Method for degrading lignin in tobacco stems
A lignin and tobacco stem technology, applied in tobacco, tobacco treatment, application, etc., to achieve the effect of weakening lignin gas, simple fermentation conditions, and increasing enzyme activity value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
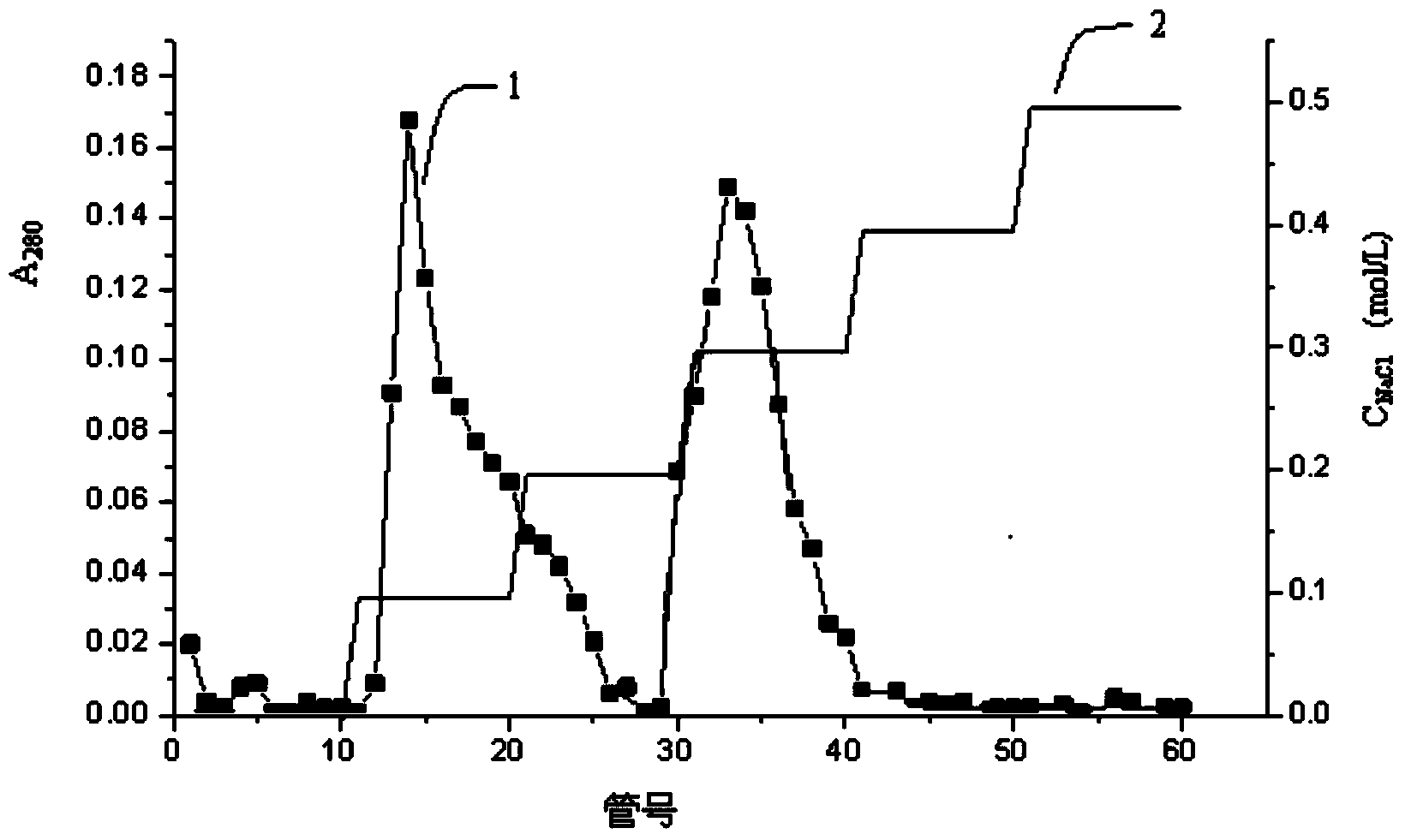
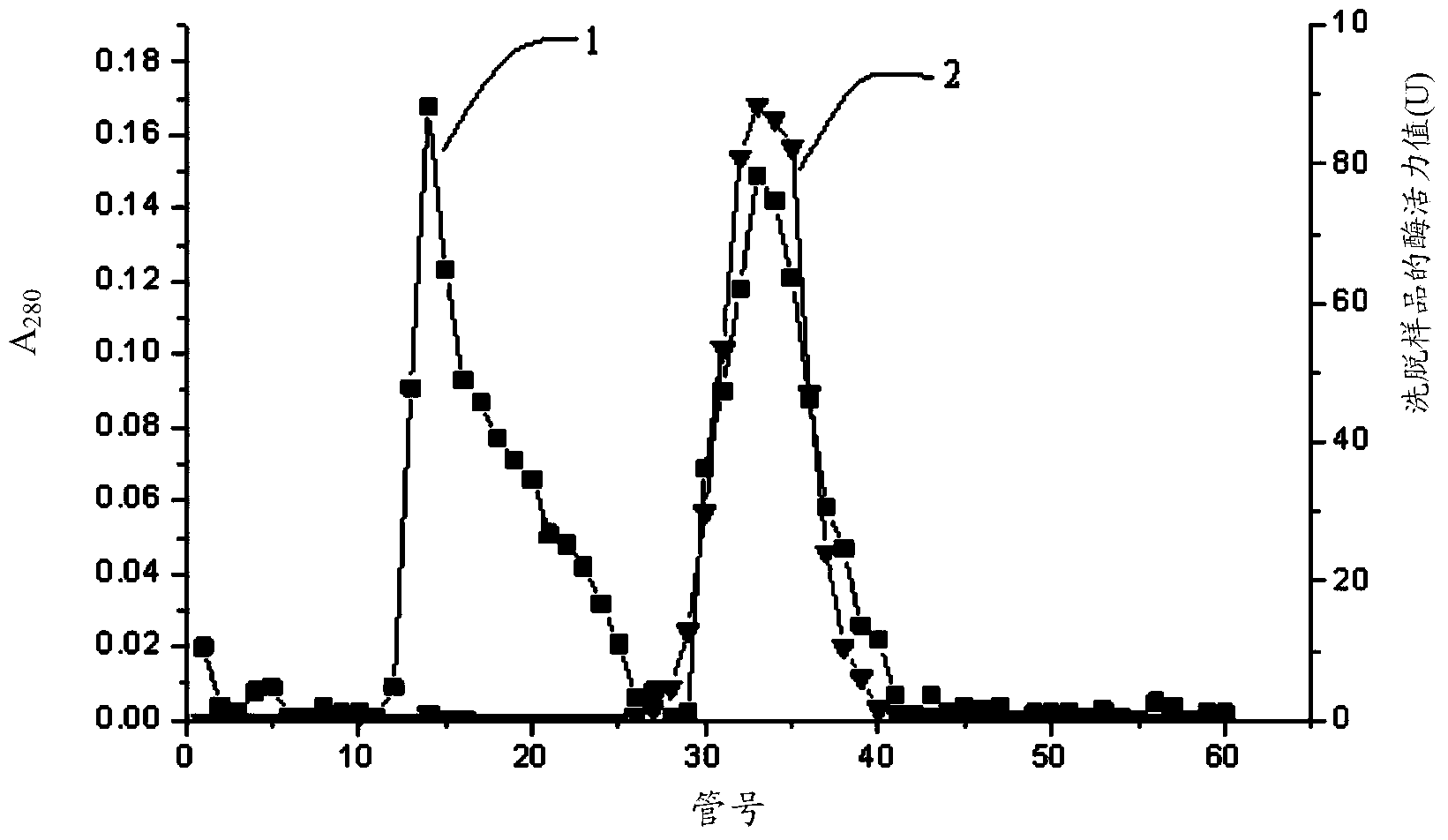
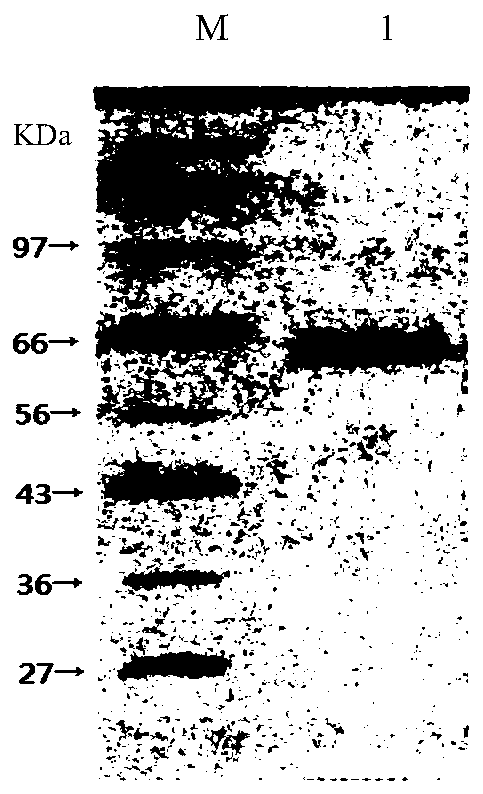
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1 Condition screening of laccase enzymatic hydrolysis of lignin in tobacco stems
[0056] Tobacco stem: provided by Zhengzhou Cigarette Factory, dried at 60°C to constant weight, then pulverized with a pulverizer, and passed through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain dry tobacco stem powder for future use.
[0057] Determination of lignin content: Wrap the accurately weighed 1g stalk end sample with filter paper, then put it into a Soxhlet extractor and extract it with a 1:2 ethanol-benzene mixture for 6 hours, take it out and air-dry it, then move it to a 250mL sample with a grinding port Add 15mL of 72% sulfuric acid to a conical flask with a glass stopper, keep it in a constant temperature water