Sodium ion secondary battery, active substance, positive electrode and negative electrode used by sodium ion secondary battery, and preparation method of active substance
A technology of active materials and secondary batteries, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of electrode material cycle instability and poor rate performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This example is used to illustrate the preparation and application of the active substance of the present invention.
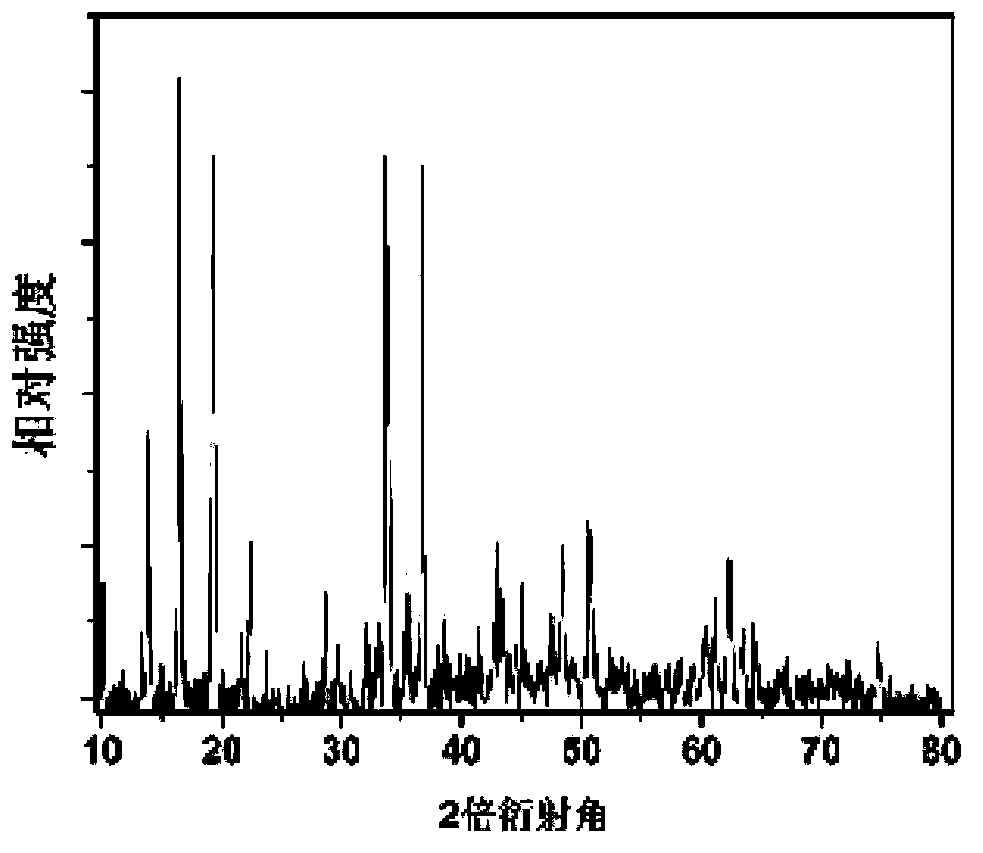
[0037] This embodiment adopts solid-phase method to prepare active material Na 0.44 mn 0.44 Ti 0.56 o 2 , the specific steps are: the nano anatase TiO 2 (Particle size is 50-100nm), Na 2 CO 3 (analytical pure) and Mn 2 o 3 Mix according to the stoichiometric ratio, mix and grind in an agate mortar for half an hour to obtain the precursor, and transfer the precursor sheet to Al 2 o 3 In the crucible, it was treated in a muffle furnace at 900°C for 20 hours, and the resulting blue powder flakes were ground and ready for use, which was the active substance Na 0.44 mn 0.44 Ti 0.56 o 2 , its XRD pattern and space group are Pbam see figure 1 and figure 2 .
[0038] The above active material is used as an electrode material to prepare a sodium ion battery. The specific steps are: the prepared active substance Na 0.44 mn0.44 Ti 0.56 o 2 The ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This example is used to illustrate the application of the active material of the present invention as an electrode material in a sodium ion battery.
[0041] This embodiment adopts embodiment 1 solid-phase method to prepare active material Na 0.44 mn 0.44 Ti 0.56 o 2 . The above active materials were prepared into sodium ion batteries. The specific steps are: the prepared active substance Na 0.44 mn 0.44 Ti 0.56 o 2 Mix the powder with acetylene black and binder PVDF at a weight ratio of 75:15:10, add an appropriate amount of NMP solution, grind in a dry environment at room temperature to form a slurry, and then evenly coat the slurry on the current collector copper foil , cut into 8×8mm pole pieces after drying, dried at 100°C for 10 hours under vacuum conditions, and then transferred into a glove box for later use. The assembly of the simulated battery was carried out in an Ar atmosphere glove box, with a metal sodium sheet as the counter electrode, 1M NaPF ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] This example is used to illustrate the preparation and application of the positive electrode active material of the present invention.
