Method for detecting transgenic tomato by using in-situ synthetic microfluidic chip
A microfluidic chip and in-situ synthesis technology, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc. It can solve the problems of not meeting the needs of food supervision, low efficiency, narrow detection range, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Embodiment 1. A method for detecting transgenic tomato by in-situ synthesis microfluidic chip, using "Huafan No. 1" tomato as the sample to be tested, and performing the following steps in sequence:
[0066] 1) Design of chip probes for exogenous gene detection in transgenic tomato: design 8957 oligonucleotide probes as described in Table 1;
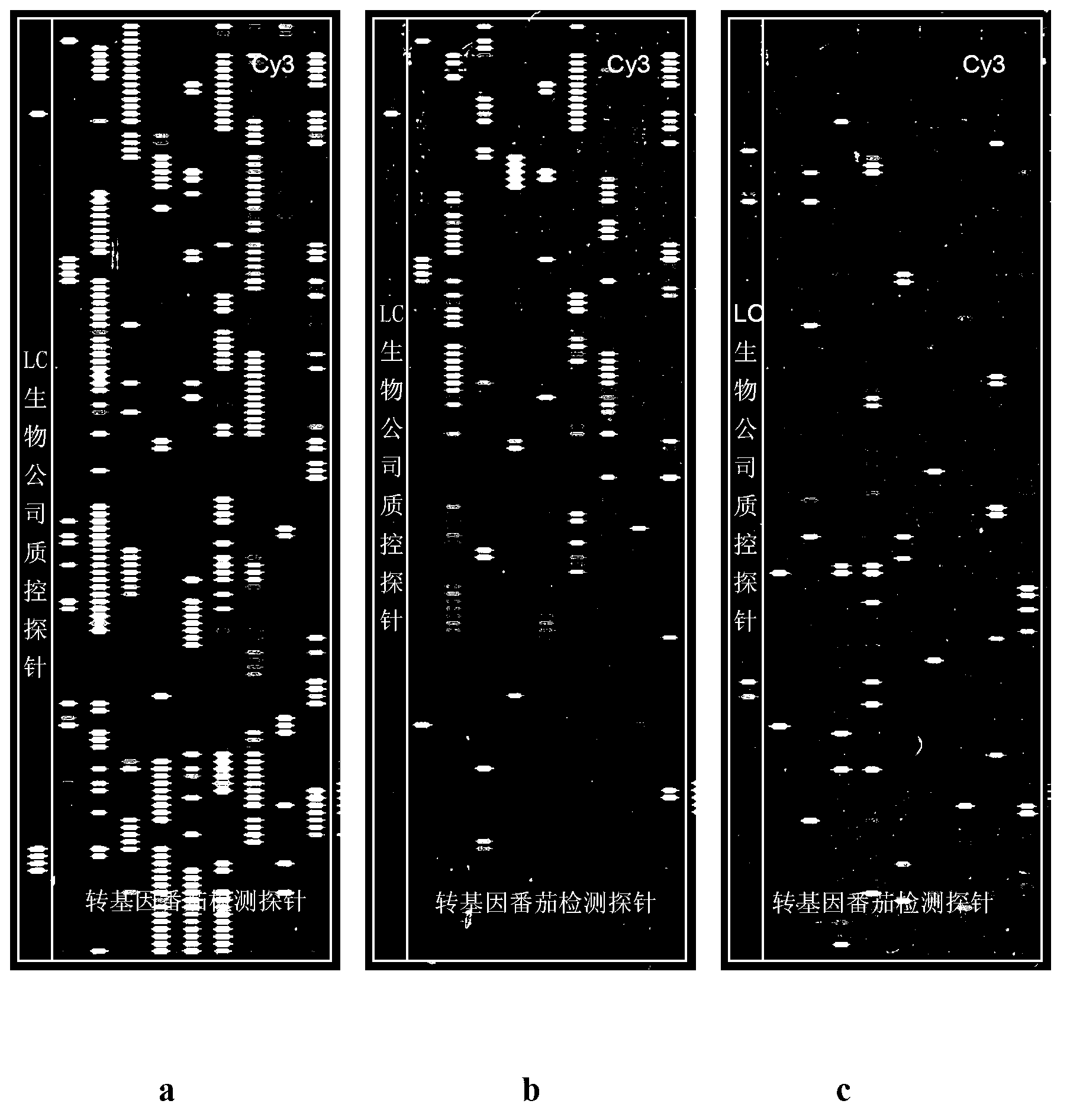
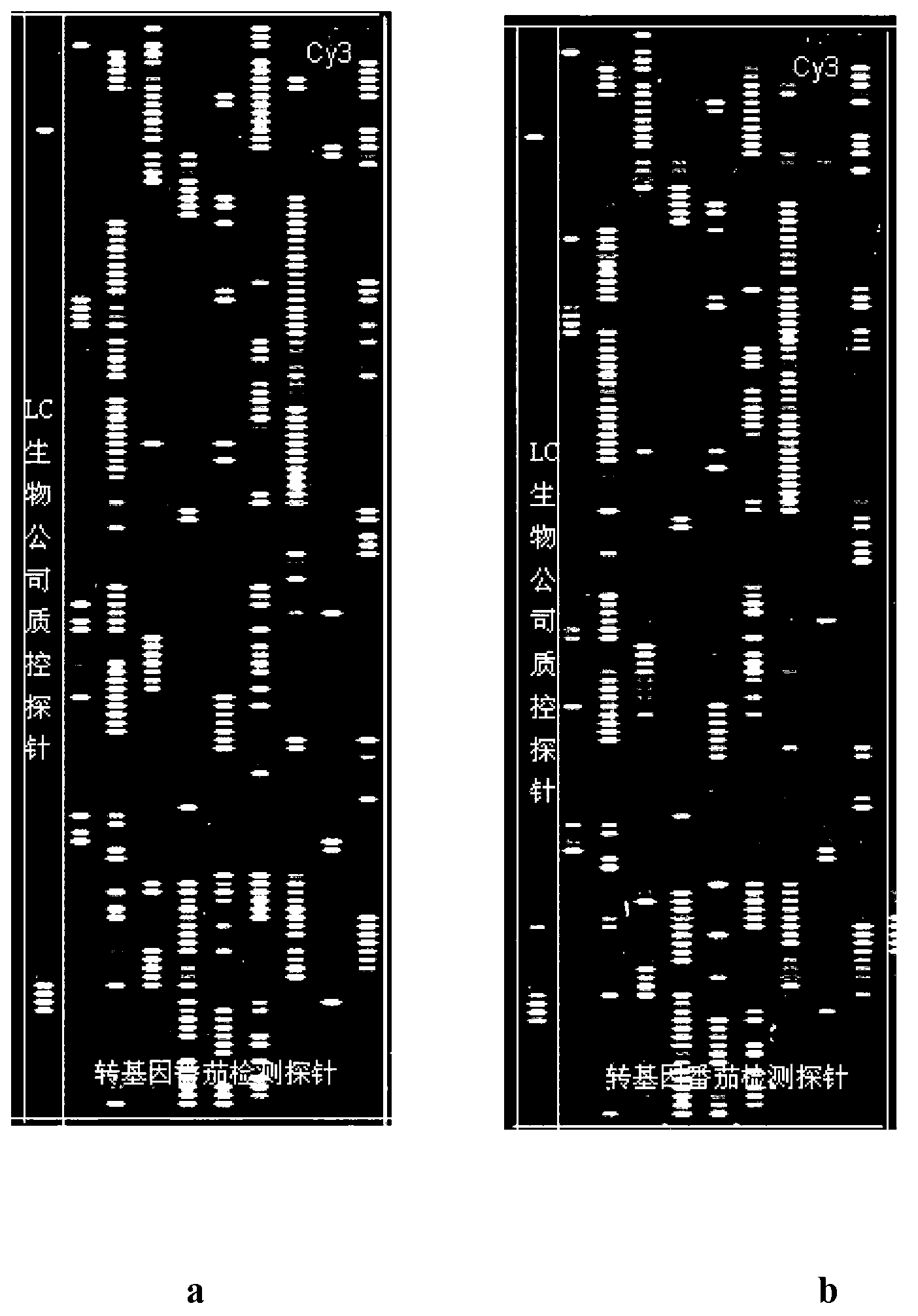
[0067] 2) Preparation of oligonucleotide chip: the schematic diagram of the arrangement of probes on the chip is as follows: Figure 4 shown. Perform fluorescence analysis on the synthesized chip on a chip scanner to detect the fluorescence background of the chip itself; when the background signal intensity of the chip is less than 20 and there is no obvious signal point, the chip is considered to meet the requirements.
[0068] Then use quality control cDNA (an artificially synthesized oligonucleotide complementary to the chip quality control probe) or a DNA fragment from a plasmid (using the plasmid PBI121 as a template, the 35s...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2 Change the sample to be tested in Example 1 from "Huafan No. 1" to "Lichun ZN", and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
[0114] Remarks: In step 4), only method A (common PCR) and method B (multiple PCR) are used.
[0115] The end result is as figure 2 Shown:
[0116] Method A--Display common PCR labeling method ( figure 2 a), exogenous genes 35s, acc, nos and nptII were detected, and the number of detected probes accounted for 79% (49), 32% (16), and 66.7 of the probes designed for these genes, respectively % (30) and 43% (86), the average signal intensities of the top 10 probes detected by each gene were 20081, 19509, 7382 and 13305 respectively; the internal reference genes fru, apx, mcpi and lat52 were detected , the number of detected probes accounted for 16.9% (13), 19.6% (20), 54.2% (13) and 51.9% (28) of the probes designed for these genes, respectively. The average signal intensities of the first 10 detected probes were 6186, 11339, 4754 and...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Example 3 Change the sample to be tested in Example 1 from "Huafan No. 1" to "He He 903", and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
[0125] Remarks: Only method A (ordinary PCR) was used in step 4).
[0126] The end result is as image 3 Shown: The internal reference genes fru, apx, mcpi and lat52 were all detected, and the number of detected probes accounted for 16.9% (13), 15.6% (16), and 50 of the probes designed for these genes, respectively. % (12) and 42.6% (23), the average signal intensities of the first 10 probes detected by each gene were 5372, 8490, 4517, and 3102; no exogenous genes were detected, indicating "Cooperation 903" Tomato samples were transgenic negative samples.
[0127] Verification experiment 3:
[0128] The genomic DNA of the "Cooperation 903" tomato sample described in Example 3 was amplified by ordinary PCR, and the amplified band was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis;
[0129] The results obtained are: the result is the same as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com