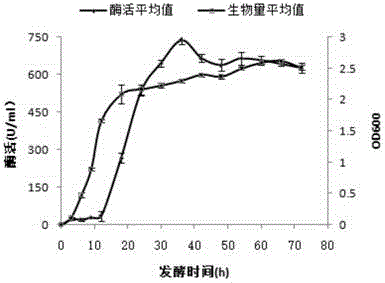
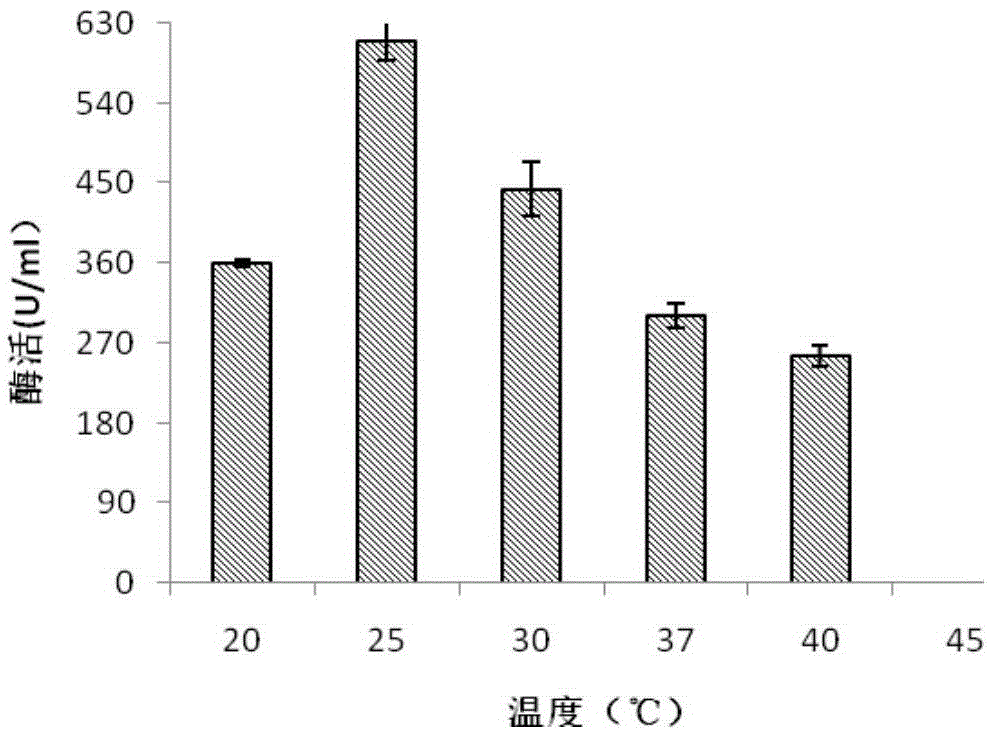
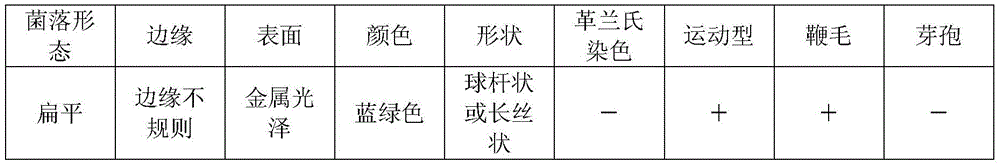
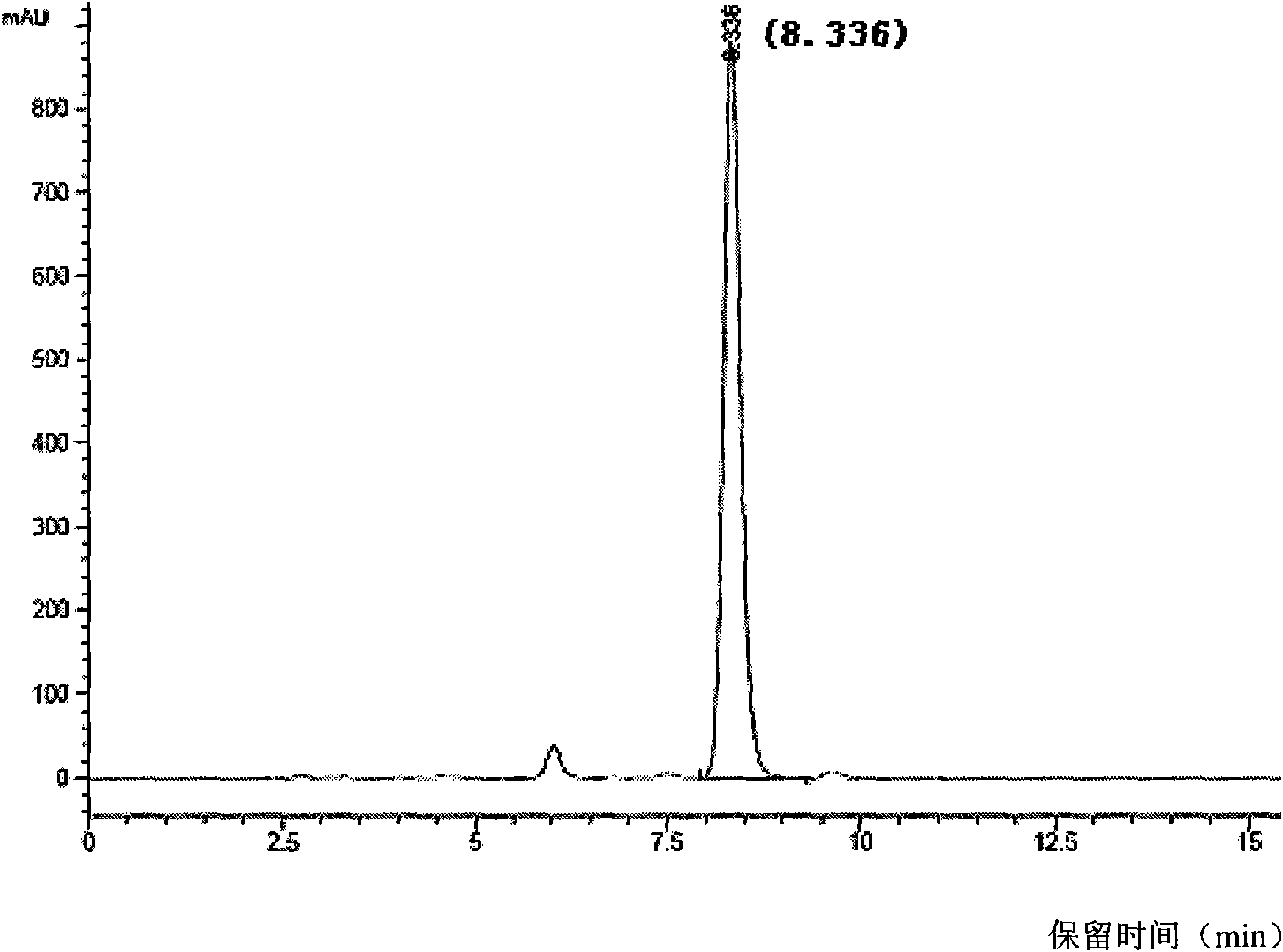
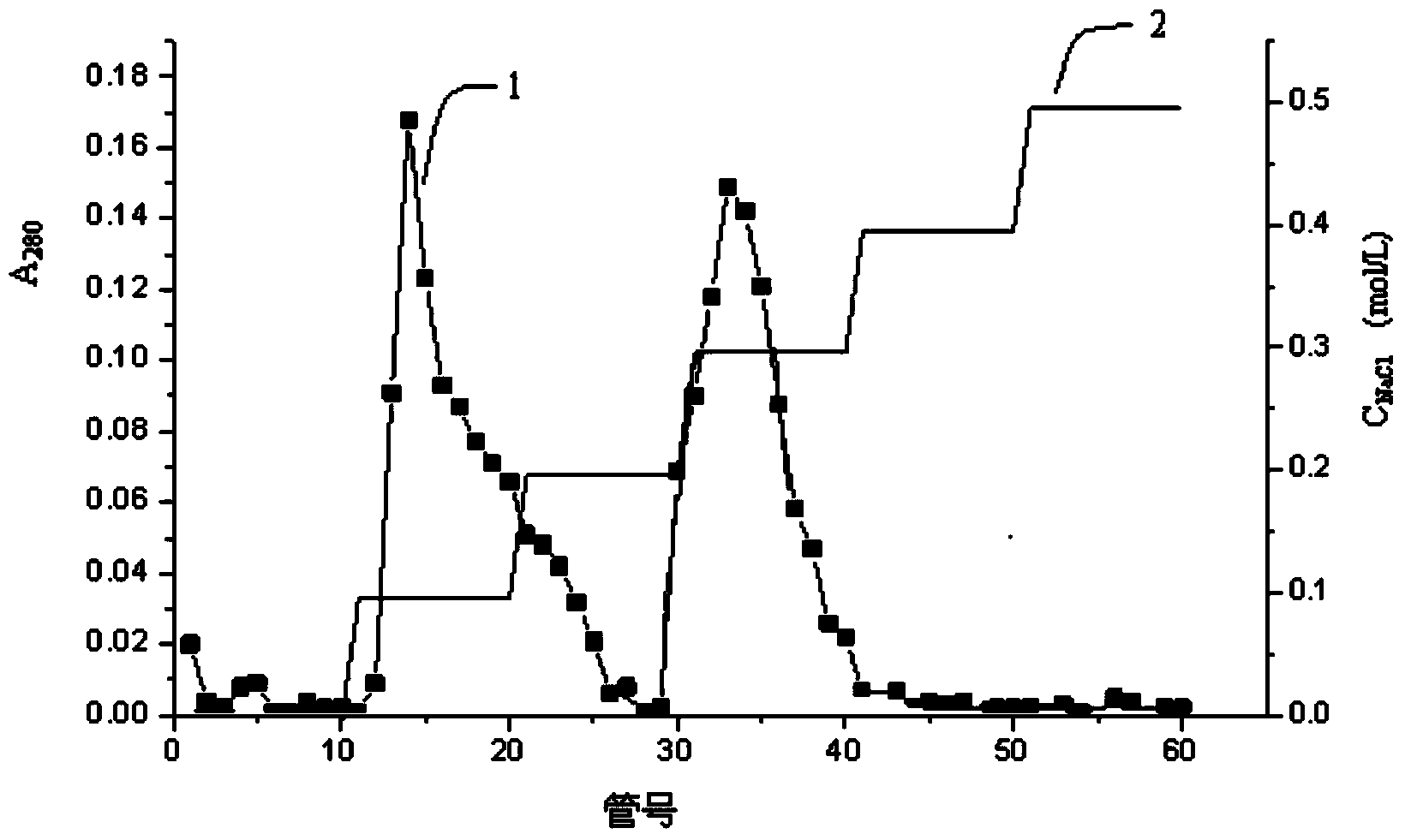
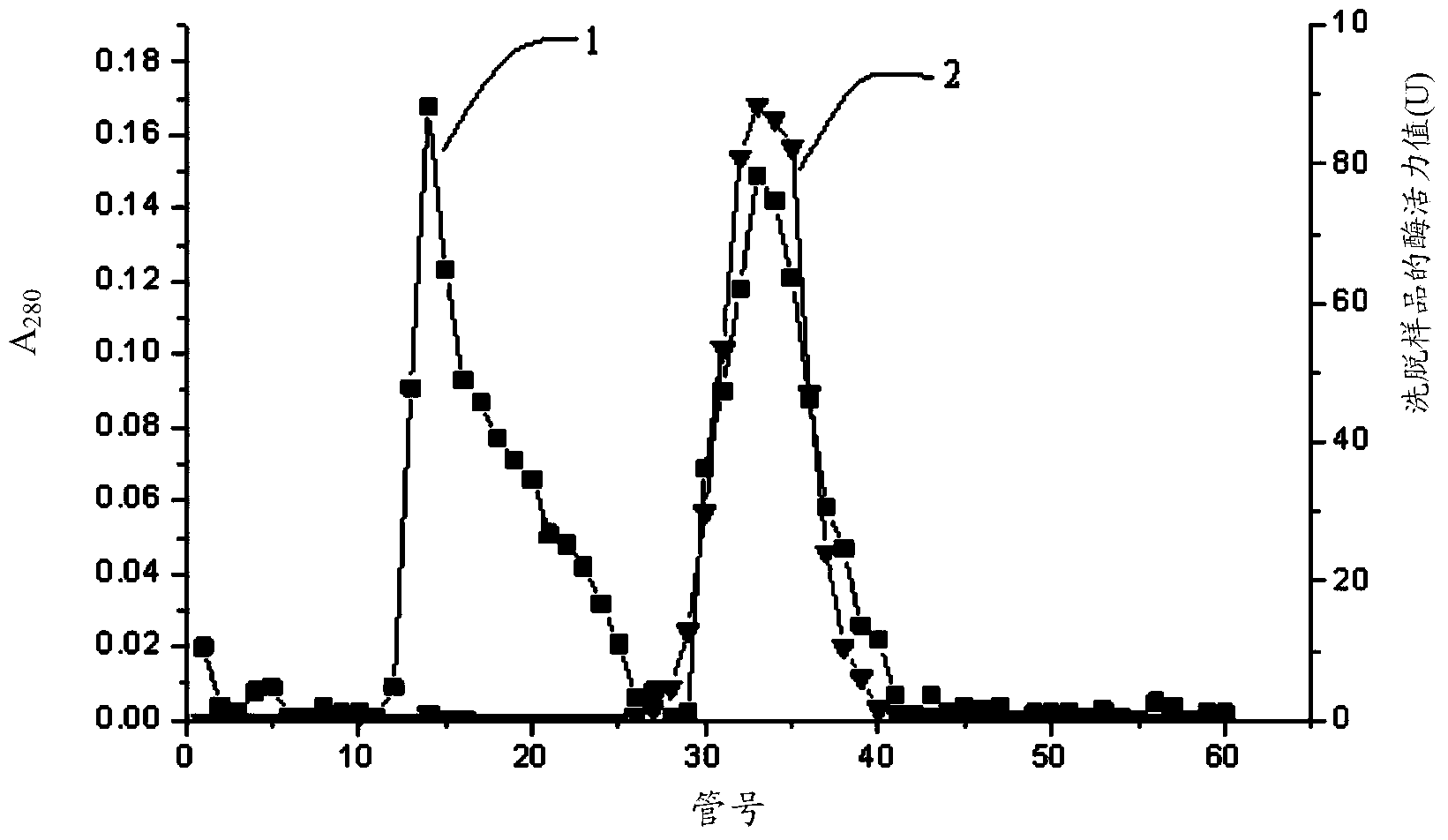
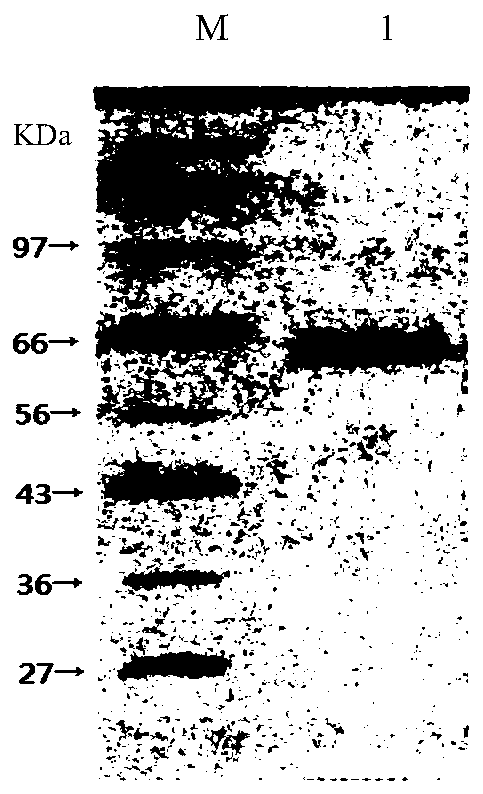
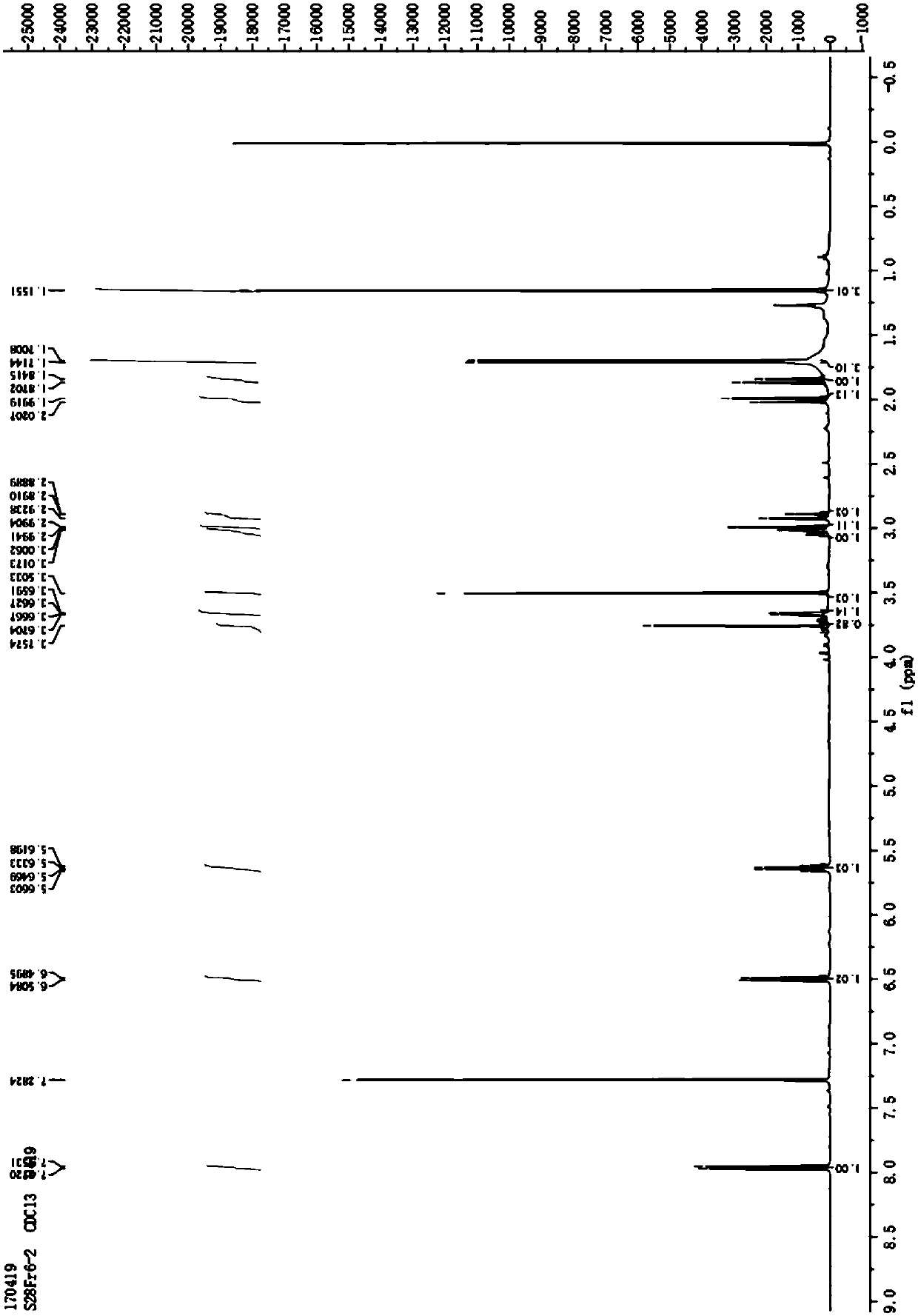
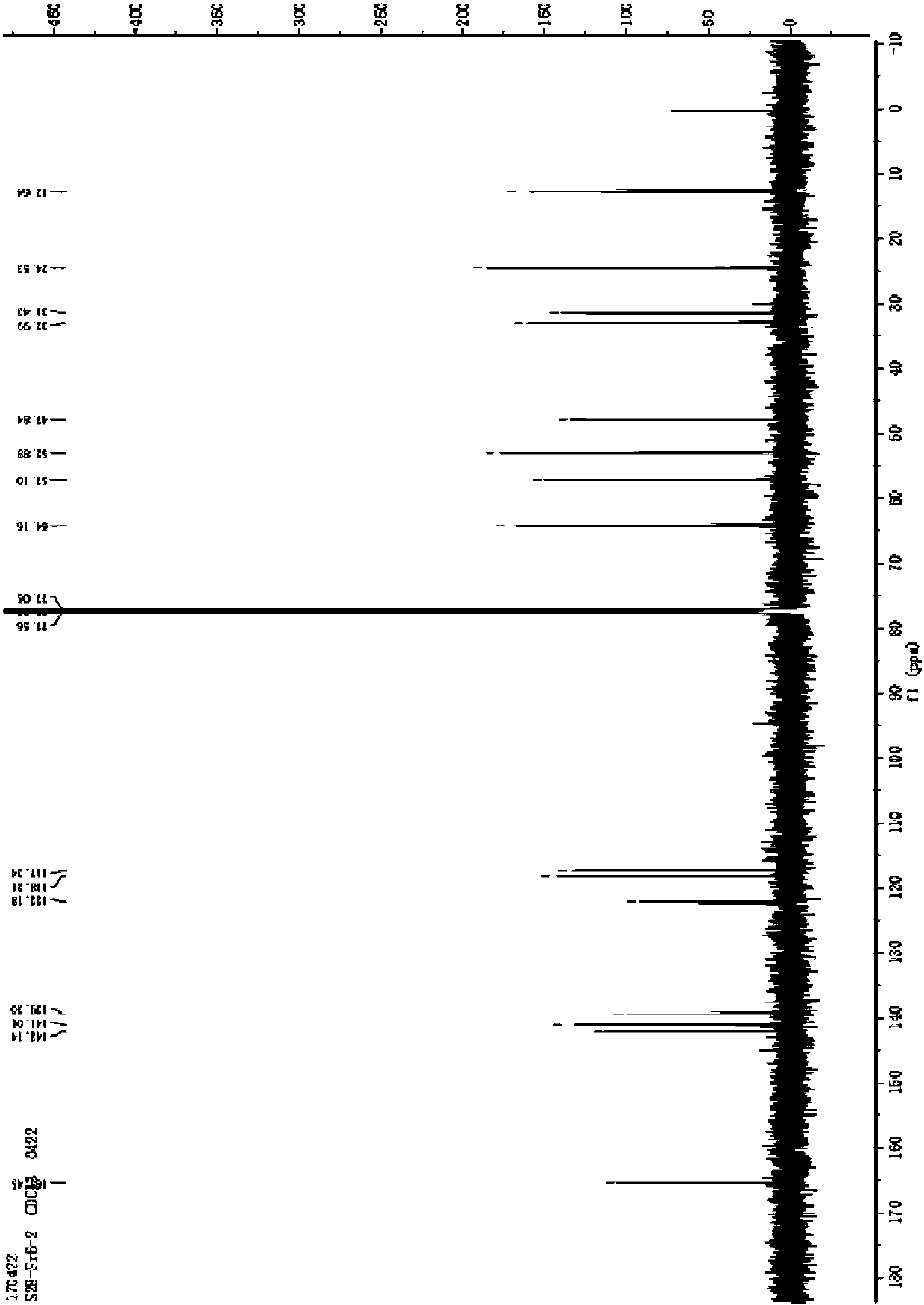
Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Simple fermentation conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fermented feed additive, preparation method and application
ActiveCN102550815ASlow down digestionPromote digestion and decompositionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffMonosodium glutamateBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a fermented feed additive, a preparation method and application thereof. The fermented feed additive is prepared by fermenting mixed strains and mixed auxiliary materials consisting of monosodium glutamate protein, bean pulp, bran, cottonseed meal, corn fibers, rice bran and powdered rice hulls, wherein the mixed strains are obtained by mixing activated strains of lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus planetarium, lactobacillus casei, saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis in a proportion of (1-5): (1-5): (1-5): (1-5): (1-5): (1-5); and the dosage of the fermented feed additive is 5 to 100 percent of the weight of the animal feed when used for the animal feed. According to the fermented feed additive, the bean pulp, the bran, the cottonseed meal and other raw auxiliary materials are sufficiently utilized, so that the food consumption in the animal feeding process is reduced; the fermented feed additive can be used to partiallyor completely replace the animal feed, and antibiotic medicaments can be reduced or prevented from being used; and no medicament is left, so that the feeding cost of farmers is reduced.
Owner:WEIFANG ZHONGKEJIAYI BIO FODDER TECH
Method for synthesizing biological plastic precursor polyhydroxyalkanoate by utilizing lignin degrading bacterium
ActiveCN106190907AReduce carbon sourceLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCupriavidus basilensisCell culture media
