A kind of anti-pilling polyester staple fiber
A technology of pilling polyamide ester and polyamide ester, which is applied in the direction of single-component polyamide rayon, fiber treatment, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., and can solve the problems of macromolecular breakage, low temperature, and different ratios
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
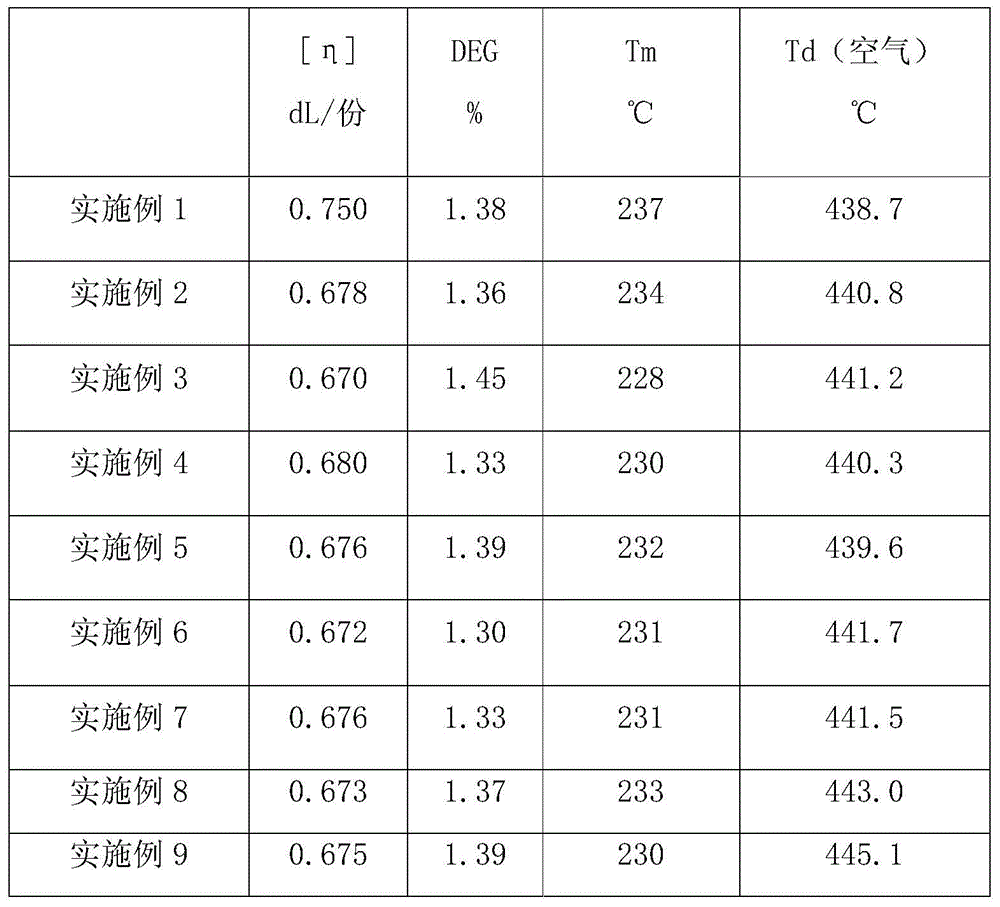
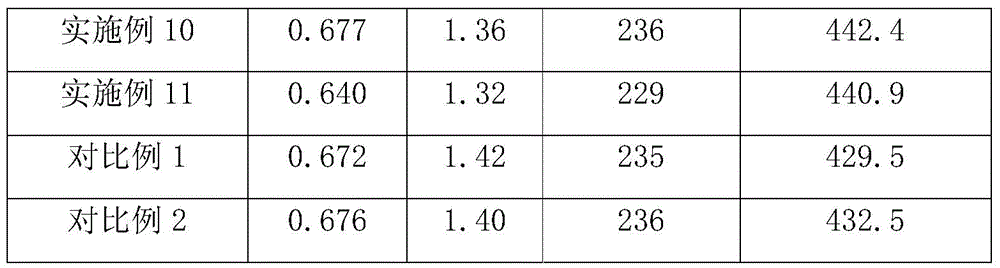
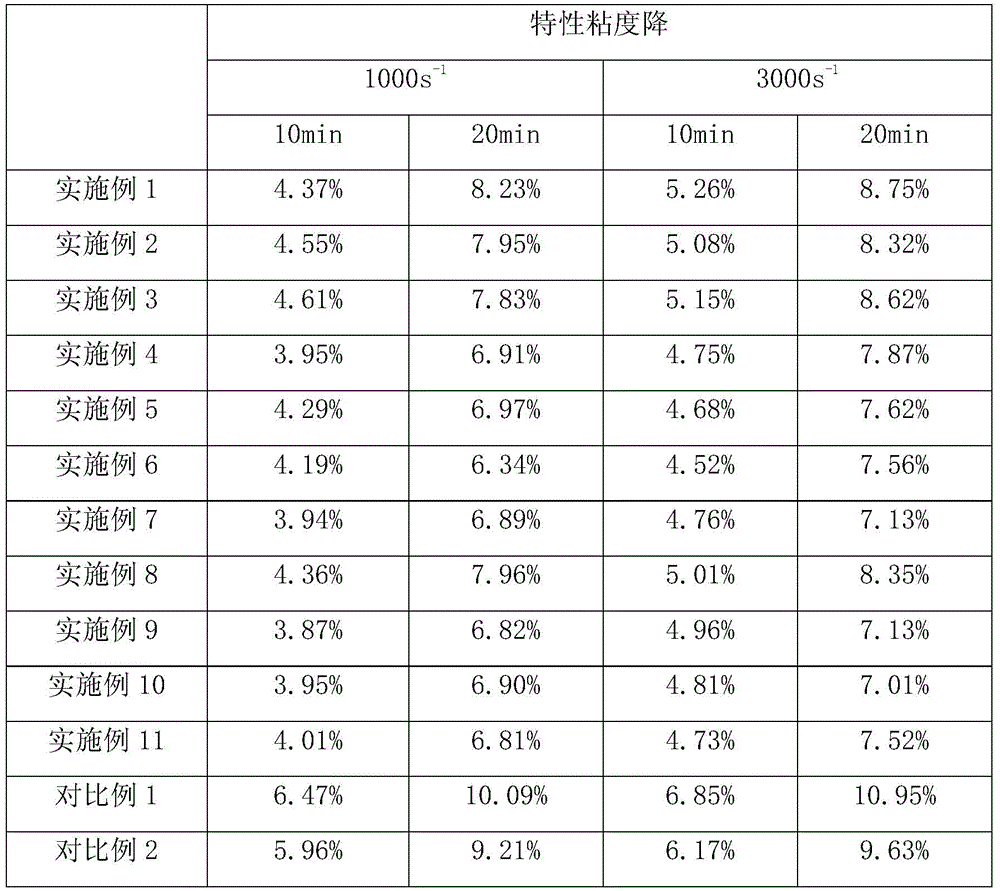
[0019] Put 100 parts of terephthalic acid, 60 parts of ethylene glycol, and 0.05 parts of antimony triacetate into a stainless steel reactor, control the reaction temperature at 235°C, and the reaction pressure at 0.25 MPa, and carry out the esterification reaction for 2 hours; after the reaction, put in PA630 with a relative viscosity of 2.0 share, 0.57 parts of L11, 0.38 parts of trimethyl phosphite, stirred for 10 minutes, then the temperature was set to 260°C, the pressure was gradually reduced to 50 Pa within 45 minutes, and the reaction was continued for 105 minutes to obtain the modified polyesteramide.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Put 100 parts of terephthalic acid, 50 parts of ethylene glycol, and 0.05 parts of antimony triacetate into a stainless steel reactor, control the reaction temperature at 265°C, and the reaction pressure at 0.2 MPa, and carry out the esterification reaction for 2 hours; after the reaction, put in PA1110 with a relative viscosity of 2.1 part, DH201-4600.5 part and stirred for 60min, then the temperature was set to 265°C, the pressure was gradually reduced to 300Pa within 50min, and the reaction was continued for 95min to obtain the modified polyesteramide.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Put 100 parts of terephthalic acid, 60 parts of ethylene glycol, and 0.05 parts of antimony triacetate into a stainless steel reactor, control the reaction temperature at 235°C, and the reaction pressure at 0.25 MPa, and carry out esterification reaction for 1 hour; after the reaction, put in PA620 with a relative viscosity of 2.2 share, 10.18 parts of H16, 0.09 parts of phosphorous acid, stirred for 10 minutes, then the temperature was set to 260 ° C, the pressure was gradually reduced to 50 Pa within 45 minutes, and the reaction was continued for 106 minutes to obtain the modified polyesteramide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| number of curls | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com