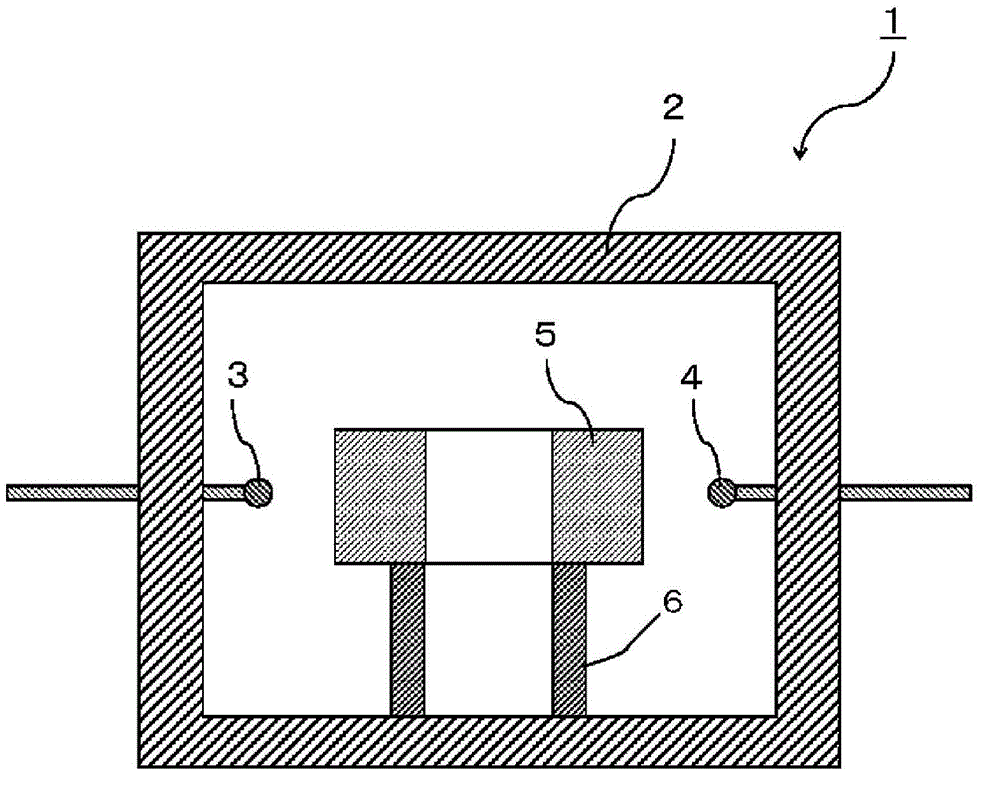
Dielectric ceramic and dielectric filter provided with same
A dielectric ceramic and quality technology, applied in the direction of fixed capacitor dielectrics, ceramics, waveguide-type devices, etc., can solve problems such as rising prices, and achieve the effects of good performance, improved Qf value, and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
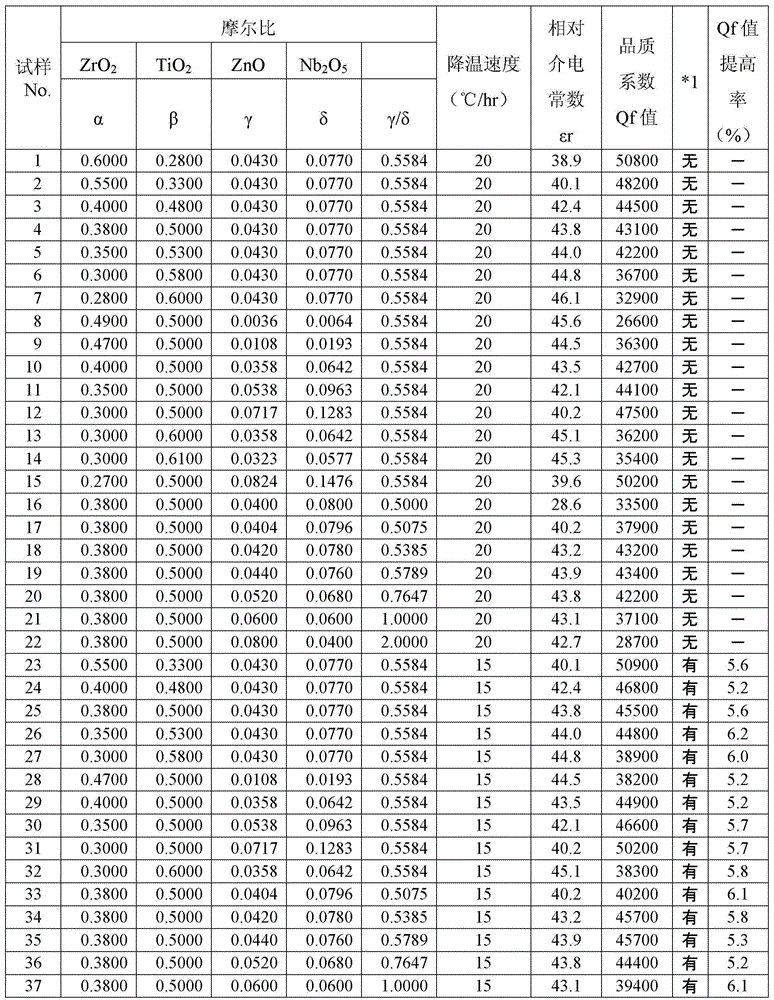
[0055] Various samples were produced in which the composition range of the main component and the cooling rate during firing were changed, and the dielectric properties were compared. The details of the manufacturing method and the dielectric characteristic measuring method will be described below.