The invention discloses a purpose of lignin degrading bacterium, and particularly relates to a method for synthesizing a biological plastic precursor-polyhydroxyalkanoate by utilizing lignin degrading bacterium (Cupriavidus basilensis B-8) with a collection number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 4240. A bacterial strain can grow by utilizing lignin (the lignin concentration of a growth medium is 1g / L to 6g / L) which is not subjected to pretreatment as a unique carbon source, and is used for synthesizing a homopolymer of biological plastic-polyhydroxyalkanoate in the condition (the concentration of nitrogen is less than 60mg / L) that a nitrogen source is short. By using a culture and a production method which are provided by the invention, the carbon source and the pretreatment cost of the carbon source are greatly decreased; the method has large-scale production and industrialization potential.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing tobacco stem cellulose through microbial solid fermentation process
ActiveCN102217786AHigh substance contentLack of aromaTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentBiotechnologyAmylase
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco processing and relates to a method for preparing basic material of a tobacco thin sheet, namely tobacco stem cellulose through the microbial solid fermentation process. Microbes including high-yield prolease, pectolase, ligninase, amylase and other enzymes are selected, and tobacco stems, tobacco smalls and crumbled tobacco are taken as raw materials for preparing microbial seeds, the prepared microbial seeds are inoculated into the tobacco stems for performing solid fermentation, soaking the tobacco stems after fermentation in buffer solution, further performing enzymolysis for degrading the tobacco stems after the enzymolysis, proteins, lignin, pectic substances and other macromolecular substances into micromolecular substances which are easy to be separated from cellulose type substances in the tobacco stems, and further stirring, pulping, filtering and separating for getting water-soluble extract and water-insoluble celluloseof the tobacco stems. The method has the advantages of being simple in process, saving energy, reducing equipment investment and improving the synthetic quality of the tobacco thin sheet, and can greatly reduce the residual quantity of the proteins, pectin, starch and other macromolecules in the tobacco thin sheet.