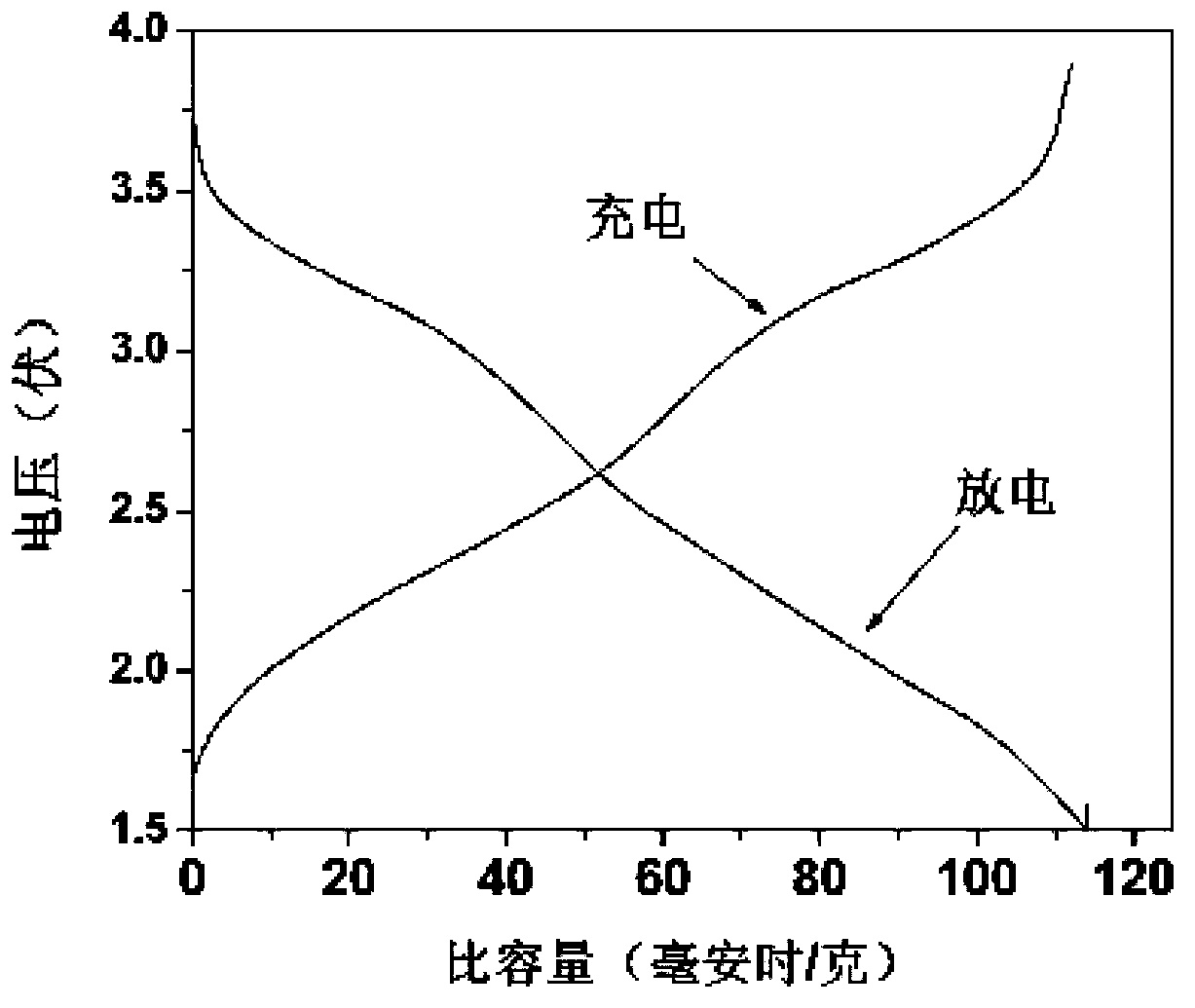
[0044] In this example, the material synthesized in Example 2 was used as the positive electrode material to assemble a sodium ion battery, and the above positive electrode active material was prepared into a sodium ion battery, and an electrochemical test was performed. Its preparation process and testing method are the same as in Example 2. The test adopts discharge first and then charge, the voltage test range is 2.6-3.8V, the test current density is 0.1C, the test results are shown in Figure 6 , Figure 6 Charge and discharge curves for its first week. Depend on Figure 6 It can be seen that the discharge capacity in the first week can reach 55mAh / g, and the efficiency in the first week is 93.8%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com