bath at 25°C for 2.5h and keep stirring, then transfer it all to a 1000mL conical flask, dilute with water until the concentration of sulfuric acid is 3 %, keep the volume and boil for 4 hours; filter with constant weight quantitative filter paper, then wash until neutral, the...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2 Utilizing laccase to enzymatically hydrolyze lignin in tobacco stems
[0086]Accurately weigh 20g of tobacco stem powder and place it in a triangular flask, add laccase 20000U (purchased from Beijing Novozymes), 900mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, and finally add water to 1000mL to adjust the pH value of the enzymolysis solution 5.0, the Erlenmeyer flask was placed in a full-temperature shaking incubator with a rotation speed of 150r / min and 45°C for enzymatic hydrolysis for 48 hours. After the enzymatic hydrolysis, the precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with 100 mL of water, and dried to obtain 17.02 g of the product. The inactivated enzymatic hydrolyzate was used as a control, and other treatment conditions were the same as above. Measure the content of lignin in the sample before and after enzymolysis according to the lignin content determination method provided in Example 1, the content of lignin in the tobacco stem before en...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3 Degradation of Lignin in Tobacco Stems by Laccase
[0088] Accurately weigh 20g of tobacco stem powder and place it in a triangular flask, add 16000U laccase (purchased from Beijing Novozymes), 700mL of buffer solution, and finally add water to 800mL to adjust the pH value of the enzymolysis solution to 5.5. The Erlenmeyer flask was placed in a full-temperature shaking incubator with a rotating speed of 160r / min, and the enzymatic hydrolysis was carried out at 40°C for 60h. After the enzymatic hydrolysis, the precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with 100 mL of water, and dried to obtain 17.18 g of the product. The inactivated enzymatic hydrolyzate was used as a control, and other treatment conditions were the same as above. Measure the content of lignin in the sample before and after enzymolysis according to the lignin content determination method provided in Example 1, the content of lignin in the tobacco stem before enzymolysis is 4.74%, the cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com