Owner:SHANGHAI TOBACCO GRP CO LTD +1
Bacillus subtilis strain as well as metabolite and application of bacillus subtilis strain
InactiveCN104830735ANo side effectsSimple fermentation conditionsBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismMetabolite
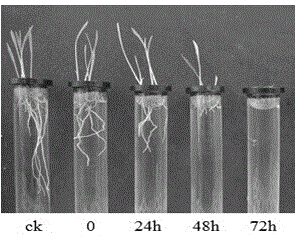
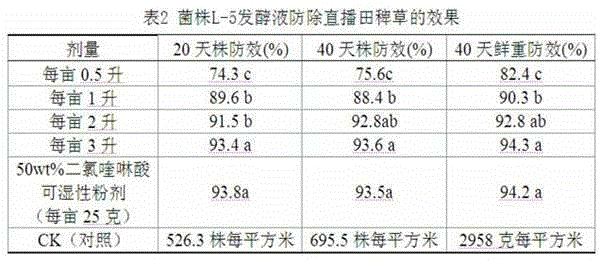
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis strain as well as a metabolite and the application of the bacillus subtilis strain. The bacillus subtilis L-5 is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on February 02, 2015, with the collection number CGMCC No: 10505. The invention also provides the metabolite of the bacillus subtilis and the application of the bacillus subtilis for preventing and removing paddy field weeds. The bacillus subtilis L-5 is used for fermenting soybean isolate protein, and the fermented liquid has obvious inhibition activity for barnyard grass and in particular for the rooting of the newly germinated barnyard grass; the fermented liquid has no influence on the root system of mature crops. If the fermented liquid is applied to weeding, the fermented liquid has the remarkable characteristics of environmental friendliness, no drug resistance of weeds, safety to crops and the like and has favorable application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT
Method for preparing ellagic acid by solid fermentation with granatum as raw material
ActiveCN102250981ASimple processGreening the manufacturing processMicroorganism based processesFermentationCulture mediumsAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for preparing ellagic acid by solid fermentation with granatum as a raw material and belongs to the field of medicines and health-care products. In the method, solid fermentation is performed by using a culture medium which takes granatum as a main ingredient and by using Aspergillusniger 3.316 as a fermenting bacterial strain. The conditions for the solid fermentation of the granatum include: the pH value is between 5 and 7; and the granatum is initially moisturized by water by 47 to 60 percent, 0.5-percent NH4NO3 is added into a moisturizing agent as an N source, and fermentation is performed at 30 DEG C for 5 to 7 days. The fermented product is purified and dehydrated to produce the high-quality ellagic acid product. The granatum serving as a raw material is cheap, and the high yield and purity of the ellagic acid product are ensured; and the method has an outstanding cost advantage and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:安徽德仁生物科技有限公司
Huperzia serrate endophytic fungus and application of huperzia serrate endophytic fungus in preparation of 8alpha,15alpha-epoxydized huperzine A
ActiveCN103667072AEasy to trainHas neuroprotective effectsFungiMicroorganism based processesPteridophyteCurative effect
The invention discloses a huperzia serrate endophytic fungus which is obtained from a pteridophyte, namely, a huperzia serrate plant by adopting a separating and purifying technology, is named Ceriporia lacerate HS-ZJUT-C13A and is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on October 28, 2012 with the collection number CCTCC M 2012433. The strain provided by the invention can be used for preparing a compound, namely, 8alpha, 15alpha-epoxydized huperzine A with a nerve protection effect. A conversion method has the advantages of simple fermentation conditions, high substrate conversion rate and the like, is easily cultures the strain, has the potential of industrial large-scale production, is a novel way for obtaining the compound, protects valuable and rare medicinal huperziaceae plant resources from being damaged and can provide a novel thought for reliving the current situation of lack of huperzine A in clinical administration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
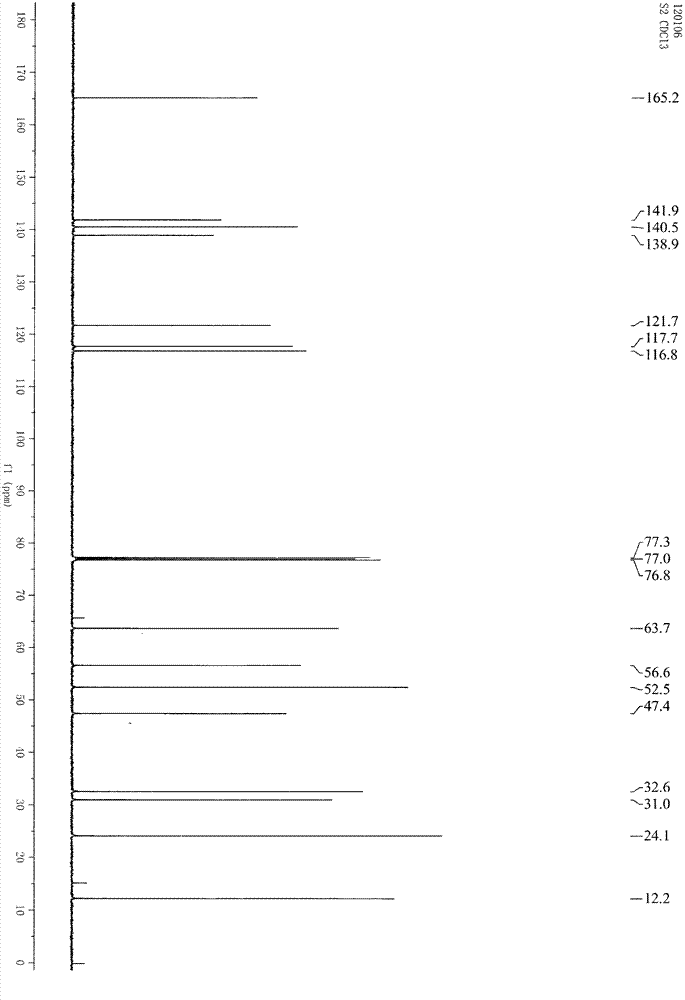
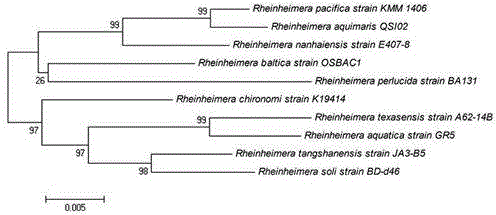
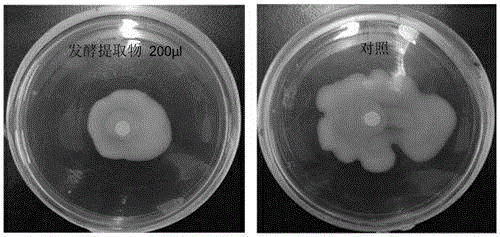
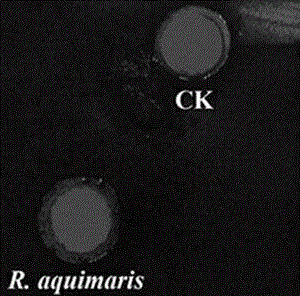
Rheinheimera aquimaris strain from ocean sludge and application thereof
ActiveCN104928220ASimple fermentation conditionsThe preparation process is simple and easy to controlBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentation brothDrug resistance
The invention relates to a rheinheimera aquimaris strain QSI02 from ocean sludge and the application of the rheinheimera aquimaris strain QSI02 to the aspect of bacterial quorum sensing inhabiting and screening. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 23rd, 2015, and the preservation serial number is CCTCC No: M2015245. The fact that the Rheinheimera type strain has the bacterial quorum sensing inhabiting activity is reported for the first time. A metabolite prepared through a fermentation liquor of the strain has the double inhibiting functions on chromobacterium violaceum and pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing system and does not have the double inhibiting functions on generation of screening model chromobacterium violaceum CV026 within an effective concentration range. A strain extract can remarkably lower the yield of purpurin of chromobacterium violaceum and the swarming motility of pseudomonas aeruginosa and weaken the drug resistance of pathogenic bacterium, and therefore the rheinheimera aquimaris strain QSI02 has broad application prospects on the aspects of solving a bacterial drug resistance problem and researching and developing novel antibacterial agents.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain and application thereof in producing proteinase
InactiveCN105543147AIncrease enzyme activityImproved salt toleranceBacteriaHydrolasesMicroorganismProteinase K
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain SWJSS3 and application thereof in producing proteinase. The strain is collected by General Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on June 10th, 2015; the collection address is Institute of Microbiology in Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yard 1, Beichenxi Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City; and the collection number is CGMCC No.10973. The application method of the strain for producing proteinase comprises the following steps: adding a fermentation culture medium into a fermentation tank, wherein the liquid filling amount is 8-12%, the initial pH value is 7.0-7.5, the strain inoculum size is 0.8-1.2%, and the initial temperature in the tank is 20-40 DEG C; and fermenting under oscillating conditions for 30-80 hours to generate abundant proteinase in the tank, and separating and extracting to obtain the proteinase. The strain SWJSS3 has high proteinase production capacity; and the obtained proteinase has the characteristics of high enzyme activity and high salt tolerance. The fermentation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple conditions and stable hereditary property, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Aspergillus fumigatus and application thereof
InactiveCN101575576AEasy to trainProtect ecological diversityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAstragaloside
The invention discloses an aspergillus fumigatus which can produce podophyllotoxin, epipodophyllotoxin biglucoside and astragaloside, and application thereof. The aspergillus fumigatus TEQA CGMCC No. 3115 has the function of producing podophyllotoxin, epipodophyllotoxin biglucoside and flavonoids astragaloside which have the physiological property the same as that of Chinese podophyllum root. The aspergillus fumigatus can be used for preparing podophyllotoxin and astragaloside. The method for preparing podophyllotoxin, epipodophyllotoxin biglucoside and astragaloside has the advantages of simple fermentation conditions, easy bacterium culture and short production period, with potential application for industrialized mass production. Besides, the aspergillus fumigatus provides a new way for resource development of podophyllotoxin and has important meaning to protect ecological diversity of plants.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for degrading lignin in tobacco stems
