Preparation and drying of copolymer fibers
A technology of copolymers and fibers, applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, artificial filament cleaning/drying, single-component synthetic polymer rayon, etc., can solve the problems of low investment economy, expensive known methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0054] Example: general situation
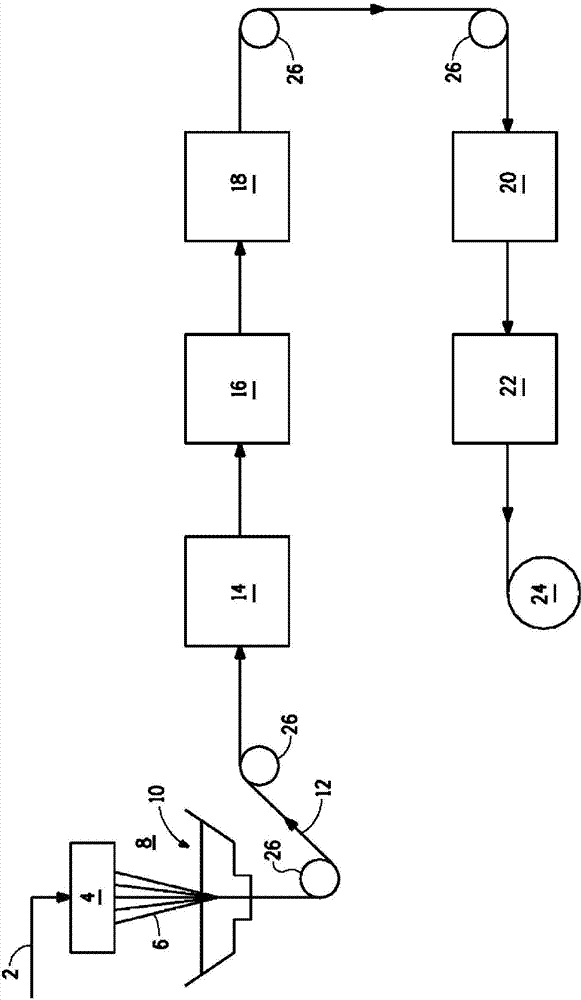
[0055] The copolymer is prepared by copolymerizing the monomers p-phenylenediamine, 5(6)-amino-2-(p-aminophenyl)benzimidazole and terephthaloyl dichloride. The molar ratio of 5(6)-amino-2-(p-aminophenyl)benzimidazole to p-phenylenediamine is 70:30 and the molar ratio of p-phenylenediamine and 5(6)-amino-2-(p-aminophenyl) ) The molar ratio of benzimidazole and terephthaloyl dichloride is 1:1. Then a spinning solution of the polymer in sulfuric acid is prepared and the filaments are spun from the air gap in the spinneret into the coagulation bath to form the copolymer yarn. The yarn is composed of 270 filaments with a linear density of 3 denier per filament. The yarn is then washed with water and suspended onto a spool. The intrinsic viscosity and sulfur percentage are measured on this yarn sample. The resulting yarn has a sulfur content of 3.08% by weight and an intrinsic viscosity of 3.54 dl / g.
[0056] The yarn is then fed from the spool t...
example 1
[0060] First a few samples of the wet yarn were run through a low temperature drying roll operating at a constant surface temperature, and then run through a high temperature oven with the roll mentioned in the comparative example. Perform separate operations at different drying roll temperatures, followed by high-temperature drying at 180°C in a roll oven. Specifically, individual samples of wet yarn were run through drying rolls operating at the following temperatures: 25°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C, 90°C, 100°C, 110°C, and 120°C. In other words, the first heating roller contacted by the wet yarn is 25°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C, 90°C, 100°C, 110°C, and 120°C. The total residence time on the drying roll is 4.5 minutes, and then it is passed through a connected roll oven to complete drying.
example 2
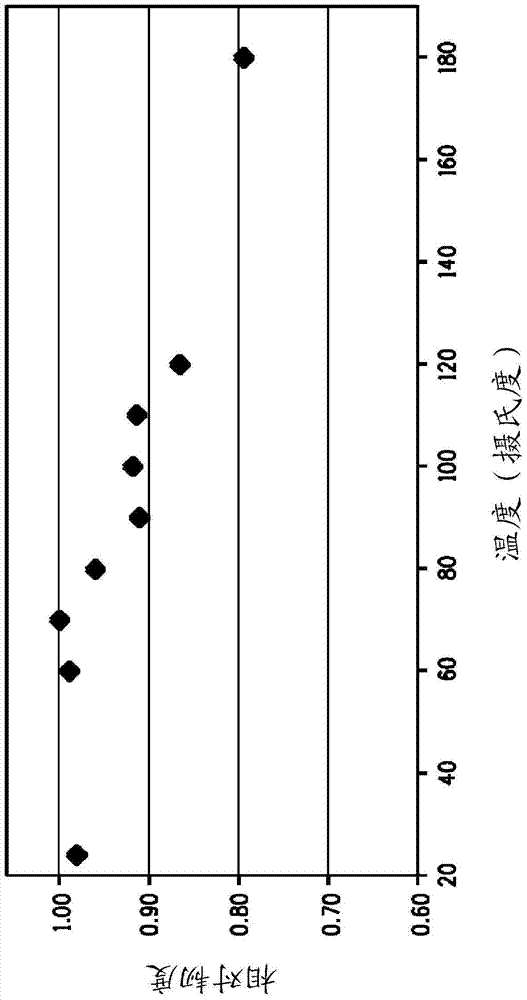
[0062] The yarn group from Example 1 and the yarn from Comparative Example A were then individually and equally heat-treated in a refractory tube oven, which was operated at a maximum temperature of 400°C. The tenacity of each yarn was then tested, and then the first roller temperature experienced by the yarn as shown in Example 1 was plotted. Then use the following formula to calculate the relative tenacity of these yarns; for convenience, the highest measured tenacity is selected as the reference tenacity:
[0063] Relative toughness=actual toughness / reference toughness
[0064] figure 2 It is a graph of the first roll temperature versus relative tenacity, and shows the higher yarn tenacity caused by controlling the initial drying temperature experienced by the yarn.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com