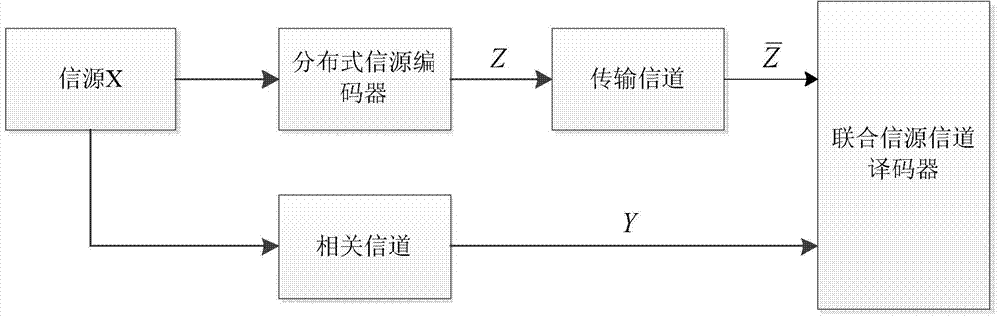
Method for designing LDPCA codes in asymmetric structure distributed source coding system
A distributed source, asymmetric structure technology, applied in the field of source coding, can solve the problem of no rate adaptation and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
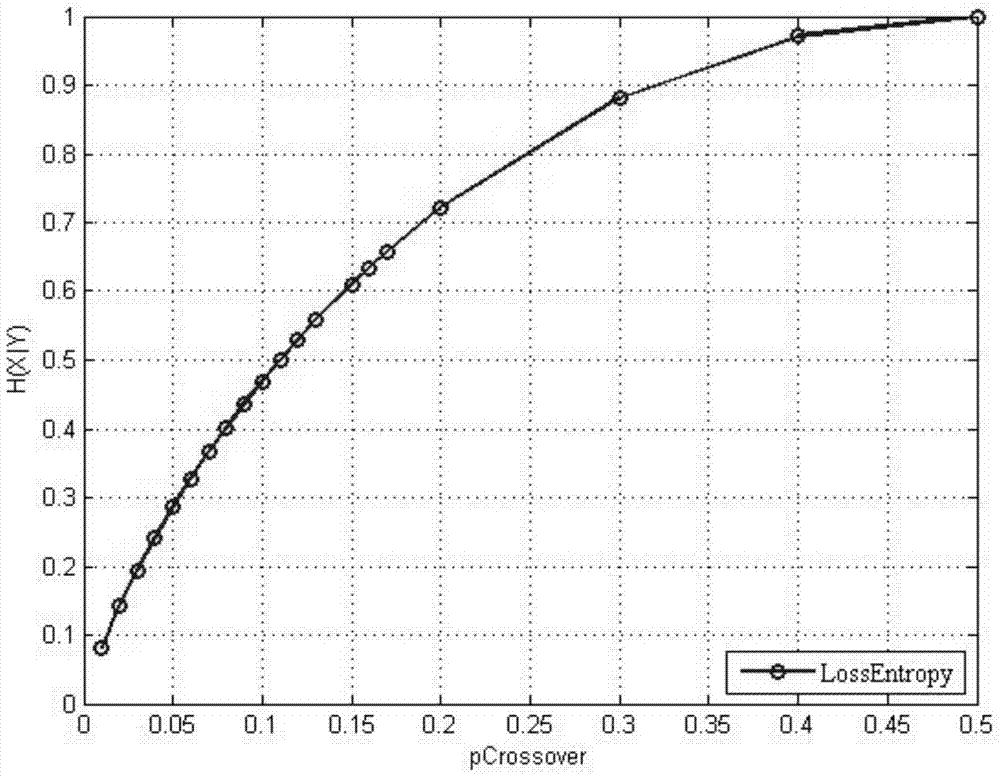
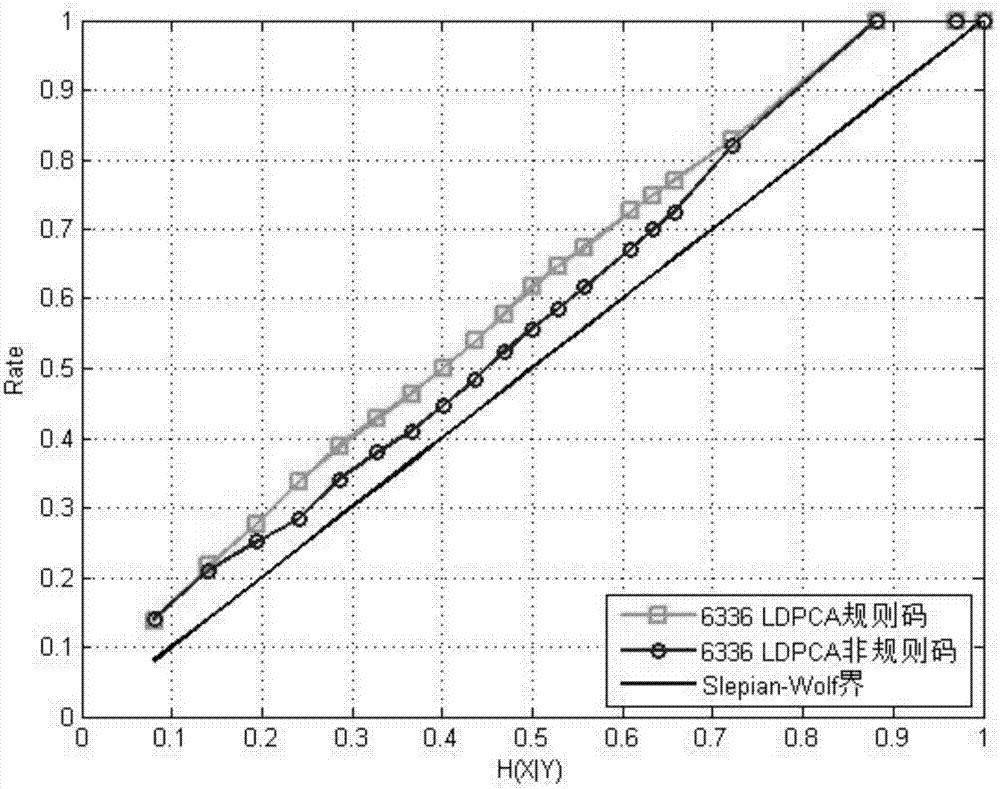
[0065] The channel in this embodiment adopts BSC channel, pCrossover is from 0 to 0.5; the code length is designed to be 6336; the variable node degree of the regular code is 3; the degree distribution characteristics of the irregular code are given in the corresponding table below. This part simulates the performance of LDPCA under different code lengths, degree distributions, and different statistical conditions between source and side information. All LDPC bipartite graph construction methods used here: first construct the bipartite graph with the highest compression rate, and other The factor graph is obtained by consecutively partitioning the syndrome nodes into pairs. It is assumed that the decoder can fully detect the distortion-free recovery of the source. The simulation results also show that under the premise that the received codeword is generated independently of the function that generates the source, if the received cumulative syndrome has the same length as the ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2: Under the condition of asymmetric structured distributed source coding, we simulated the LDPCA coding method. The non-regular traditional LDPCA with variable node degree distribution from 2 to 21 is the most comparable. In the simulation results, the code length n is set to 6336. The number L of different compression ratios of the LDPCA code is 66, and the compression ratios range from 65 / 66 to 0. Therefore, each step of compression transmits 96 symbols. In the proposed method, the compression rate from 1 / L to k / L still adopts the original LDPCA code, and the compression rate from (k+1) / L to 1 adopts the proposed method. After removing the maximum degree of variable nodes, the redesigned optimal degree distribution characteristics are as follows:
[0080] λ(x)=0.3264x+0.4254x 2 +0.1384x 6 +0.0794x 7 +0.0304x 18 (6)
[0081] In all simulations, the decoding side adopts the BP decoding method, and the maximum number of iterations is 100.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com