Preparation method of molybdenum alloys for isothermal forging die
An isothermal forging and molybdenum alloy technology, which is applied in the field of molybdenum alloy material preparation, can solve the problems of low performance and poor alloy composition uniformity, and achieve the effect of low oxygen content, good performance and uniform chemical composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
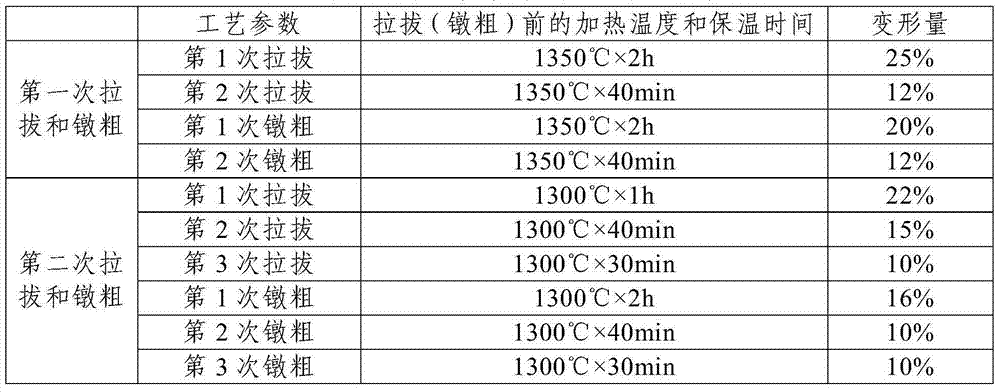
[0030] Step 1: 5000g of molybdenum powder with a Fischer particle size of 3.5 μm, 35.43 g of titanium carbide powder with a Fischer particle size of 2.0 μm, 6.7 g of zirconium carbide powder with a Fischer particle size of 2.0 μm, and zirconium hydride with a Fischer particle size of 2.0 μm 0.3g of powder and 0.52g of carbon powder of -325 mesh were placed in a three-dimensional mixer and mixed evenly to obtain alloy powder. The mixing time was 8h;
[0031] Step 2, cold isostatic pressing the alloy powder described in step 1 to obtain a compact with a diameter of 50 mm; the pressing pressure is 250 MPa, and the holding time is 4 minutes;
[0032] Step 3. Place the compact described in step 2 in a sintering furnace, first heat the sintering furnace under vacuum conditions, and when the temperature in the furnace rises to 1850°C, keep it warm for 3 hours, and the heating time is 16 hours, and then heat it to the sintering furnace Introduce hydrogen with a flow rate of 60L / h, con...
Embodiment 2
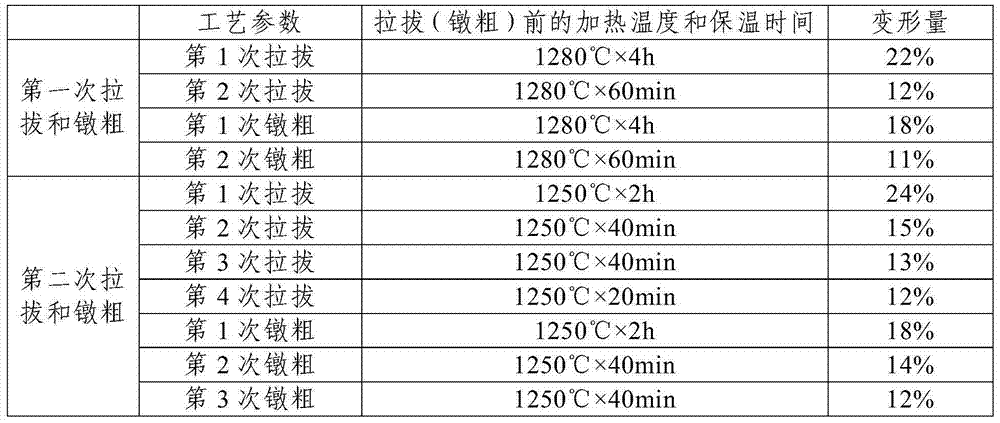
[0040] Step 1: Put 5000g of molybdenum powder with a Fisherman’s particle size of 2.0 μm, 25.83 g of titanium carbide powder with a Fisher’s particle size of 3.0 μm, 6.35 g of zirconium hydride powder with a Fisher’s particle size of 5.0 μm and 1.02 g of -325 mesh carbon powder in the Mix evenly in a three-dimensional mixer to obtain alloy powder, and the mixing time is 24 hours;
[0041]Step 2, cold isostatic pressing the alloy powder described in step 1 to obtain a compact with a diameter of 50mm; the pressing pressure is 200MPa, and the holding time is 8min;
[0042] Step 3. Place the compact described in step 2 in a sintering furnace, first heat the sintering furnace under vacuum conditions, and when the temperature in the furnace rises to 1700°C, keep it warm for 4 hours, and the heating time is 15 hours, and then heat it to the sintering furnace Introduce hydrogen with a flow rate of 70L / h, continue to heat up to 1950°C, heat-preserve and sinter for 6 hours, and heat up ...
