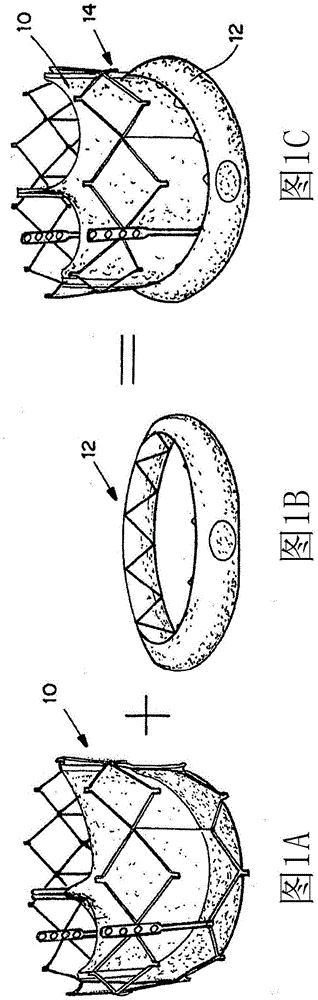
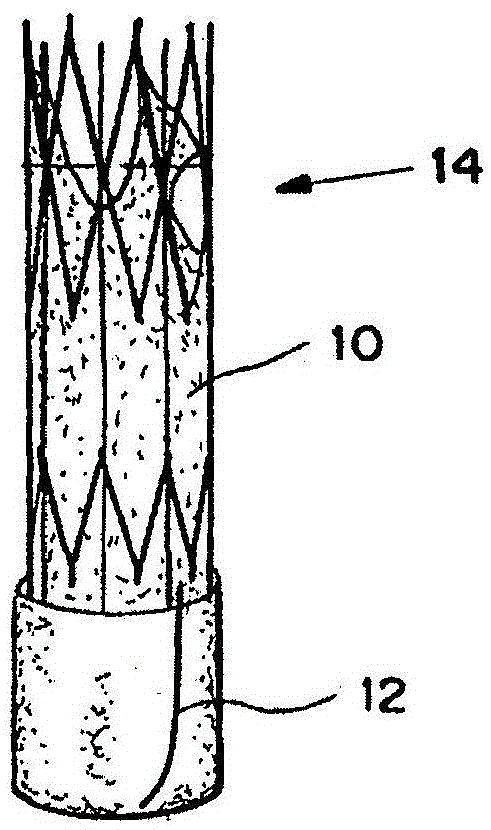
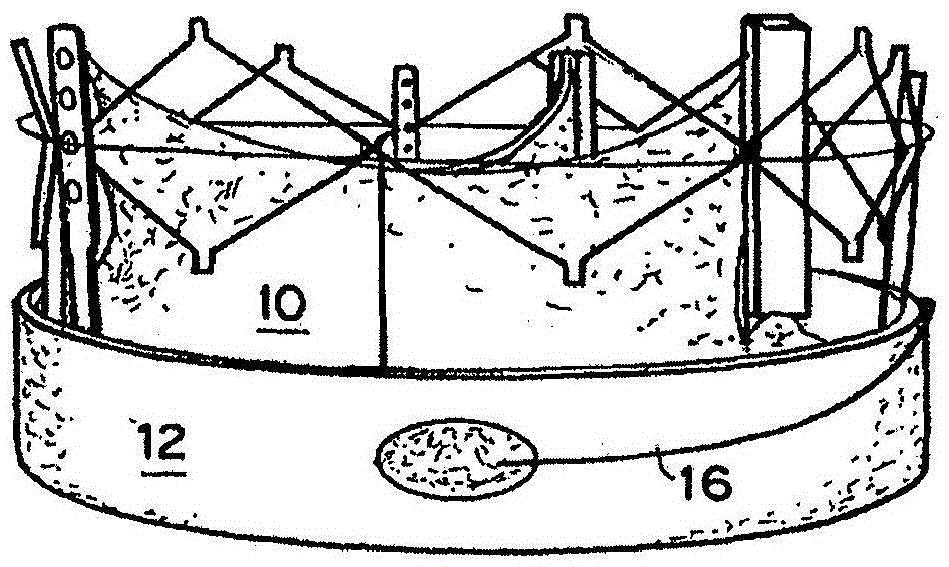
Components for controlled sealing of intravascular devices
A technology of intracavity seals and seals, which can be applied to devices, blood vessels, and applications of tubular structures in the human body, and can solve problems such as mechanical constraints that are difficult to achieve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0204] Example 1: Preparation of Rapidly Swelling Hydrogels
[0205] Studies were performed to identify hydrogels that swelled substantially over a short period of time. The main factors affecting the swelling of polymerized and crosslinked hydrogels based on synthetic monomers are:
[0206] monomer type
[0207] Type of crosslinker
[0208] Concentration of monomer and crosslinker in the gel
[0209] Monomer to Crosslinker Ratio
[0210] Acrylic polymers are capable of rapid swelling and are considered to be well biocompatible. The polymers can be crosslinked to form hydrogels using a variety of commercially available crosslinking agents. These crosslinkers include bisacrylamide, di(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, and poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (MW 500 Da).
[0211] Materials and methods
[0212] Studies were performed to identify the appropriate combination of acrylic acid concentration, type of crosslinker, concentration of crosslinker, and ratio of monomer to c...
example 2
[0231] Example 2: Evaluation of Alternative Crosslinkers for Hydrogels
[0232] The rationale behind the chosen crosslinker is that instead of short crosslinkers with only two polymerizable groups, polyvalent crosslinkers (i.e. long-chain hydrophilic polymeric groups with multiple polymerizable groups) are used. things). Hydrogels that are much stronger than short-chain divalent crosslinkers are obtained. Although these gels are extremely firm, they have very good swelling characteristics. Extremely strong gels usually don't swell very well.
[0233] Derivatization of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with allyl glycidyl ether under alkaline conditions. Gels were prepared by combining acrylic acid with a PVA-based crosslinker followed by polymerizing the mixture by free-radical polymerization using ammonium persulfate and TEMED as initiators.
[0234] In principle, crosslinkers can be made from many different starting materials: a range of PVA as well as partially hydrolyzed polyvin...
example 3
[0245] Example 3: Demonstration of sealing in an in vitro model
[0246] Materials and methods
[0247] Figures 15A-15B The in vitro model of TAV implantation shown in was constructed using a tube in which a TAV formed from a detachable mesh 102 securing the heart valve leaflets 104 is placed. In the model, the mesh 102 is not evenly fixed into the tube, creating a paravalvular leak site 106 between the area of the mesh 102 and the tube 100 .
[0248] TAV includes as above see Figures 2A-2C The expandable seals described. The seal 12 expands by exposing the seal 12 to the surrounding fluid (blood) using the thread 16, causing the hydrogel to expand and compress the seal 12 against the inside of the tube 100, causing the seal 12 to seal the perivalvular membrane Leakage site 108.
[0249] result
[0250] Figure 15A A paravalvular leak site 106 due to improper device placement is shown. Figure 15B Sealing of the leak site with the sealing bladder 108 is shown w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com