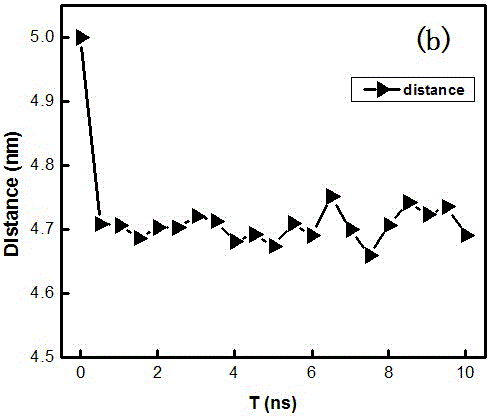
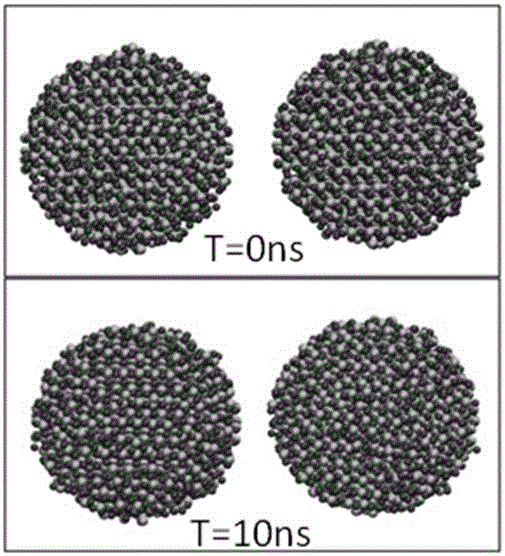
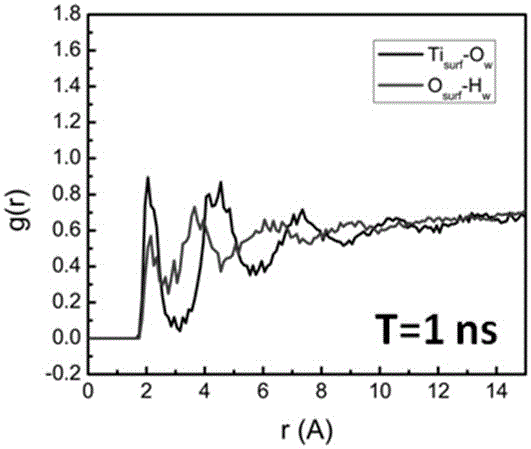
A computer-based method for simulating interfacial interactions of nanomaterials aggregated in aqueous environments
A technology of interaction energy and water environment, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to meet the requirements of microscopic characteristics and dynamic changes of nanoscale material surfaces, and achieve accurate and reliable research results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific implementation mode 1: This implementation mode uses LAMMPS computing software (http: / / lammps.sandia.gov / ), VMD (http: / / www.ks.uiuc.edu / Research / vmd / ) and OVITO (http: / / www.ovito.org / ) analysis software simulates the interfacial interaction of nanomaterials aggregated in the water environment on the computing server, mainly including the following aspects:
[0023] 1. Construct a geometric model of the nanomaterial interface in the water environment and give it physical meaning;
[0024] 2. Using the energy minimization method to optimize the model to make its structure more realistic and reliable;
[0025] 3. Under the thermodynamic parameters consistent with the real environment, carry out molecular dynamics simulation calculations, and obtain the motion trajectory files and related calculation files of each atom;
[0026] 4. Through the motion trajectory files and related calculation files obtained by simulation, the dynamic characteristics and key functio...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0036] Specific implementation mode two: In this implementation mode, the aggregation of nano-titanium dioxide particles in water is taken as an example, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) Use the Materials Visualizer module of the Materials studio to construct a super-large unit cell of crystal redite titanium dioxide, and cut it into a nanoparticle with a diameter of 4nm, and delete excess titanium or oxygen atoms on the surface to keep the entire particle charge neutral. Hydroxyl groups are added to the surface of the particles, and the number of hydroxyl groups added is different at different pH values.
[0038] (2) Construct a square water box with a side length of 105 Å, place the constructed nano-titanium dioxide particles in the center of the water box, and delete the water molecules overlapping with the nano-titanium dioxide particles and within 3 Å of the surface atoms of the nano-titanium dioxide particles. A certain number of sodium ions, calcium i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com