Method for batch extraction of rice endosperm DNA
An endosperm and rice technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of grain damage, cumbersome operation steps, and inability to extract in batches, and achieve the effects of flexible schedule, operator safety, and rapid extraction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 This method was used to extract the DNA of rice varieties R173, Nipponbare, Xianxiaozhan, Hanghui 7, and Yuejingsimiao 2.
[0041] The specific method is:
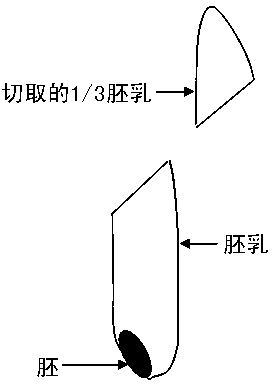
[0042] S1. Take 96 rice seeds with lemma husks, peel off the lemma husks, and cut out 1 / 3 endosperm (about 5-8 mg) with a blade; S2. Put the cut endosperm into the wells of a 96-well PCR plate (T1 plate). The remaining part of the kernel (embryo
[0043] milk and embryo) into the wells of another 96-well PCR plate (T2 plate).
[0044] S3. Use a multi-channel pipette to add 100 μL of 1 mol / L NaOH solution to each well of the T1 plate, put it into a PCR machine, keep it at 99°C for 15 min, and put the T2 plate into a 4°C refrigerator for later use;
[0045] S4. Take out the T1 plate, put 1 tungsten alloy bead into each well, and use a multi-channel pipette to draw 180 μL of 1×DNA extraction solution into each well, and cover the silica gel cover;
[0046] S5. Re-place the T1 plate in the PCR instrument at...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 The concentration and purity of DNA extracted by the two methods of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were determined.
[0062] Specific methods: 1) UV-240 ultraviolet spectrophotometer is turned on and preheated for 10 minutes; 2) Wash the cuvette with double distilled water, blot it dry with absorbent paper, add TE buffer, put it on the S cell rack in the sample room, and close it. Cover plate; 3) Calibrate to zero after setting the slit; 4) After properly diluting the standard sample and the sample to be tested (DNA 5 μl or RNA 4 μl diluted to 1000 μl with TE buffer), record the number and dilution; 5) Put the standard sample Put the sample or the cuvette of the sample to be tested on the S shelf of the sample room, and close the cover; 6) Set the wavelength of ultraviolet light, and measure the OD value at 230nm, 260nm, and 280nm wavelength respectively; 7) Calculate the OD value of the sample to be tested Concentration and purity, DNA sample concentrati...
Embodiment 3
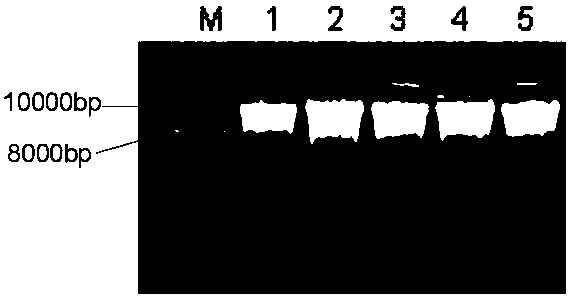
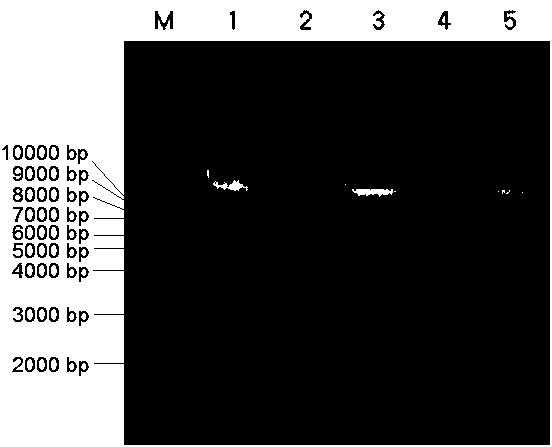
[0063] Example 3 Using gel electrophoresis to detect the extracted DNA in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1
[0064] Specific method: Prepare 1% agarose gel for electrophoresis detection, observe the results and save them by taking pictures.
[0065] The concentration and purity of DNA extracted by the two methods were compared. The DNA extracted by this method can reach about half of the amount of DNA extracted by the CTAB method. The concentration of DNA extracted by the CTAB method is between 740-1100ng / μL, and the concentration of DNA extracted by this method is 300-480ng / μL. The OD260 / OD280 of the DNA extracted by the CTAB method is between 1.8 and 2.0, indicating that the quality is intact; the OD260 / OD280 of the DNA extracted by this method is between 1.8 and 2.0. The results of electrophoresis showed that the DNA extracted by the two methods could be used in the next research. In terms of time consumption, taking the extraction of 96 samples of rice as an example, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com