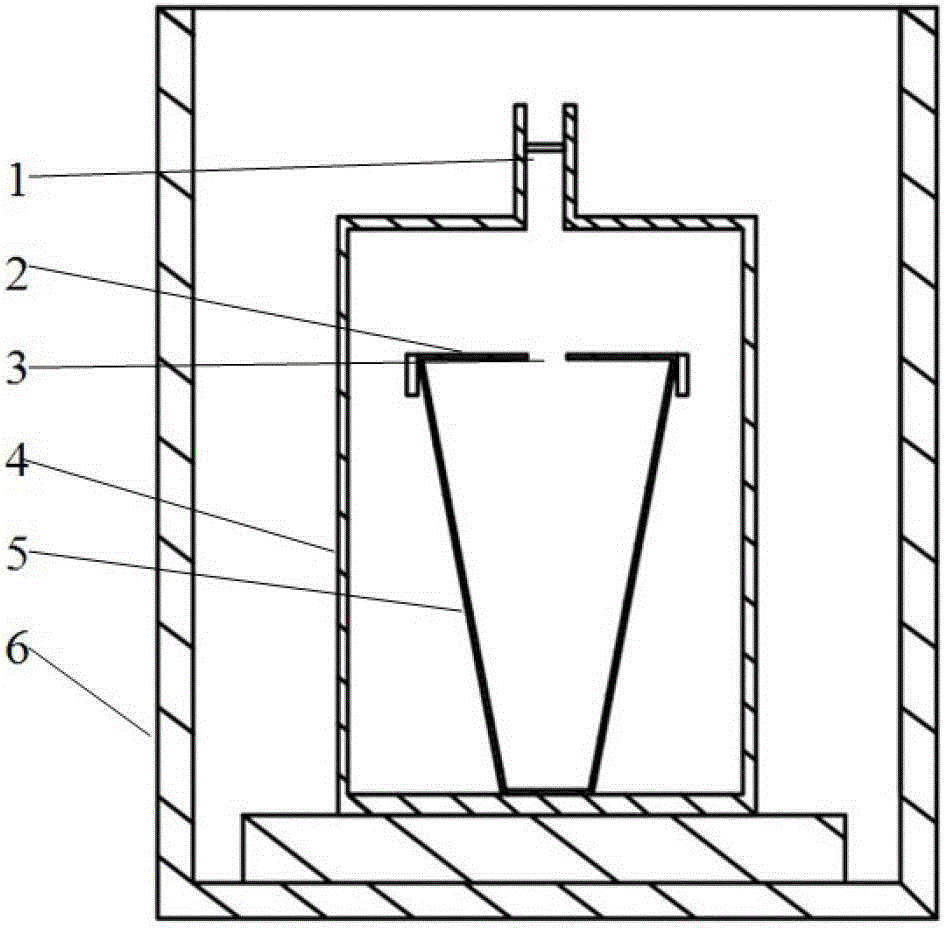
Method and device for producing thermoelectric conversion material and method for producing sputtering target
A technology for thermoelectric conversion materials and sputtering targets, which can be used in thermoelectric device junction lead-out materials, thermoelectric device manufacturing/processing, sputtering plating, etc., and can solve problems such as crystal defects, high cost, segregation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] First, put 59.4% bismuth (Bi), 18.2% tellurium (Te) and 22.4% selenium (Se) into the same crucible; the crucible is usually made of materials such as quartz or zirconia.
[0039] Place the crucible in a stainless steel vacuum vessel. The vacuum container is then placed in a well-type electric furnace, or placed directly in a vacuum well-type electric furnace.
[0040] Vacuumize the vacuum container or well-type vacuum electric furnace directly to make the vacuum degree in the container reach 1×10 -1 Pa to 1×10 -3 Pa, then seal the exhaust pipe or turn off the vacuum valve. Vacuum is no longer applied during heating.
[0041] The material in the crucible is heated by electromagnetic induction. Heating from room temperature to 610°C to 630°C, the heating rate is controlled at 90°C / hour to 100°C / hour. Keep at this temperature for 180 minutes to 185 minutes.
[0042] Let the raw materials in the crucible fully react under vacuum and high temperature conditions for 180...
Embodiment 2
[0044] First, 55% bismuth (Bi), 15% tellurium (Te) and 30% selenium (Se) are put into the same crucible according to the weight ratio; the crucible is usually made of materials such as quartz or zirconia.
[0045] Place the crucible in a stainless steel vacuum vessel. The vacuum container is then placed in a well-type electric furnace, or placed directly in a vacuum well-type electric furnace.
[0046] Vacuumize the vacuum container or well-type vacuum electric furnace directly to make the vacuum degree in the container reach 1×10 -1 Pa to 1×10 -3 Pa, then seal the exhaust pipe or turn off the vacuum valve. Vacuum is no longer applied during heating.
[0047] The material in the crucible is heated by electromagnetic induction. Heating from room temperature to 610°C to 630°C, the heating rate is controlled at 80°C / hour to 100°C / hour. Keep at this temperature for 170 minutes to 190 minutes.
[0048] Let the raw materials in the crucible fully react under vacuum and high te...
Embodiment 3
[0050] First, 60% bismuth (Bi), 20% tellurium (Te) and 20% selenium (Se) are put into the same crucible according to the weight ratio; the crucible is usually made of materials such as quartz or zirconia.
[0051]Place the crucible in a stainless steel vacuum vessel. The vacuum container is then placed in a well-type electric furnace, or placed directly in a vacuum well-type electric furnace.
[0052] Vacuumize the vacuum container or well-type vacuum electric furnace directly to make the vacuum degree in the container reach 1×10 -1 Pa to 1×10 -3 Pa, then seal the exhaust pipe or turn off the vacuum valve. Vacuum is no longer applied during the heating process.
[0053] The material in the crucible is heated by electromagnetic induction. Heating from room temperature to 620°C to 640°C, the heating rate is controlled at 90°C / hour to 120°C / hour. Keep at this temperature for 180 minutes to 190 minutes.
[0054] Let the raw materials in the crucible fully react under vacuum ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com