Method for detecting microbial community structure of pu'er tea
A microbial community and Pu'er tea technology, applied in the direction of microbial measurement/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient comprehensiveness and system, lack of simultaneous quantitative analysis of microbial quantity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
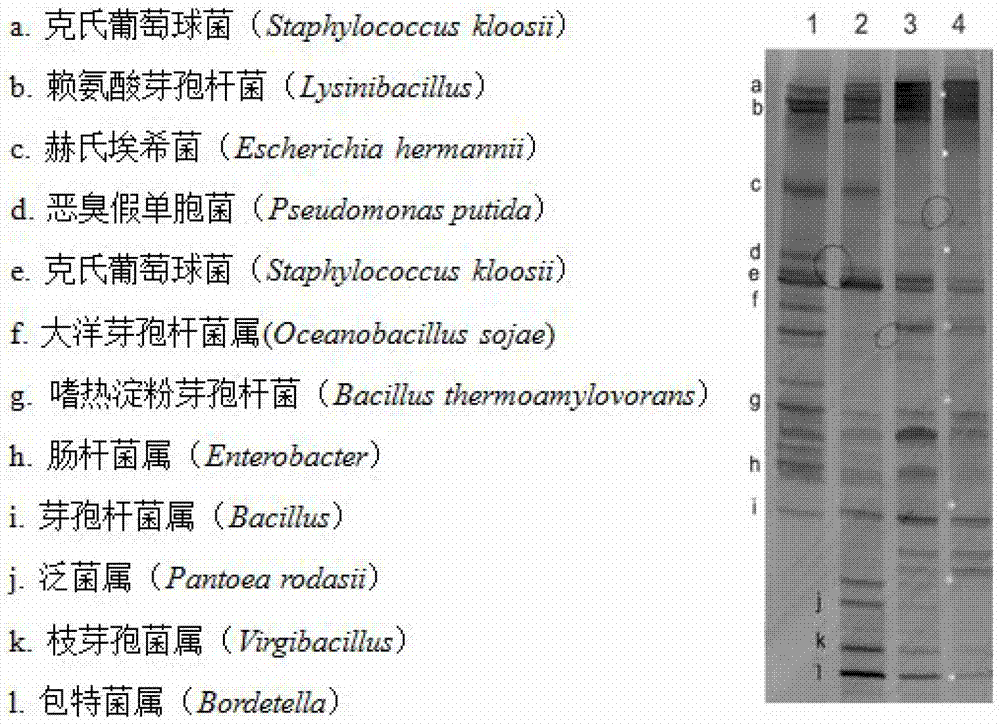
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for detecting Pu'er tea microbial community structure and relative quantity, comprising the steps of:
[0034] 1. Take a Pu-erh tea product for daily drinking as a sample;
[0035] 2. Collect the microbial cells of tea samples by glass bead shaking method: Weigh 5g of tea samples and place them in 45mL sterile phosphate buffer solution filled with acid-washed glass beads, shake at 200rpm for 2 hours at room temperature; Filter with a layer of gauze, transfer the filtrate to a 2ml EP tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 3min, remove the supernatant, wash the precipitate with 1mL of sterile deionized water, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 3min, the obtained precipitate is the microbial cell on the tea;
[0036] 3. Extraction of total microbial DNA: use a combination of liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw + enzymatic method and CTAB method, 600 μL cell lysate to fully suspend bacterial sediment, freeze-thaw repeatedly in liquid nitrogen and 65°C water bath for 6 times, and 37°C wa...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A method for detecting microbial community structure and relative quantity in the Pu'er tea fermentation process, comprising the steps of:
[0044] 1. Use the 5-point sampling method to sample the Pu’er tea during the fermentation process in a Pu’er tea processing factory in Yunnan. Before the Pu’er tea is fermented and turned over, take 10g of the surface and inner tea leaves, and fully mix them in a sterile sealed bag. Turn the pile every 6 days, and sample 4 times in total.
[0045] 2. Collect microbial cells of tea samples at various stages of fermentation by glass bead shaking method: Weigh 10 g of tea samples and place them in 40 mL of sterile phosphate buffer solution with acid-washed glass beads, shake at 200 rpm for 1.5 h at room temperature; Filter with sterile double gauze, transfer the filtrate to a 2ml EP tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 3min, remove the supernatant, wash the precipitate with 1mL sterile deionized water, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 3min, the...
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for detecting the microbial community structure and relative quantity of Pu'er tea from different origins, comprising the steps of:
[0055] 1. Select three Pu-erh tea products from different origins of A, B, and C from the market as samples;
[0056] 2. Collect the microbial cells of tea samples by glass bead shaking method: Weigh 8g of tea samples and place them in 42mL sterile phosphate buffer solution filled with acid-washed glass beads, shake at 200rpm for 1h at room temperature; Filter with a layer of gauze, transfer the filtrate to a 2ml EP tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 3min, remove the supernatant, wash the precipitate with 1mL of sterile deionized water, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 3min, the obtained precipitate is the microbial cell on the tea;
[0057] 3. Extraction of total microbial DNA: use liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw + enzymatic method and CTAB method, 600 μL cell lysate to fully suspend bacterial sediment, freeze-thaw repeatedly in liquid nitr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com