[0056] As a raw material, zirconia (ZrO 2 ), titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), zinc oxide (ZnO) and niobium oxide (Nb 2 o 5 ) of each powder. Next, the composition of the sintered body was adjusted to the ratio (molar ratio) in Table 1, and each powder was weighed. Then, the weighed zirconia (ZrO 2 ), titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), zinc oxide (ZnO) and niobium oxide (Nb 2 o 5 ) together with pure water into a ball mill using zirconia balls or the like, wet mixing and pulverization until the average particle diameter becomes 2 μm or less, thereby obtaining a primary raw material.
[0057] Next, after drying the primary raw material, it was calcined at 1100° C. for 2 hours, and the calcin...
Embodiment 2
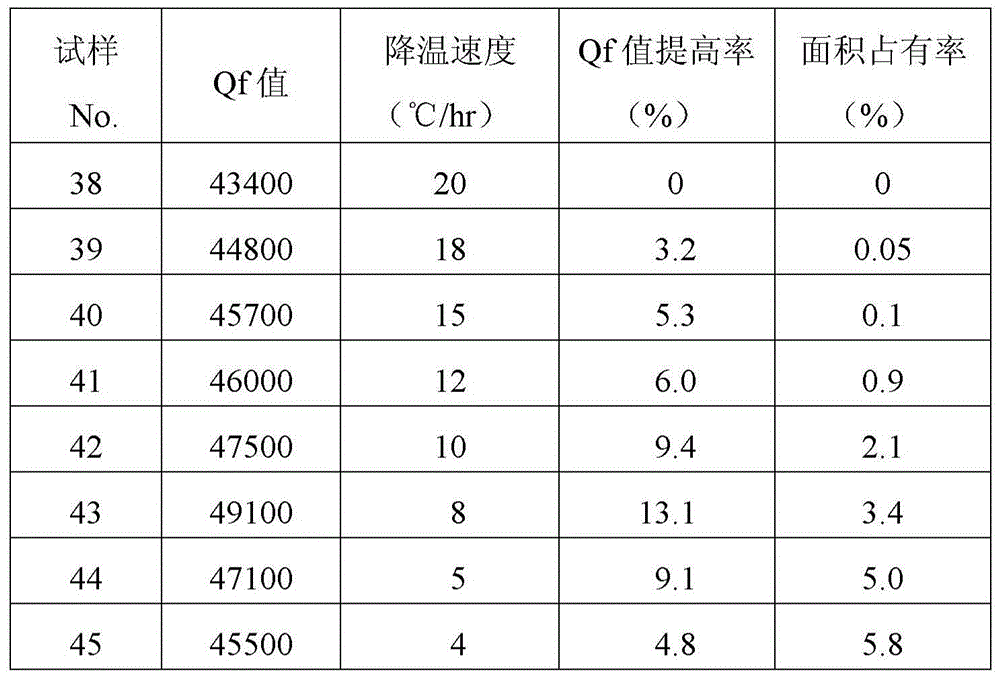
[0071] Next, Sample Nos. 38 to 45 were produced by the same composition and method as Sample No. 19 in Example 1, except that the cooling rate from the highest temperature to 700°C was changed in various ways as shown in Table 2. . In addition, sample No. 38 is the same as sample No. 19, and sample No. 40 is the same as sample No. 34.
[0072] In addition, for samples No. 38 to 45, the Qf value was measured by the same method as in Example 1, and the improvement in the Qf value calculated by using the measured value as the numerator and the Qf value of sample No. 19 as the denominator Rates are shown in Table 2.
[0073] In addition, regarding the surface of the sintered body as each sample, Zn was measured with an electron beam microanalyzer under the same conditions as in Example 1. Then, the area occupancy ratio of Zn concentration of 5% or more was calculated from the color mapping result obtained by recording the detected characteristic X-ray intensity of Zn in X-Y coor...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Next, Sample Nos. 46 to 50 were produced by the same composition and method as Sample No. 43 of Example 2 except that CaO was converted into CaO content as shown in Table 3, except that Ca was variously changed. In addition, sample No. 46 has the same composition as sample No. 43. In addition, calcium oxide as a Ca source was added before calcining.
[0079] Moreover, about the said sample No. 46-50, Qf value was measured by the method similar to Example 1. In addition, the resonance frequency in the temperature range of -40 to 80°C was measured, and the temperature coefficients τf1 and 20 to 80 of the resonance frequency at -40 to 20°C (low temperature range) were calculated based on the resonance frequency at 20°C. The temperature coefficient τf2 of the resonant frequency in °C (high temperature range) was obtained by subtracting τf2 from τf1 as Δ, τf, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0080] In addition, a part of each sample was pulverized, and the obtained ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| relative permittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| relative permittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com