sound L 2 and L 3 Both are overhead lines with lengths of 5km and 15km respectively. The fault feeder is arranged on the right side of the busbar in the distribution network L 1 , the sound feeder is arranged on the left side of the busbar L 2 and L 3 , T is the main transformer, the voltage ratio is 110kV / 35kV, and the connection group is YN / d11; the arc suppression coil L is switched through the isolating switch K; the point M is the measurement terminal of the fault traveling wave at the busbar, and the busbar system is ground equivalent capacitance C E is 0.0001μF, the equivalent capacitance to ground of the step-down transformer on the load side is as follows figure 1 Shown in dashed box.
[0041] Suppose the fault ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: The model in Embodiment 1 is also used, assuming that the fault occurs in the cable part, the fault point is 11km away from the measurement end, 1km away from the cable node, the fault time is 0.084ms, and the transition resistance is 0.01Ω. Three B-spline wavelet transforms are performed on the fault current traveling wave detected at the busbar measurement terminal to obtain the maximum value of the traveling wave modulus. The result is as follows Figure 8 shown. Such as Figure 8 As shown in , the traveling wave ① is the initial traveling wave of the fault, the traveling wave ② is the reflected traveling wave of the cable node, and the traveling wave ③ is the reflected traveling wave at the end of the healthy feeder line, where, Δt 1 =0.015ms, Δt 2 =0.03ms. calculate first =0.015×300 / 2=2.25km, because l f0 The length of the short and healthy feeder is quite different, so it can be directly used Δt 1 Four simulated fault distances are calc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com