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and discloses a method for degrading lignin in tobacco stems. The method for degrading the lignin in the tobacco stems comprises the steps of mixing the tobacco stems with laccase and water, and performing enzymolysis on the mixture for 36 hours to 60 hours at the temperature of 40 DEG C-48 DEG C at a pH of 4.5 to 5.5. The method for degrading the lignin in tobacco stems is simple in operation, small in damage to the tobacco stems serving as raw materials, and capable of remarkably increasing the degradation rate of the lignin in the tobacco stems, improving quality of cut tobacco stems, and fully utilizing tobacco stem resources. Offensive odor and irritation of cigarettes added with tobacco stem enzymolysis products prepared by the method can be decreased remarkably, lignin odor is weakened greatly, and fragrance and agreeable aftertaste of the cigarettes can be improved.
Owner:JILIN TOBACCO IND +1
Plant endophytic fungus and application thereof
ActiveCN107868757AEasy to trainHas neuroprotective effectsFungiMicroorganism based processesCurative effectMicrobiology
The invention discloses a plant endophytic fungus. The endophytic fungus is classified and named as Bjerkandera adusta ZJUT-HS8; and the strain (the endophytic fungus) is preserved in China Center forType Culture Collection with preservation number of Bjerkandera adusta CCTCC M2017159 on March 31, 2017 in Wuhan University, Wuhan Province of China. According to the strain provided by the invention, a compound, namely 8[alpha], 15[alpha]-epoxidized huperzine A, which has a neuroprotection curative effect, can be prepared by virtue of a biological transformation method. The method, as a novel way for preparing huperzine A derivatives having a neuroprotection effect, has the advantages of being simple in fermentation conditions, easy in strain culture and high in transformation yield, and themethod has a potential of industrial development and the like; therefore, a new idea is provided for the preparation of the active huperzine A derivatives.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
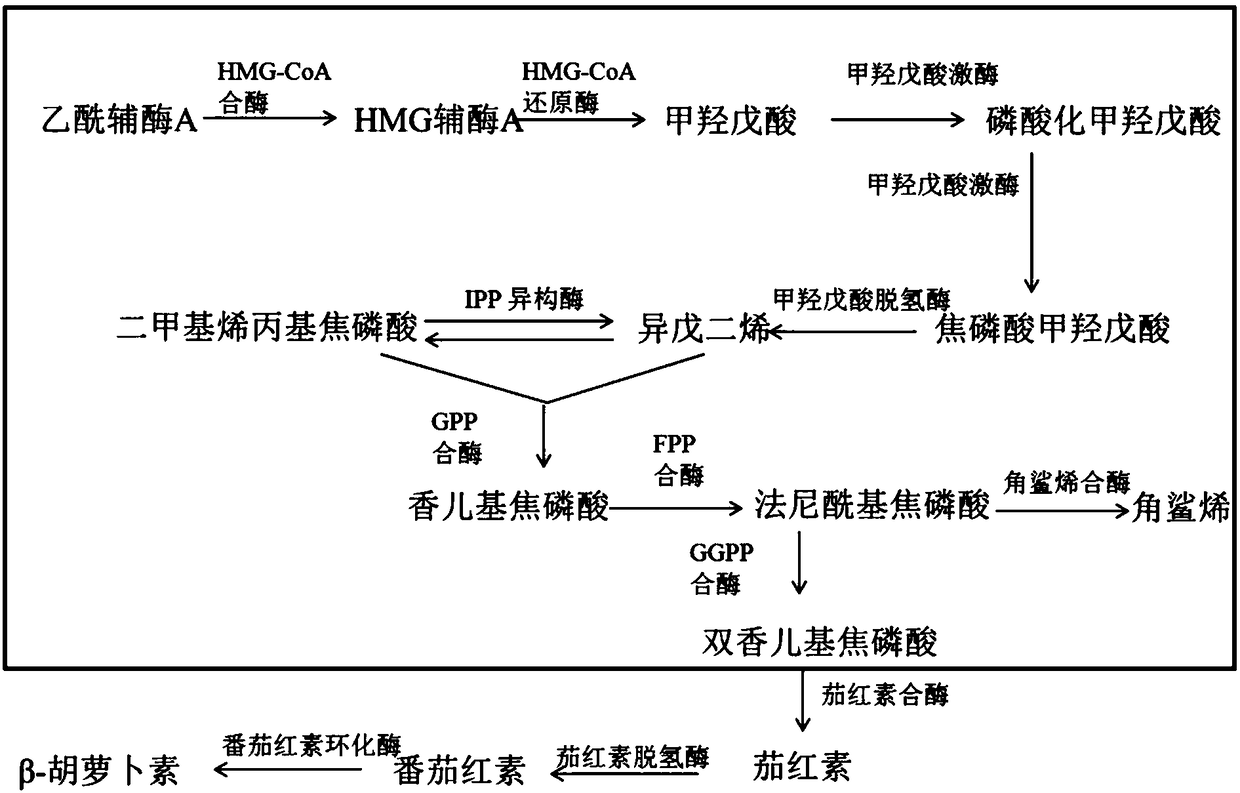
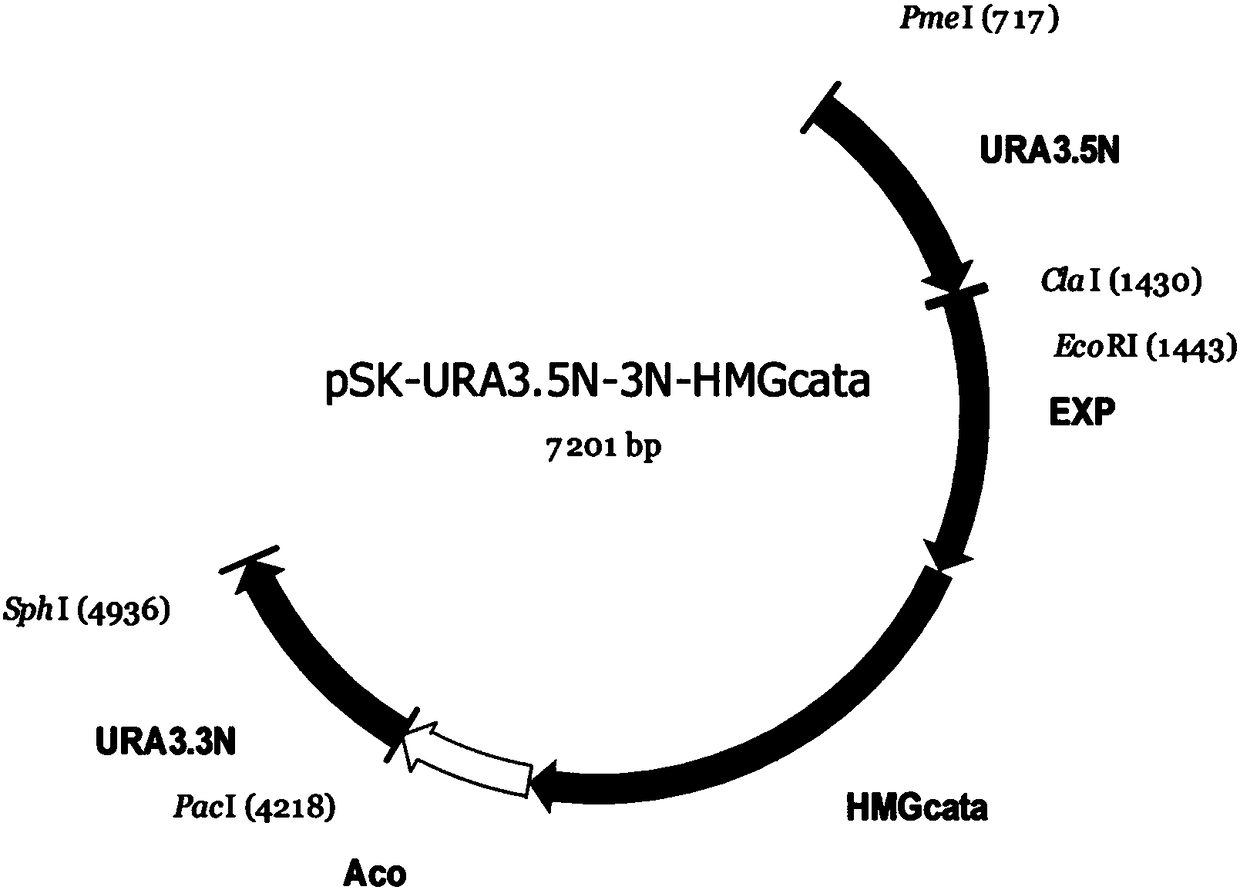
Method of producing beta-carotene by genetically engineered bacterium and genetically engineered bacterium thereof
InactiveCN108118007AIncrease productionSimple fermentation conditionsFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousBiotechnology
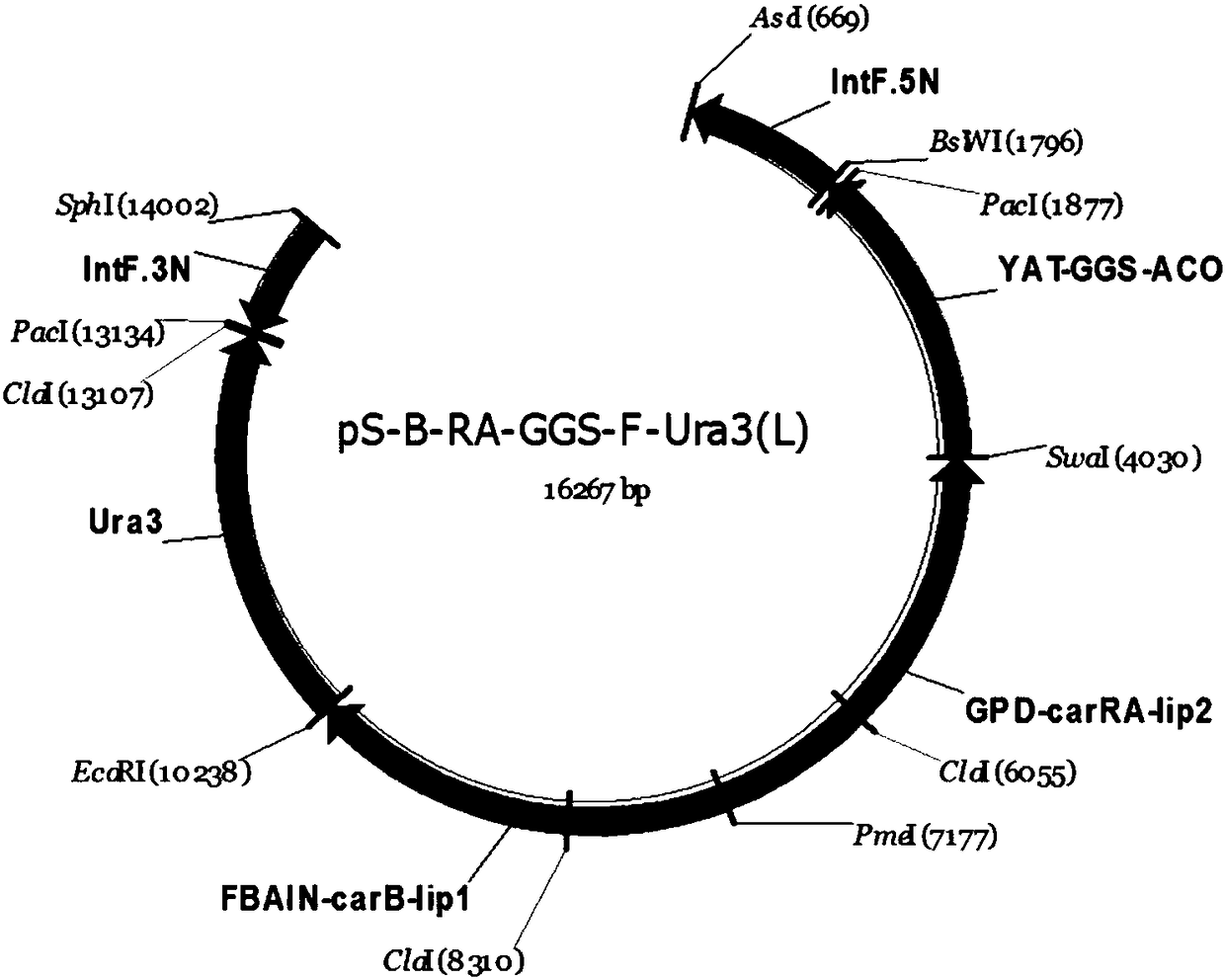
The invention discloses a method of producing beta-carotene by a genetically engineered bacterium and the genetically engineered bacterium thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium is a yarrowia lipotica genetically engineered bacterium comprising a carRA gene and a carB gene. By introducing the carRA gene and the carB gene originated from blakeslea trispora into the yarrowia lipotica yeast bymeans of a genetic engineering method, expression of GGS and 3-hydroxyl-3-methyl acetyl coenzyme A reductase is further enhanced. 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase (Gut2) and peroxidase (Pox2) are knocked out to obtain a yarrowia lipotica strain expressing beta-carotene heterologously. The method is simple in fermenting condition and relatively high in output of beta-carotene, and has important production value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Non-immetsed type liquid fermentation process of lingin catabolic enzymes from Phanerochaete chrysosporium
InactiveCN1563369AHigh degradative enzyme activityEasy to harvestHydrolasesAir atmosphereMicroorganism
This invention relates to thelephoroid lignin non-immersion liquid fermentation method which inlets the thelephoroid liquid seeds in a liquid culture medium with carrier to be cultivated in oscillation under air atmosphere of 35-39deg.C. Said solid cultivation carrier is either inert or non-inert and a 0.5-2.5cm size block. Stacked height of the carrier is higher than the surface of the liquid culture medium for about 1-5times higher and the carrier is at un-immersion state. Said fermentation culture medium adopts either carbon limit liquid medium or nitrogen limit liquid culture medium PH is controlled at 4.0-6.0 the medium contains reratryl alcohol of 0-2.5mM.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fermented compound drink and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109566933ATo promote metabolismRegulating the structure of intestinal floraSugar food ingredientsYeast food ingredientsLactobacillus plantarumTraditional Chinese medicine
The invention discloses fermented compound drink and a preparation method thereof. The probiotic fermented traditional Chinese medicine compound drink is prepared by enabling a fermentation substrateto be subjected to mixed fermentation of lactobacillus casei, lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus rhamnosus, wherein extracting solutions of traditional Chinese medicines such as radix ginseng,rhizoma dioscoreae and fructus jujubae are used as the fermentation substrates. The probiotic fermented traditional Chinese medicine compound drink can be used for preparing medicines, health food orfood, and has a definite effect of improving the treatment of chronic constipation of middle aged and elderly people.
Owner:JINAN OBOSON BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Brewer's yeast engineering bacterium producing 2-phenylethyl alcohol, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN105647958AShort fermentation cycleSimple fermentation conditionsFungiMicroorganism based processesAlcohol ethylMicrobiology
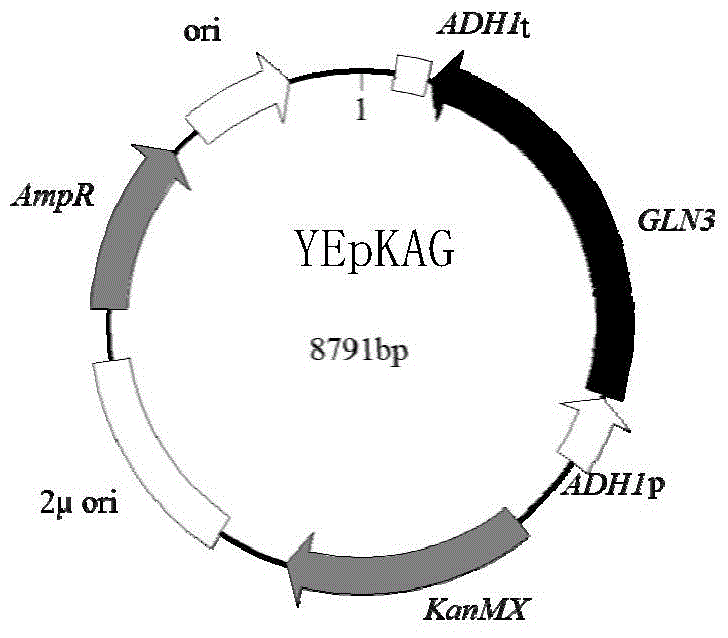
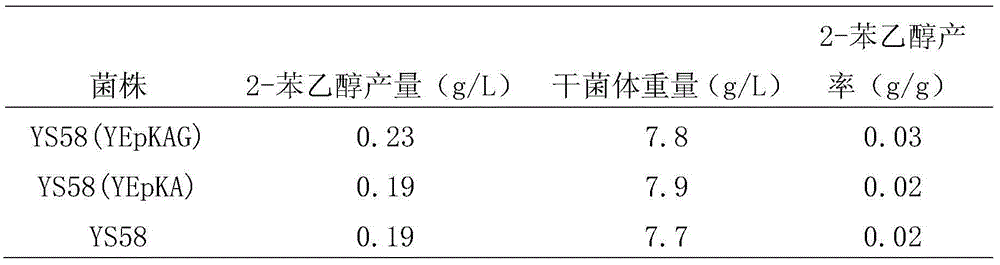
The invention discloses a brewer's yeast engineering bacterium producing 2-phenylethyl alcohol, a preparation method and applications thereof. The invention discloses a preparation method of a brewer's yeast engineering bacterium producing 2-phenylethyl alcohol. According to the preparation method, an encoding gene of GATA transcription factor Gln3p is introduced into an acceptor (brewer's yeast) to obtain the brewer's yeast engineering bacterium producing 2-phenylethyl alcohol. Compared with the host bacterium, the substrate conversion rate and cell's 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesizing performance of brewer's yeast engineering bacterium are prominently improved; moreover, the fermentation conditions of the engineering bacterium are simple, the fermentation period is short, and the engineering bacterium can be applied to industrial production of 2-phenylethyl alcohol.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing L-malic acid through aspergillus oryzae fermentation
ActiveCN105861574ARaw materials are cheapLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationToxinSpore
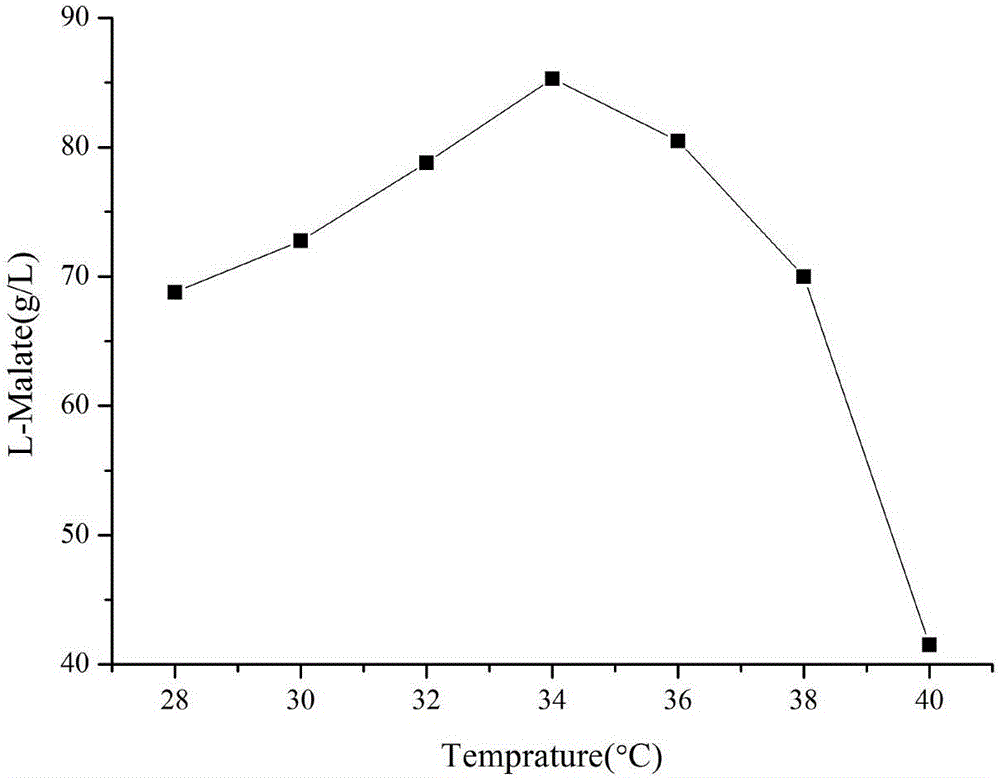
The invention discloses a method for producing L-malic acid through aspergillus oryzae fermentation, belonging to the field of fermentation technology. The method comprises the following steps: with aspergillus oryzae as a production strain, inoculating a fermentation medium with 20% of liquid volume with 10% of spore suspension; adding 60-80g / L CaCO3; and performing ventilated culture for 120h at 30-34 DEG C. In the invention, a sugar-containing raw material is fermented by aspergillus oryzae to produce malic acid, the maximum acid yield can reach 103.2g / L, the raw materials are cheap, and the cost is low; moreover, by adopting single-bacterium fermentation, the required medium composition is simple, the fermentation conditions are simple and easy to control, and the problem of toxin generation caused by mixing aspergillus flavus for fermentation is avoided; and the technology for producing L-malic acid by fermenting the sugar-containing raw material, provided by the invention, has an important economic value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
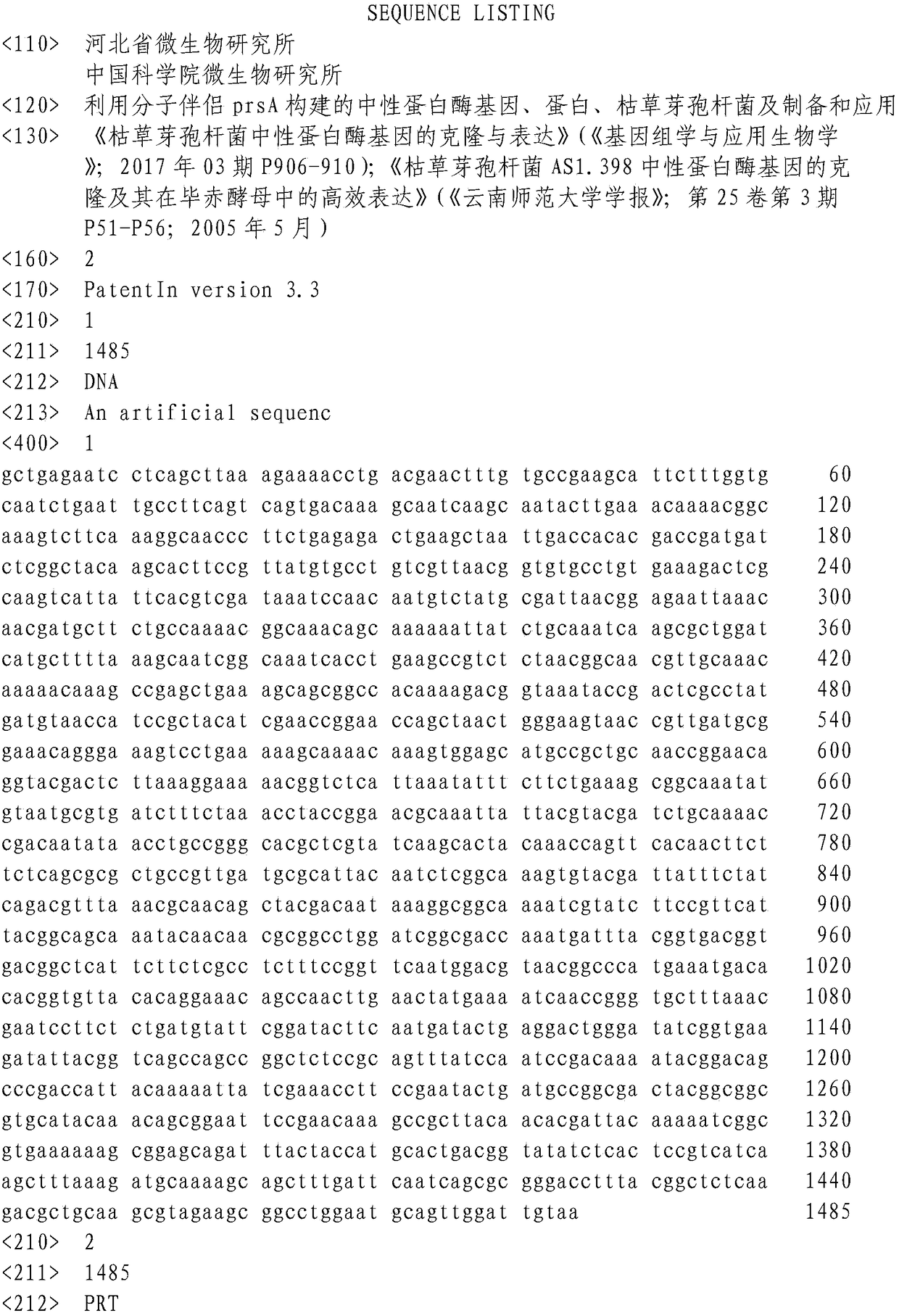
Neutral proteinase gene constructed by molecular chaperone prsA, protein, bacillus subtilis, preparation and application
InactiveCN108070606AImprove expression levelStrong secretory abilityBacteriaHydrolasesNeutral proteinaseMicrobiology
The invention belongs to preparation of a new gene and construction of an engineering bacterium, and particularly relates to a neutral proteinase gene constructed by a molecular chaperone prsA, a protein, bacillus subtilis, preparation and an application. The molecular chaperone PrsA and the neutral proteinase gene are integrated to construct pHT43-npr-PrsA recombinant plasmid by a molecular biology technology and finally converted into a host bacterium, namely the bacillus subtilis WB800N, to construct a new bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium CGMCC No. (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center number) 14837; the molecular chaperone PrsA and the neutral proteinase gene are co-expressed; and an expression level of neutral proteinase is effectively increased.
