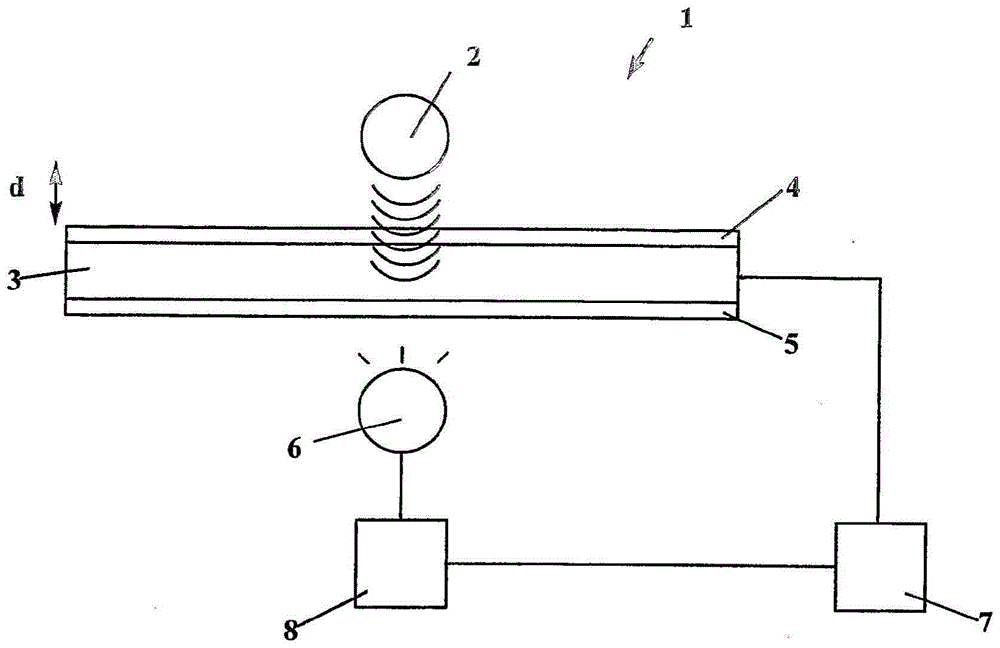
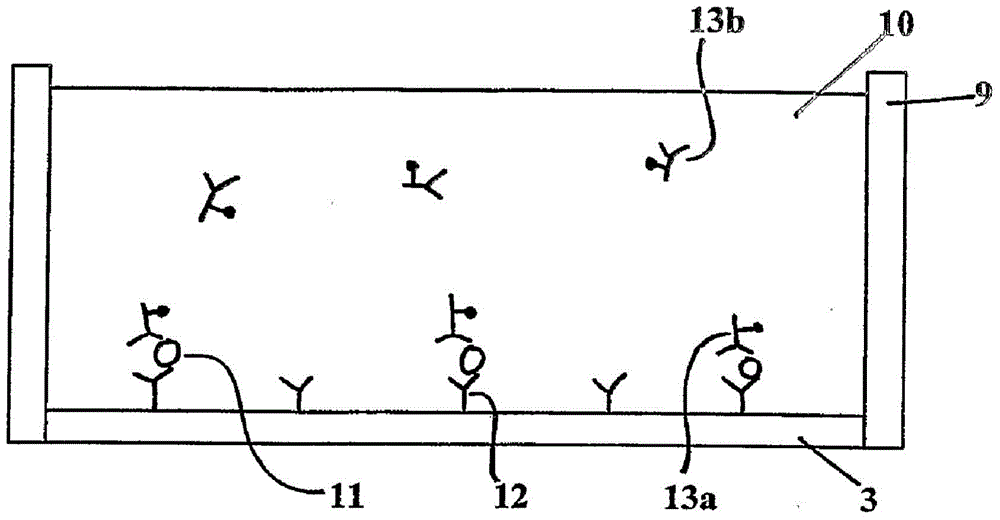
Devices, kits and detection methods for detecting analytes
A technology for analytes and complexes, applied in measurement devices, analytical materials, material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, etc., and can solve problems such as interference signal measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0095] PVDF film
[0096] In the following examples, polarized piezoelectric / pyroelectric polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) bimorph films coated with indium tin oxide were used as sensing devices. The ITO surface is coated with a layer of parylene (approximately 1 micron thick) through a vapor phase gas deposition process. This method involves the sublimation and subsequent pyrolysis of cycloarane precursors, followed by free-radical polymerization on the surface. See WO2009 / 141637 for further details. Then, by overnight incubation at room temperature, the resulting film was coated in a streptavidin solution (200 μg / mL-10 mmol / L phosphate buffer containing 2.7 mmol / L KCl, 137 mmol / L NaCl and 0.05% polysorbate). Streptavidin was prepared as described by Tischer et al. (US 5,061,640).
