Nickel-zinc soft magnetic ferrite and preparation method thereof
A technology of soft magnetic ferrite and ferrite, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, iron compounds, and the magnetism of inorganic materials. Effect of grain boundary resistivity and high uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
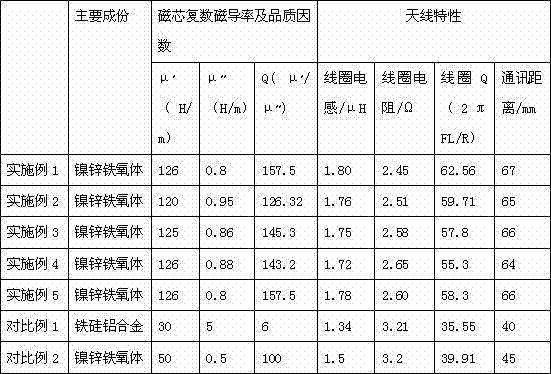
[0039] Fe in the main component 2 o 3 51.5mol% of NiO, 14.5mol% of NiO, 16mol% of ZnO, 17mol% of CuO, Al in auxiliary components 2 o 3 is 0.4mol%, V 2 o 5 0.2mol%, CaO 0.15mol%, MnO 2 0.1mol%, Bi 2 o 3 is 0.15mol%.
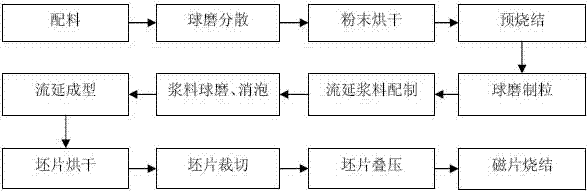
[0040] The preparation process is:
[0041] (1) Weigh the metal oxide raw material according to the above ratio, and wet ball mill it at a speed of 200r / min for 12h.
[0042] (2) Dry the powder after wet ball milling at 120°C for 4 hours.
[0043] (3) Pre-sinter the metal powder by raising the temperature to 1050°C at a heating rate of 2°C / min, and cool it with the furnace after holding for 2 hours.
[0044] (4) Secondary ball milling at 400r / min for 10h.
[0045] (5) Tape casting, the solvent used in the organic system is a mixture of ethanol and toluene, the binder is polyvinyl butyral, the plasticizer is dibutyl phthalate, and the thickness is 0.08 mm blank.
[0046] (6) Overlapping, keeping the pressure between the two layers of blanks at a pressu...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Main component Fe in this embodiment 2 o 3 52mol%, NiO 14.5mol%, ZnO 15mol%, CuO 17.5mol%, the auxiliary component Al 2 o 3 is 0.4mol%, V 2 o 5 0.2mol%, CaO 0.15mol%, MnO 2 0.1mol%, Bi 2 o 3 is 0.15mol%.
[0051] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The main component of this example is Fe 2 o 3 51mol%, NiO 14.5mol%, ZnO 17mol%, CuO 16.5mol%, auxiliary component Al 2 o 3 is 0.4mol%, V 2 o 5 0.2mol%, CaO 0.15mol%, MnO 2 0.1mol%, Bi 2 o 3 is 0.15mol%.
[0054] The preparation process is the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com