Owner:河北省微生物研究所有限公司 +1
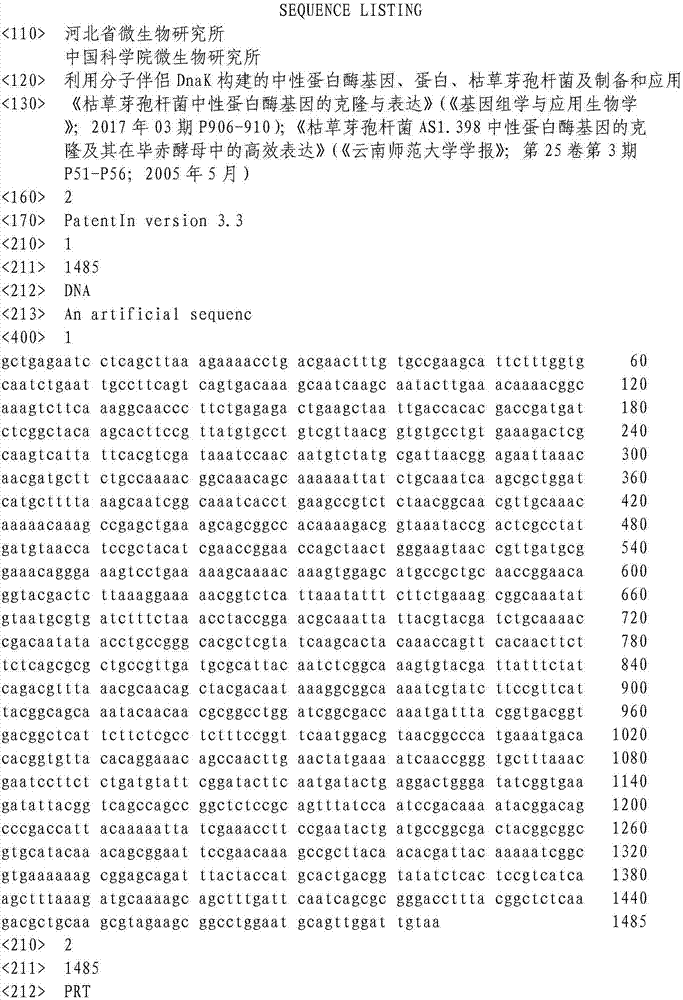
Neutral protease gene built by molecular chaperone DnaK, protein, bacillus subtilis, and preparation and application of neutral protease gene built by molecular chaperone
InactiveCN107881181AImprove expression levelStrong secretory abilityBacteriaHydrolasesNeutral proteaseBacillus subtilis
The invention belongs to new gene preparation and engineering bacterium building, and particularly relates to a neutral protease gene built by a molecular chaperone DnaK, protein, bacillus subtilis, and preparation and application of the neutral protease gene built by the molecular chaperone DnaK. The molecular biology technology is used for integrating the molecular chaperone DnaK with the neutral protease gene; the pHT43-npr-DnaK recombinant plasmids are built and are finally converted into a host bacterium of bacillus subtilis WB800N; a novel bacillus subtilis engineering strain CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.14836 is built, so that the molecular chaperone DnaK and the neutral protease gene realize the coexpression; the expression level of the neutralprotease is effectively improved.
Owner:河北省微生物研究所有限公司 +1
Bacillus coagulans with functions of preventing diarrhea and degrading cholesterol
ActiveCN113528367ASimple fermentation conditionsLow cost of industrializationBacteriaMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of functional microorganism screening and application, and particularly provides a novel bacillus coagulans and application of thereof. The bacillus coagulans is screened from a sour cabbage sample, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2019738, and the bacillus coagulans has high oxidation resistance and cholesterol degradation capacity, can effectively regulate intestinal tract movement, prevent diarrhea, recover the microbial barrier function of intestinal tracts and shorten the disease course, and is very remarkable in effect.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH INC +1
Method for preparing ellagic acid by solid fermentation with granatum as raw material
ActiveCN102250981BStrong specificityHigh purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationAdditive ingredientBacterial strain
The invention discloses a method for preparing ellagic acid by solid fermentation with granatum as a raw material and belongs to the field of medicines and health-care products. In the method, solid fermentation is performed by using a culture medium which takes granatum as a main ingredient and by using Aspergillusniger 3.316 as a fermenting bacterial strain. The conditions for the solid fermentation of the granatum include: the pH value is between 5 and 7; and the granatum is initially moisturized by water by 47 to 60 percent, 0.5-percent NH4NO3 is added into a moisturizing agent as an N source, and fermentation is performed at 30 DEG C for 5 to 7 days. The fermented product is purified and dehydrated to produce the high-quality ellagic acid product. The granatum serving as a raw material is cheap, and the high yield and purity of the ellagic acid product are ensured; and the method has an outstanding cost advantage and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:安徽德仁生物科技有限公司
Antibiological inoculant for preventing and controlling tobacco rhizome type diseases and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108384734AHarm controlEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganism application, and particularly relates to an antibiological inoculant for preventing and controlling tobacco rhizome type diseases and a preparation method thereof. The antibiological inoculant for preventing and controlling tobacco rhizome type diseases is characterized by comprising the major ingredients consisting of fermentation liquid obtained through mixed fermentation of strains 16029 and strains 16098. The antibiological inoculant can achieve the strong inhibition effects on three kinds of major pathogenic bacteria of rhizomediseases of tobacco bacterial wilt, tobacco black shank and black root rot diseases, and can be used as the biocontrol bacterial agent for the tobacco rhizome type diseases. The bacteria agent has good application prospects on the prevention and control of tobacco rhizome type diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Process for producing butyric acid through co-culture and fermentation of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and clostridium butyricum
PendingCN112625980ALow costIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus amylolyticus
The invention discloses a process for producing butyric acid through co-culture and fermentation of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and clostridium butyricum. The process comprises the following steps: a fermentation process is divided into three stages including primary seed culture, secondary seed culture and fermentation culture; bacillus amyloliquefaciens and clostridium butyricum are subjected to shake-flask seed culture, inoculated into a primary seed culture medium for primary seed culture, then inoculated into a secondary seed culture medium for secondary seed culture, and finally inoculated into a fermentation tank culture medium for fermentation culture; the fermentation culture is divided into two stages; in the first stage, when the culture temperature is 30-35 DEG C and the fermentation pH is reduced to 4.5-5.0, reducing sugar is controlled in 10-20 hours; the temperature is increased to 35-37 DEG C for secondary culture; and the pH value is controlled to be 6.0. According to the invention, the starch is used for producing small molecular sugar to replace glucose in a fermentation culture medium; therefore, the cost of glucose in raw materials is reduced; the production efficiency of butyric acid is improved; the production cost is reduced; and the fermentation efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHUMADIAN HUAZHONG CHIA TAI
Bacteria for degrading cellulose and microbial inoculum prepared by same
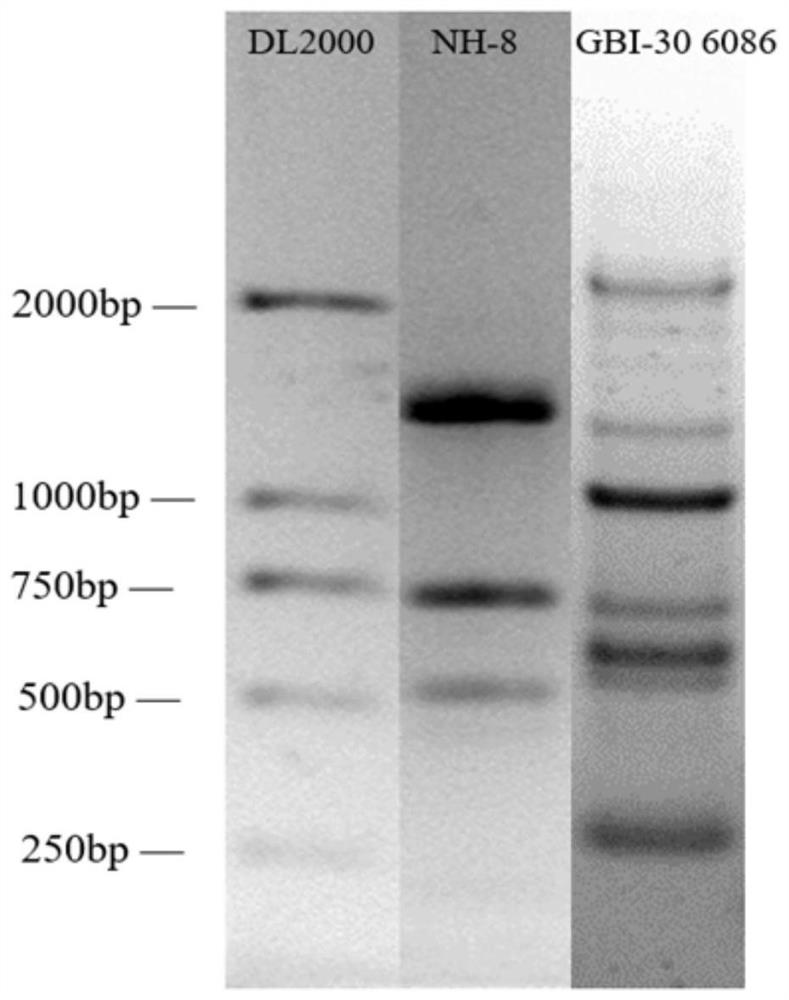
InactiveCN101724570AEfficient degradationSimple fermentation conditionsFungiMicroorganism based processesHuskCellulose degradation
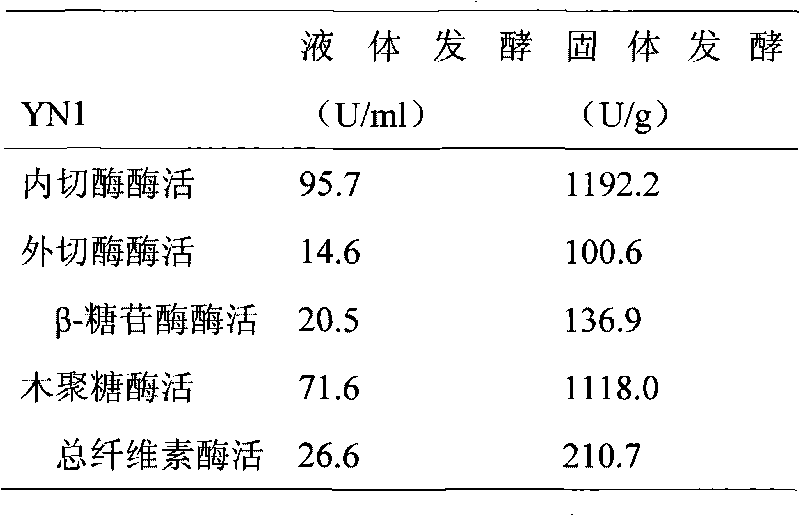
The invention provides bacteria for degrading cellulose and microbial inoculum prepared by same, which both belong to the bio-technology field. YN1 microbial strain is added to a PDA plating culture medium, PDA liquid culture medium, a seed tank culture medium and a production culture medium, and the effectively live bacteria of the microbial strain reaches over 100 million / ml. After the YN1 bacterial strain is cultivated through fermentation, the activity of incision enzyme, excision enzyme, beta-glycosidase, xylanase and cellulase is respectively 95.7 U / mL, 14.6 U / mL, 20.5 U / mL, 71.6 U / mL and 26.6 U / mL. After the YN1 bacterial strain is cultivated through solid fermentation, the activity of incision enzyme, excision enzyme, beta-glycosidase, xylanase and cellulase is respectively 1192.2 U / g, 100.6 U / g, 136.9 U / g, 1118.0 U / g and 210.7 U / g. The YN1 microbial strain can degrade 41.87% straws and 31. 59% rice husks in 7 days.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Huperzia serrata endophytic fungus and application in preparation of pyrrole type liver-protecting medicines
ActiveCN103667073AEasy to trainAlleviate shortagesFungiMicroorganism based processesPteridophyteMicrobiology
The invention discloses a huperzia serrata endophytic fungus which is obtained by separation from a stem part of a living body of a pteridophyte huperzia serrata plant and classified and named as peyronellaea glomerata HS-ZJUT-XW12, wherein the strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on the collection date of October 28, 2012 with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2012434. The strain provided by the invention is found by inventors after years of creative experimental labor, and the strain is firstly used for fermentation and culture so as to prepare a compound FPBA with liver-protecting activity; the preparation method has the advantages of simple fermentation conditions, easiness in culture of the strain, few process steps, short production period and the like, and further has potential for realizing industrial large-scale production; a new way is provided for seeking sources for developing pyrrole type liver-protecting medicines, and the shortage of clinical medicines can be alleviated to a certain extent.
