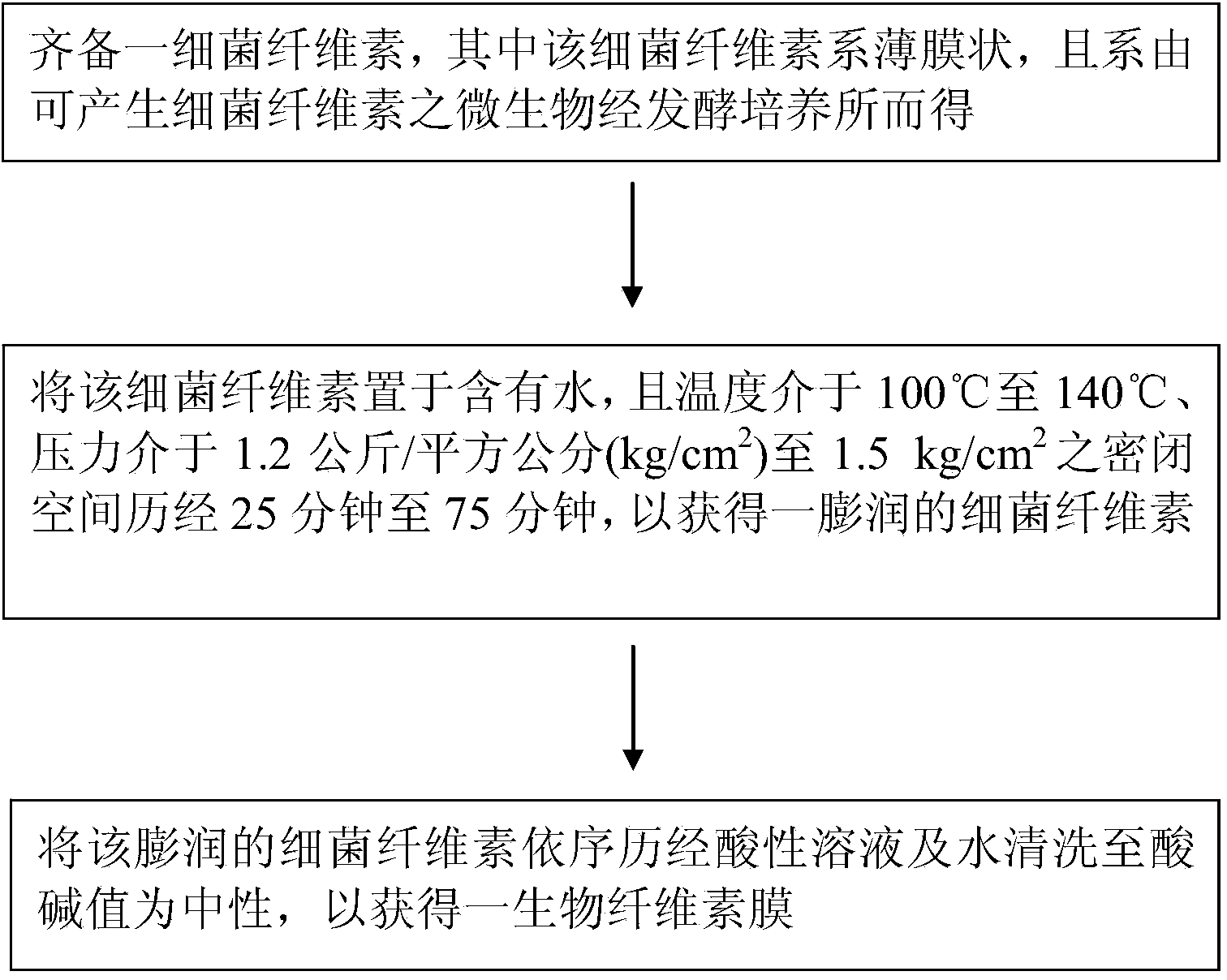
Biological cellulose membrane manufacturing method
A biocellulose, manufacturing method technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of biocellulose film embrittlement, secondary waste environment, and reduced tensile strength, etc. To achieve the effect of reducing toxicity, reducing production costs and improving safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1. prepare bacterial cellulose
[0029] Acetobacter sp. is placed in a colloidal culture solution with a pH value between 0.5 and 6, wherein the colloidal culture solution is at least one selected from animal glue, acacia gum, agaric gum or natto A group composed of colloidal culture fluid such as glue; and the culture fluid containing the acetic acid bacteria is filled into a stackable container and sealed; after the fermentation of the acetic acid bacteria that can produce bacterial cellulose is completed, it can be formed on the surface of the colloidal culture fluid Film-like bacterial cellulose in water; the bacterial cellulose is mainly composed of β-1,4 polyglucose (β-1,4glucan); and the thickness of the film-like bacterial cellulose is between 0.2mm (Km centimeters) to 5mm.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2. swelling condition test
[0031] As shown in Table 1 below, place the bacterial cellulose obtained in Example 1 in a water-containing environment with a temperature of 100°C to 140°C and a pressure of 1.2kg / cm 2 (kg / cm²) to 1.5kg / cm 2 In the airtight container of each, respectively through 25 minutes to 75 minutes, to obtain the swollen bacterial cellulose of sample 1 to sample 5 respectively. Among them, the bacterial cellulose of sample 3 has better water retention after 30 minutes at 121° C., and the water retention is 150 to 200 times the dry weight.
[0032] Table 1 swelling condition test
[0033]
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3. Bleaching condition test
[0035]As shown in Table 2 below, each swollen bacterial cellulose obtained in Example 2 is placed in a solution containing 0.27wt% (weight percent) citric acid and 0.20wt% chlorine dioxide, and the temperature is between 100°C and In a container at 140° C., wash with citric acid solution for 25 minutes to 90 minutes, and then wash with water for 30 minutes to obtain a biocellulose film. And measure the degree of bleaching of each sample with Kent-Jones and Martin color grader (Kent-Jones and Martin color grader) at a wavelength of 530nm (nanometer), wherein the degree of bleaching of the biological cellulose film of sample 3 is between -2 to -3, equivalent to general bleaching effect, and the pH value (pH value) of the biological cellulose film is between 6.8 and 7.2.
[0036] Table 2 Bleaching condition test
[0037]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com