Embodiment 3
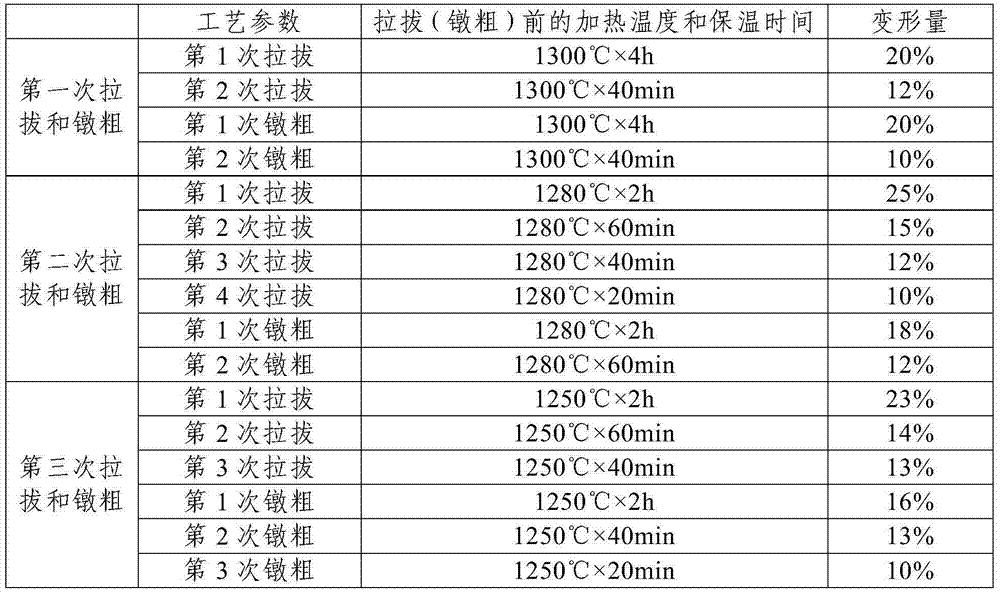
[0050] Step 1: 5000g of molybdenum powder with a Fischer particle size of 5.0 μm, 33 g of titanium carbide powder with a Fischer particle size of 5.0 μm, 3.5 g of zirconium carbide powder with a Fischer particle size of 5.0 μm, and zirconium hydride powder with a Fischer particle size of 3.0 μm 3.0g and -325 mesh carbon powder 0.52g were placed in a three-dimensional mixer and mixed evenly to obtain alloy powder, and the mixing time was 10h;
[0051] Step 2, cold isostatic pressing the alloy powder described in step 1 to obtain a green compact with a diameter of 50 mm; the pressing pressure is 150 MPa, and the holding time is 10 min;
[0052] Step 3. Place the compact described in step 2 in a sintering furnace, first heat the sintering furnace under vacuum conditions, and when the temperature in the furnace rises to 1500°C, keep it warm for 5 hours, and the heating time is 15 hours, and then heat it to the sintering furnace Introduce hydrogen gas with a flow rate of 80L / h, con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com