Owner:郎溪品旭科技发展有限公司
Metallothionein transgenic yeast construction and heavy metal adsorbing material preparation method by utilizing metallothionein transgenic yeast
InactiveCN103205454AImprove adsorption capacityImprove toleranceFungiWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMaterials preparation
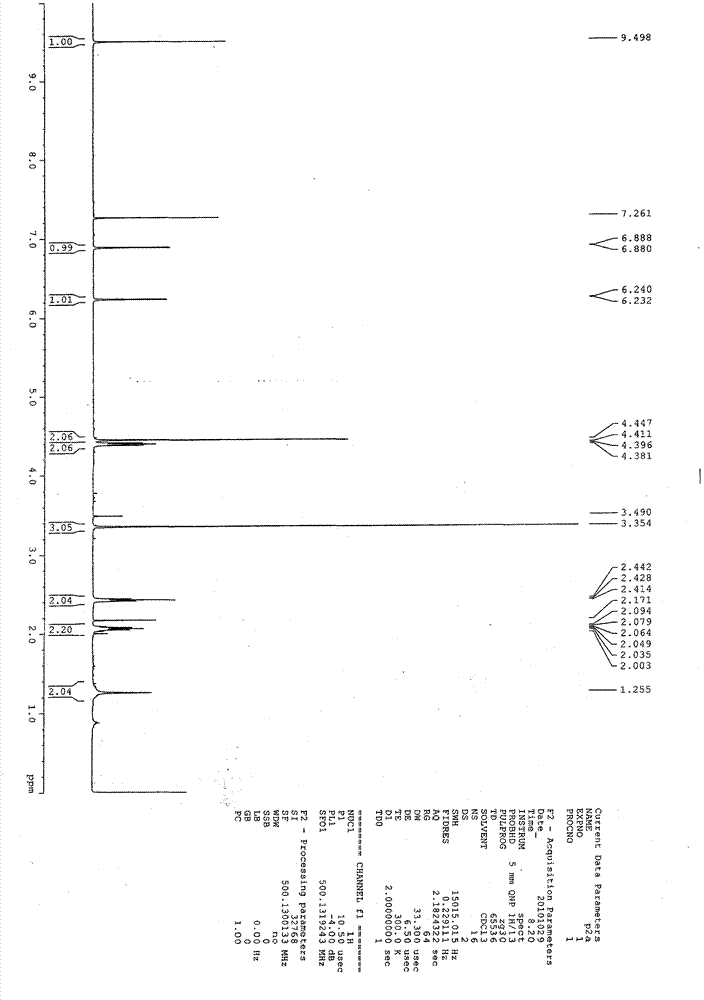
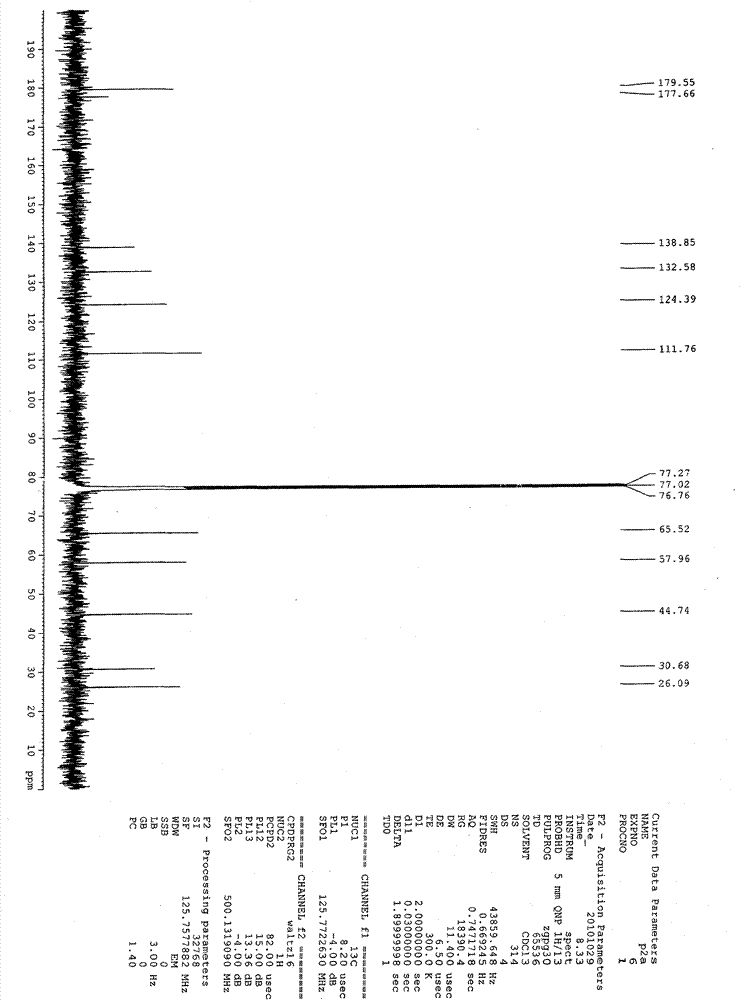
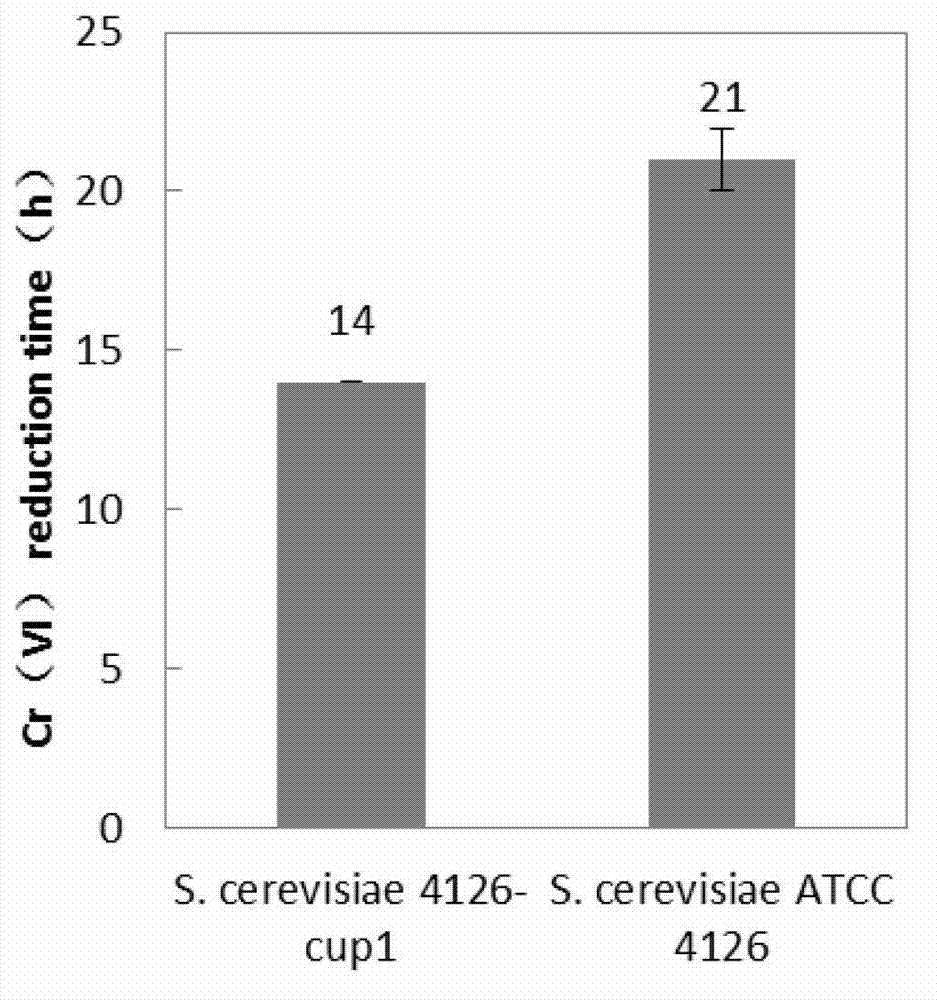
The invention belongs to the environmental engineering heavy metal pollution regulation field, and relates to metallothionein transgenic yeast construction and a heavy metal adsorbing material preparation method by utilizing the metallothionein transgenic yeast. According to the charactristics that rDNA has 100 to 200 repetitive units in a yeast cell, the rDNA is taken as a multi-copy integrated expressive vector of a consanguinity integrated site to establish yeast metallothionein, and an S.cerevisiae288c3 phosphoglyceric acid kinase gene (PGK1) promoter is utilized by the rDNA in S.cerevisiae4126 to express, so that yeast metallothionein multi-copy expression can be realized, the metallothionein transgenic yeast with high tolerance and adsorption to heavy metal is obtained, and the economic and safe heavy metal adsorbing material preparation method by utilizing the metallothionein transgenic yeast is provided.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
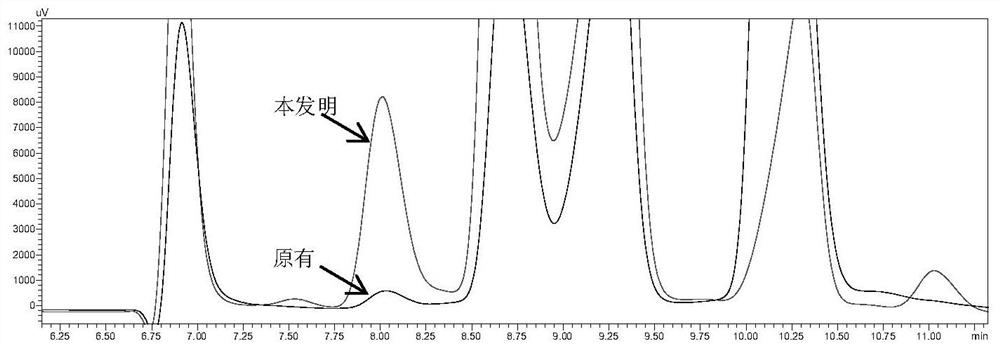
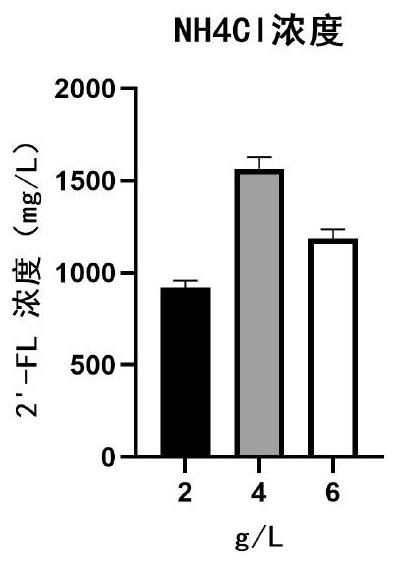
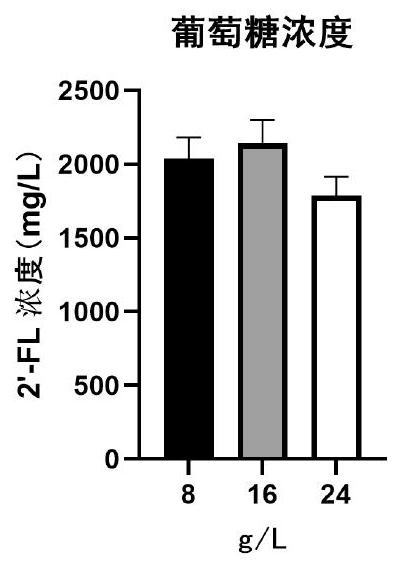
Batch fermentation method of 2'-fucosyllactose
InactiveCN112662715ASimple componentsNo toxic and harmful ingredientsMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention discloses a batch fermentation method of 2'-fucosyllactose. The method is more suitable for large-scale fermentation on the original basis, is higher in production efficiency and final yield, is easier for industrial enlarged culture, and has higher application prospect and economic value. A fermentation medium used in the method is simple in component, free of toxic and harmful components, economical, cheap and easy to obtain, and an excellent fermentation effect and high 2'- fucosyllactose yield can be obtained.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
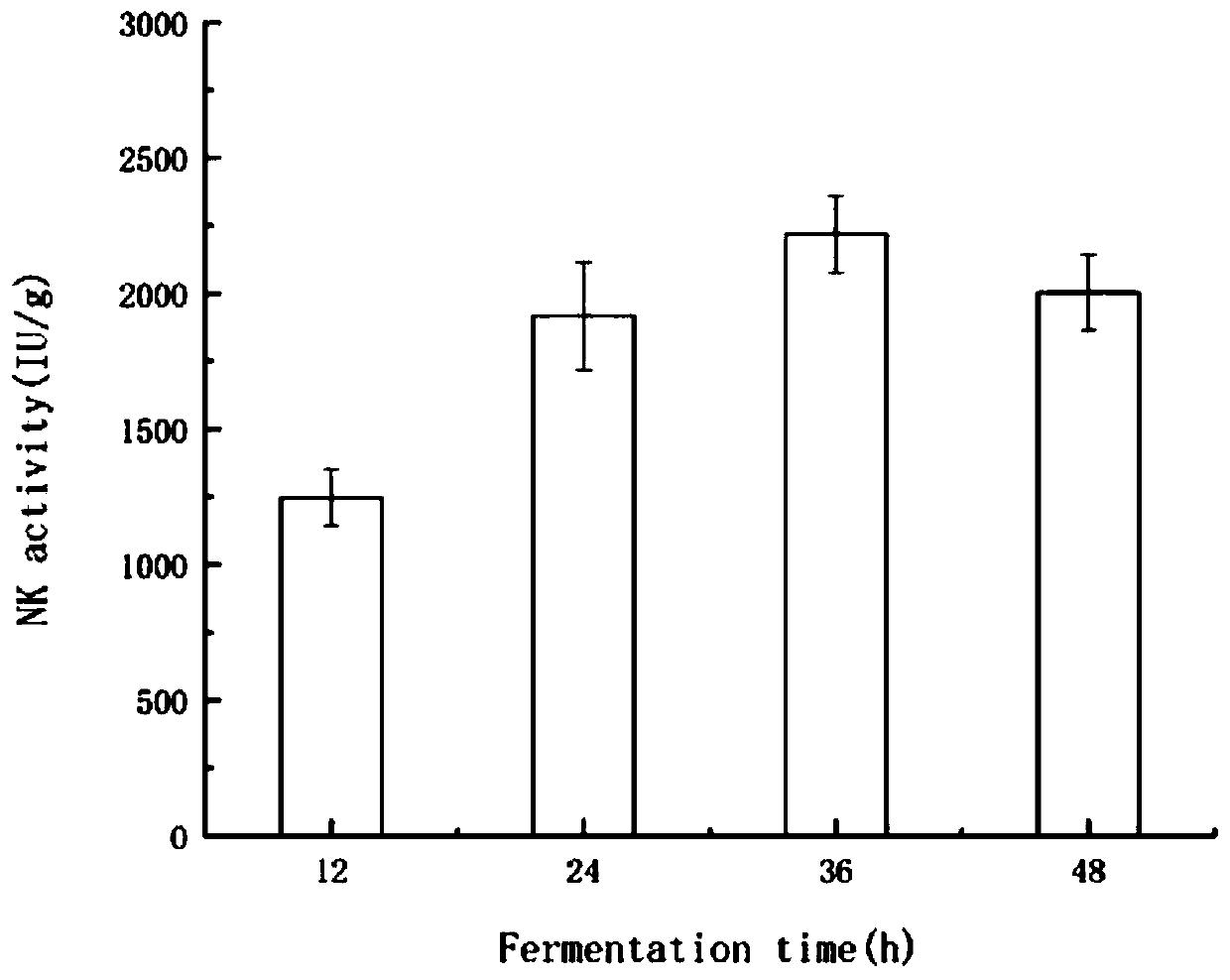
Method for fermenting vegetable soybeans and other foreign products by bacillus natto to produce nattokinase
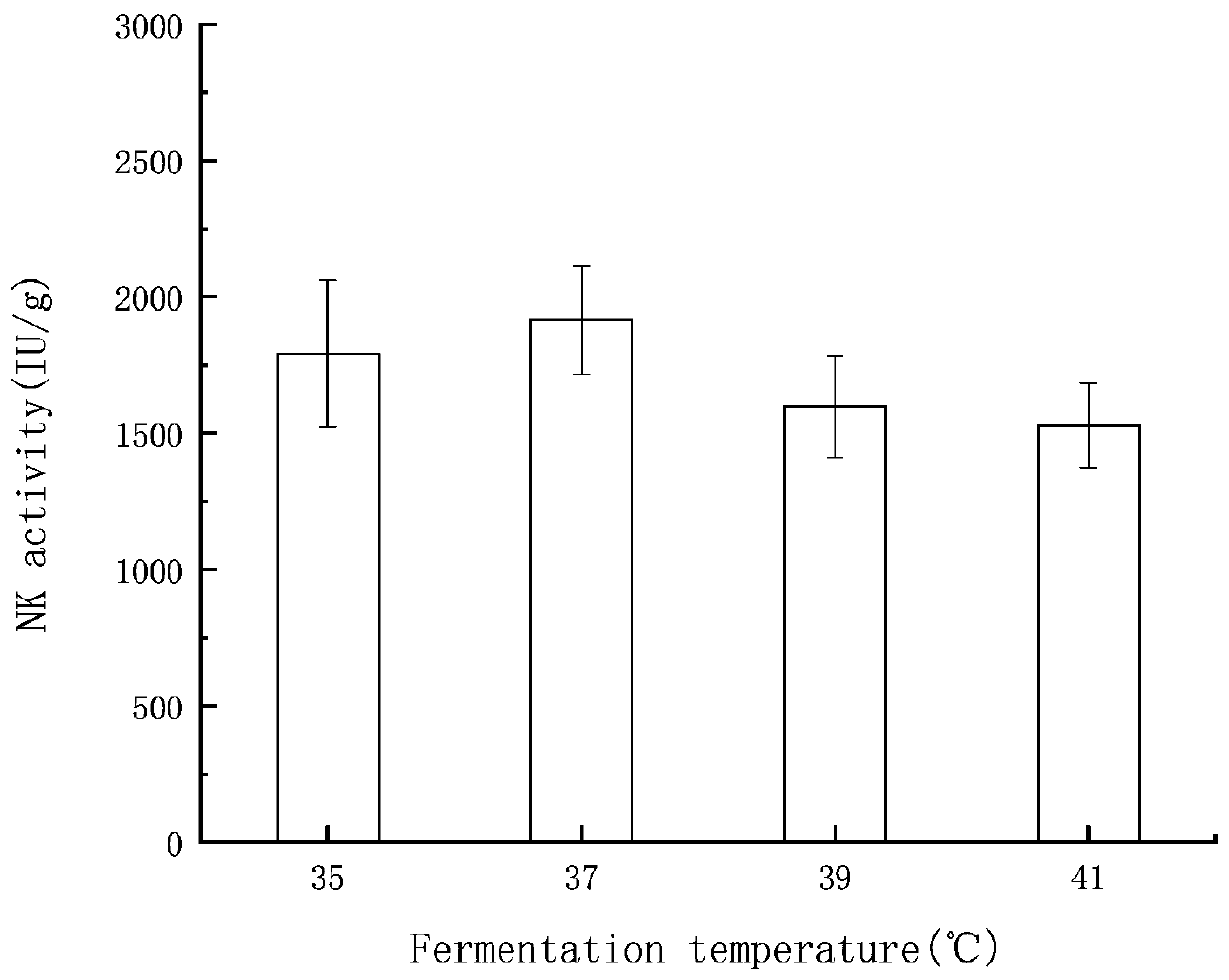
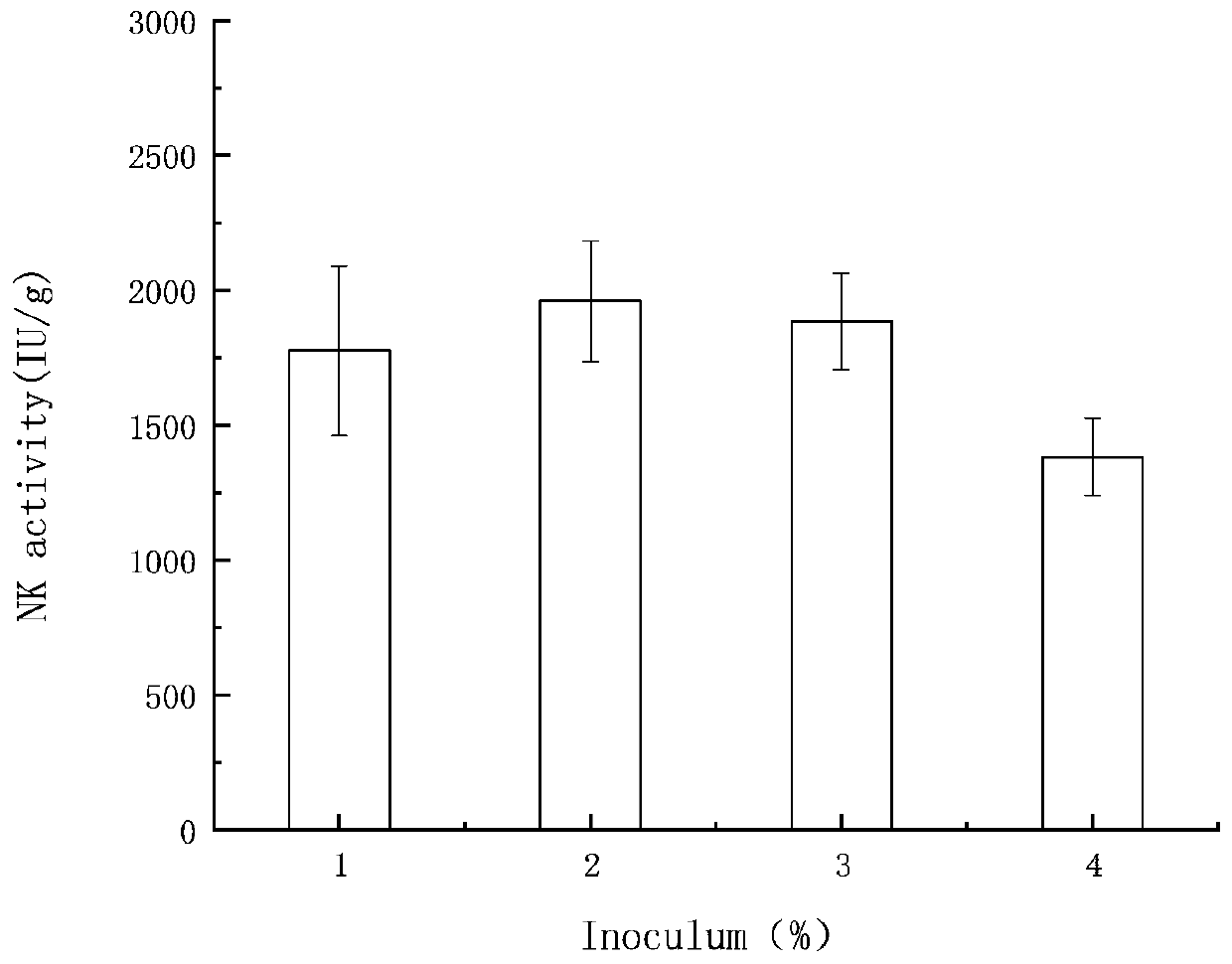
ActiveCN111454932AImprove stabilityGood in vitro thrombolytic effectMicroorganism based processesPeptidasesBiotechnologyElectrophoreses