example 2
[0098] Material
[0099] Monoclonal antibodies are produced essentially as described in "Monoclonal Antibodies: Properties, Manufacturing and Applications" by J.R. Birch and E.S. Lennox, Wiley-Blackwell, 1995, and are biotinylated by methods well known in the art. Carbon-labeled reporter conjugates were prepared essentially as described by VanDoorn et al. (US 5,641,689).
example 3
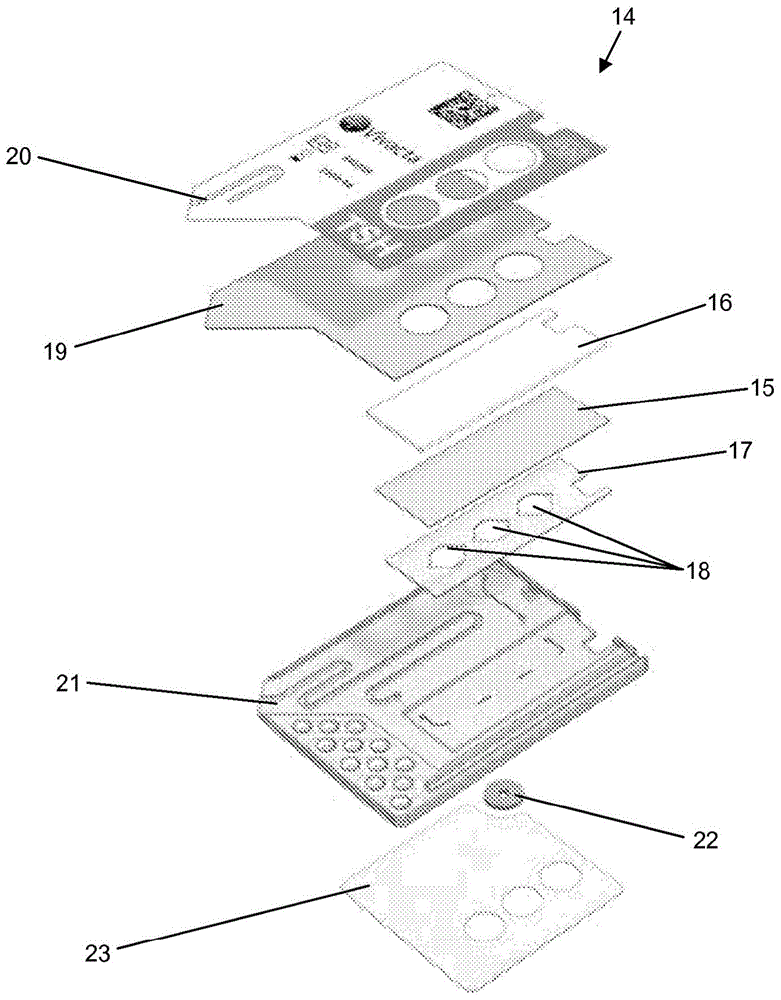
[0101] Preparation of the cartridge
[0102] Such as image 3 As shown in , a cassette 14 was fabricated to perform the assay. The cassette 14 is made of an antibody-coated piezoelectric / pyroelectric film 15 supported on a reinforcement 16 . A polyester film 17 coated with pressure sensitive adhesive, which is die cut to form three sample chambers 18, is applied to the surface. Provisions allow electrical connection to the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric / pyroelectric film 15 to detect the generated charges. The cassette 14 is then formed by sandwiching the above assembly between the top cover 19 and the core 21 coated with the marker 20 , the sealant 22 and the bottom cover 23 .
[0103] Assays are performed by loading the sample chamber with sample using capillary channels in the core 21 . The piezo / pyroelectric film 15 is illuminated through a hole in the top cover 19 with continuous chopped LED light from the LED. For each LED pulse, the voltage across th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com