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fermentation, in particular to a method for fermenting vegetable soybeans and other foreign products by bacillus natto to produce nattokinase.The method comprises the steps of inoculating 2% of prepared bacillus natto solution into selected, cleaned, steamed and sterilized vegetable soybeans and other foreign products; carrying out fermentation in a constant-temperature incubator of 37 DEG C for 36 hours; carrying out after-ripening for 18 hours; carrying out salting-in and centrifuging to obtain an original extracting solution; carrying out ammonium sulfate precipitation and preliminary purification to obtain a crude enzyme solution; and then carrying out further purification by using DEAE ion-exchange column chromatography. The invention aims to provide a new idea for producing the nattokinase through fermentation and to provide a scheme for solving the problem of processing the foreign products of a company. The activity ofthe nattokinase produced under an optimum fermentation process can reach 2326.60 IU / g; an SDS-PAGE electrophoresis test verifies that the molecular weight of the extracted nattokinase is 25-35 kDa, and the recovery rate and the purification multiple are 4.9% and 11.2 separately; and a theoretical basis is provided for production of the nattokinase and follow-up in vivo tests.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV +1
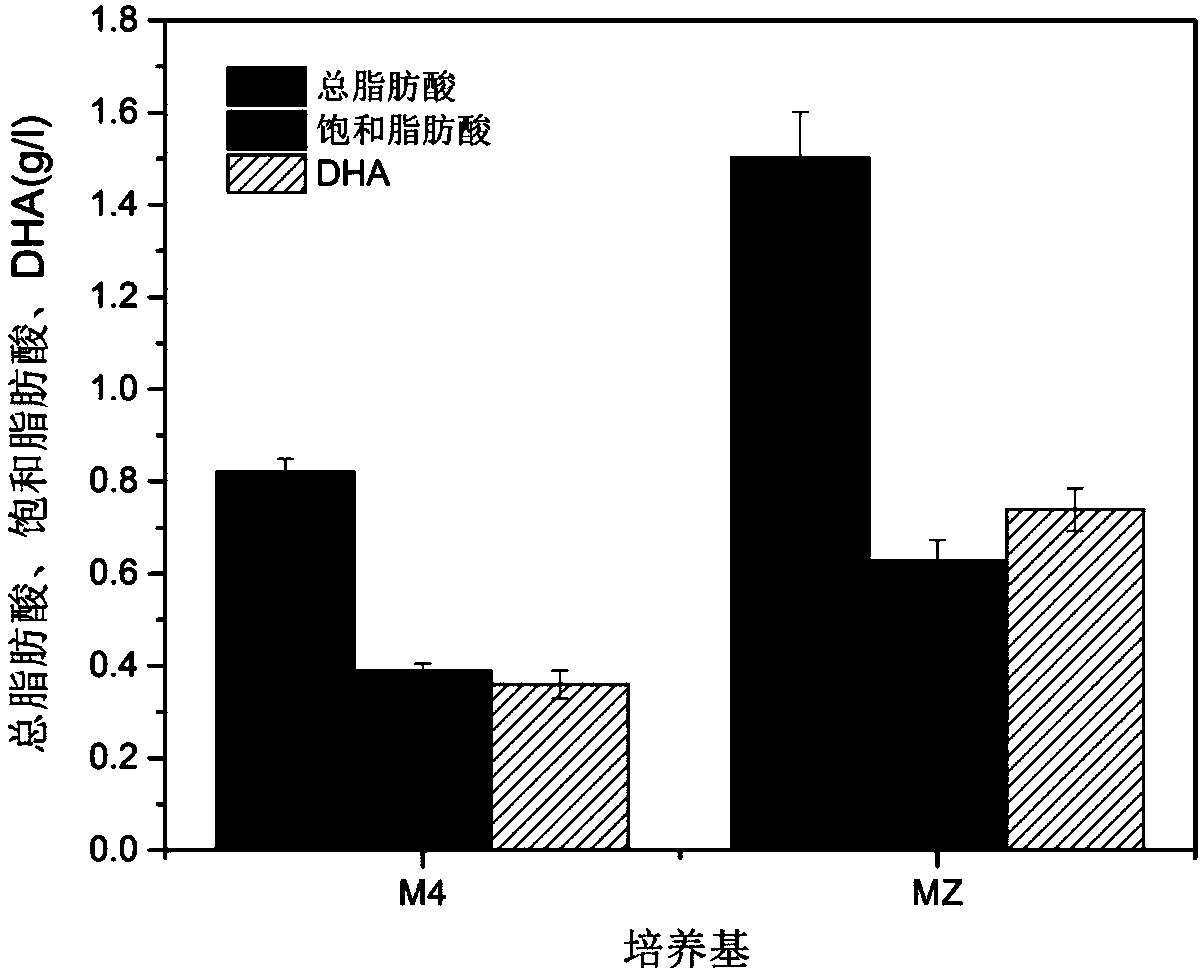
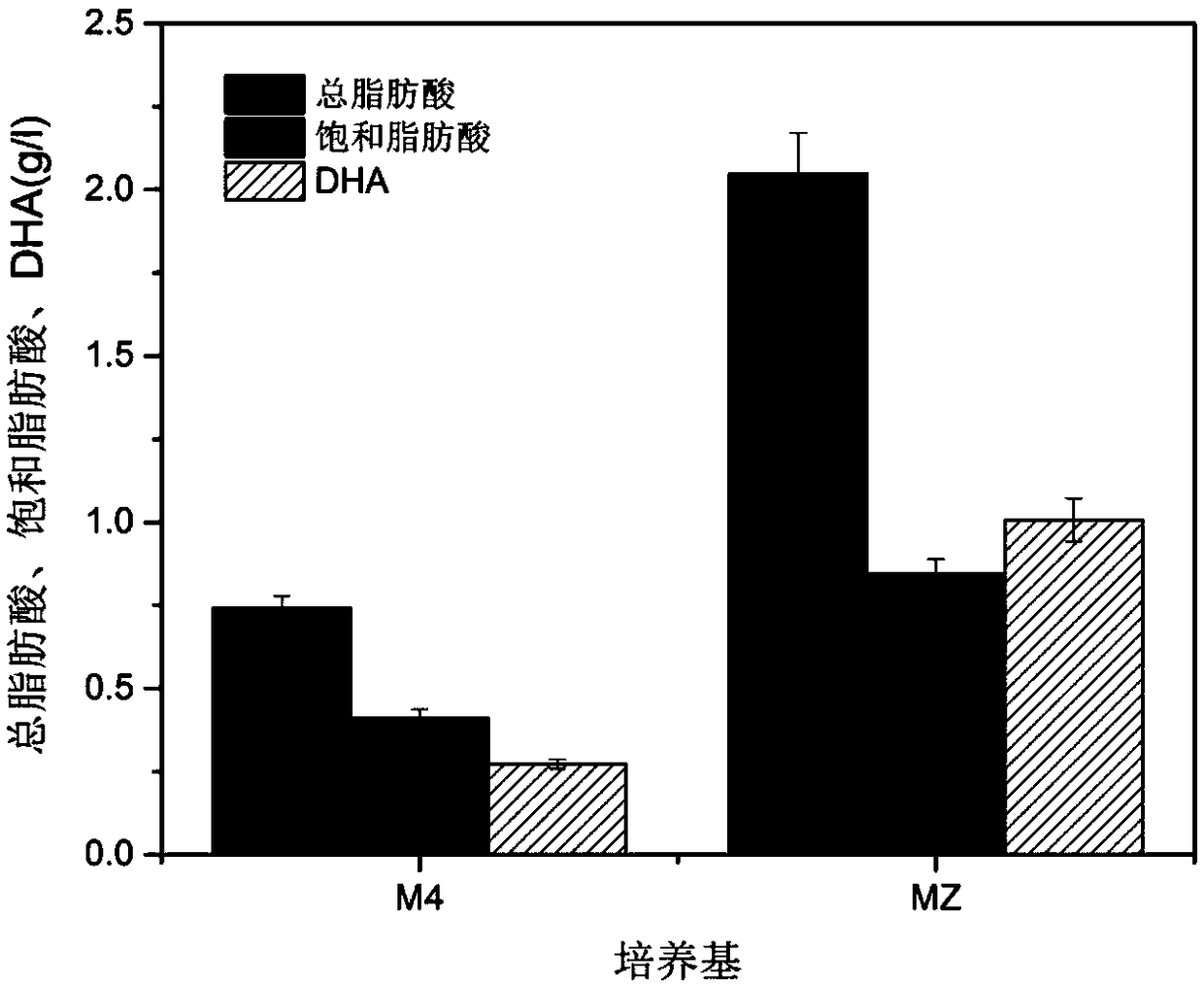
Fermentation culture medium for high-yield production of fatty acids through Thraustochytrids, and applications thereof
InactiveCN108424938AReduce manufacturing costIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhosphateGlycerol
The invention discloses a fermentation culture medium for high-yield production of fatty acids through Thraustochytrids, and applications thereof. The preparation method of the fermentation culture medium comprises: weighing 45-65 g of glycerol, 1-2 g of peptone, 0.5-1.5 g of a yeast extract, 0.2-0.3 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 25-40 g of artificial sea salt according to a certain ratio, adding ultrapure water to achieve a volume of 1000 ml, uniformly stirring, sterilizing for 21 min at a temperature of 115 DEG C, and cooling to a room temperature to obtain the product. According to the present invention, the production cost is saved by using the glycerol; compared to the original culture medium, the fermentation culture medium of the present invention has the significantly-increased total fatty acid yield, the significantly-increased saturated fatty acid yield and the significantly-increased DHA content, and improves the utilization rate of the raw material; and the fermentation culture medium has characteristics of simple fermentation condition, convenient operation, low production cost, easy large-scale fermentation and energy saving.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
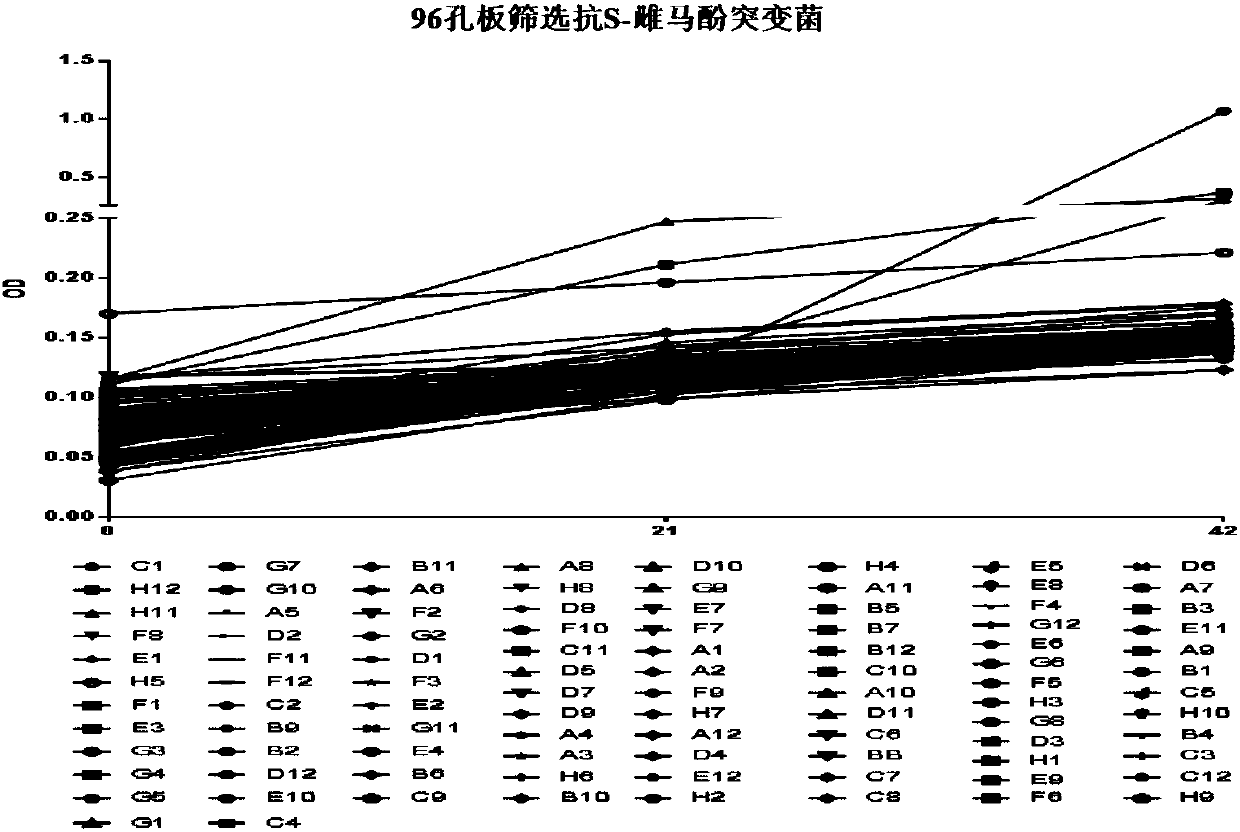
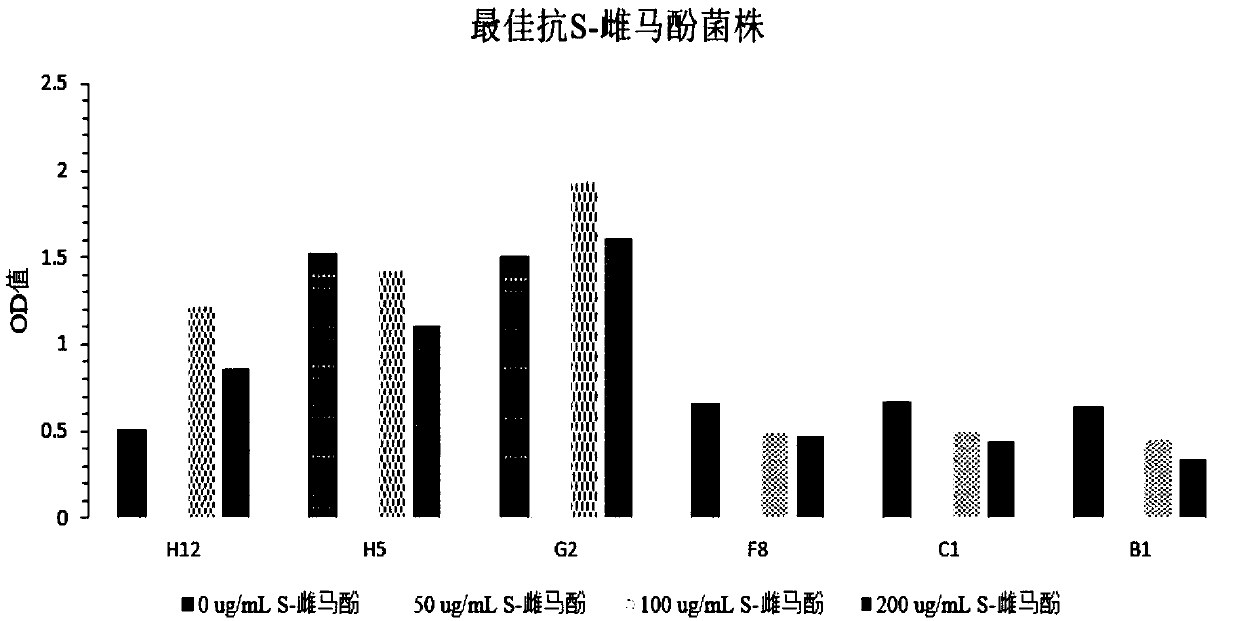
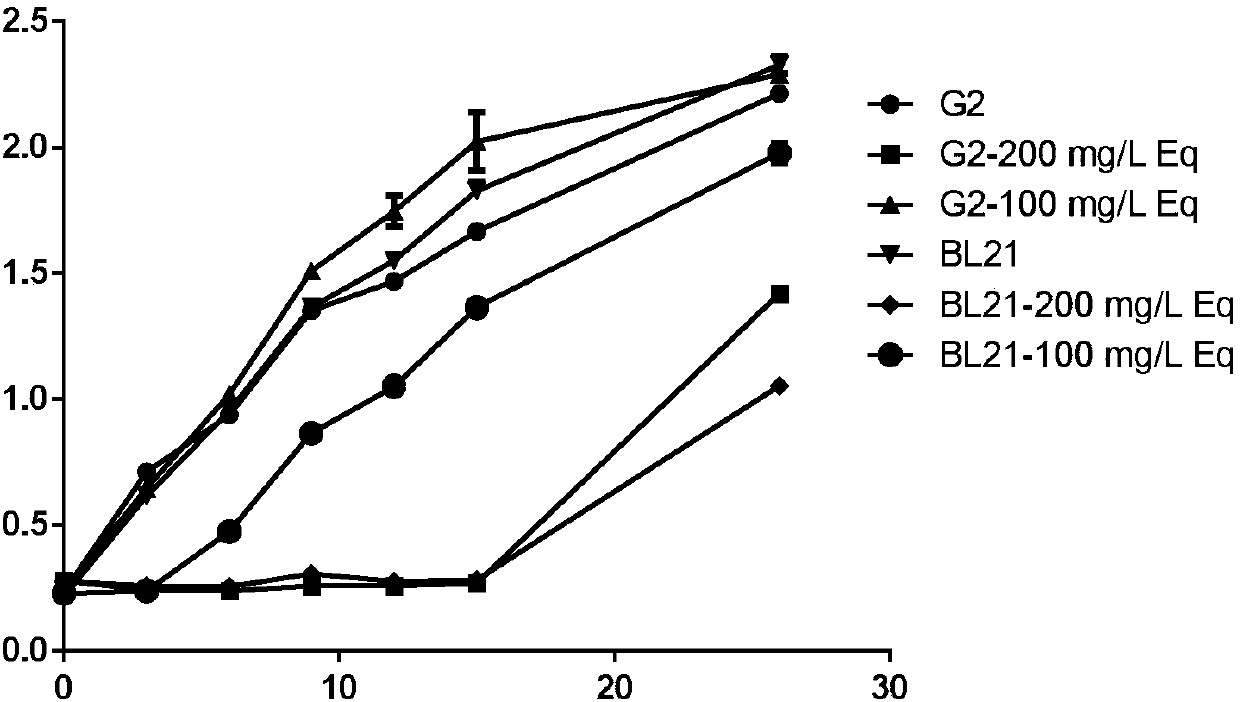
Escherichia coli mutant strain with S-equol resistance and application
ActiveCN107641611ASimple fermentation conditionsEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactococcus sp.Escherichia coli
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli mutant strain with S-equol resistance and application. The Escherichia coli mutant strain is obtained by cloning L-DDRC, L-DZNR, L-DHDR and L-THDR genes coming from Lactococcus sp. 20-92 to Escherichia coli BL21-G2 for converting. The Escherichia coli mutant strain is simple in fermentation condition, convenient to use, stable in system and wide in application range, has S-equol resistance and has ability of converting daidzein in LB culture media into S-equol. Equol yield of engineering bacterium DDDT-G2 is 1.25-2 times that of engineering bacteriumDDDT-BL21 in the patent application 2014102431488.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for ferment production of arachidonic acid grease with low-content nervonic acid and EPA
InactiveCN101153298BIncrease production capacityIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesNervonic acidMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method for producing arachidonic acid oil (AA oil) low in nervonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). The method provided by the invention adopts the mortierella isabelina as the original strain, which undergoes strain activation, preparation of the strain in a shake bottle, and fermentation, then the bacteria are harvested, and the AA oil low in nervonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid is extracted from the bacterium. With the eicosapentaenoic acid as the original strain for fermentation, the capability of oil production can be improved for 1-3 times, the yield of AA can be raised for 1-3 times; the invention has the simple fermentation condition with controllable process, and capability to produce the mixed oil of AA with high quality which is low in nervonic acid and EPA.
Owner:武汉麦可得生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com