Agmatine is used for the purposes of preparing medicine for treating post-traumatic immunosuppression
A technology of immune function and agmatine, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of decreased antigen-presenting cell scavenging ability, urgent improvement of curative effect, and exacerbation of the latter.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Corrective effect of agmatine on hypofunction of splenocytes in traumatized mice
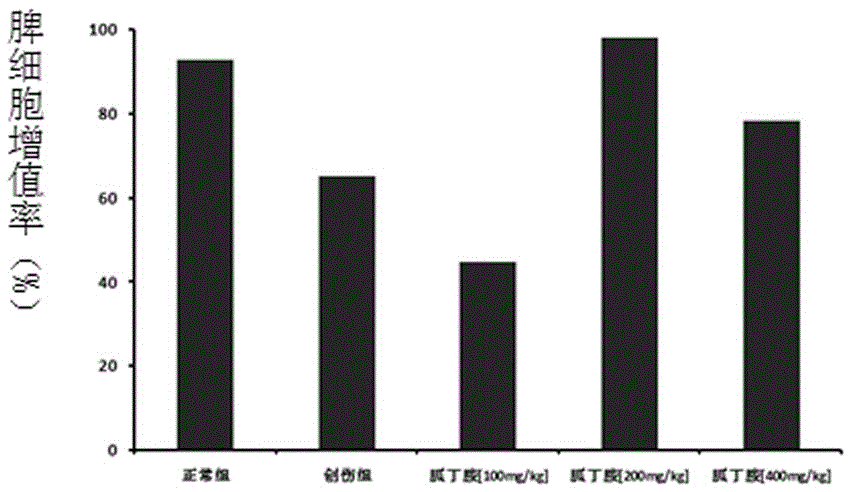
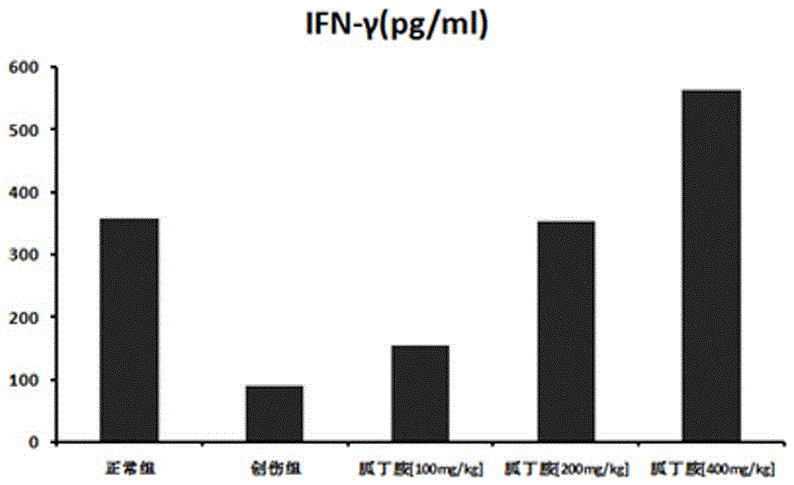
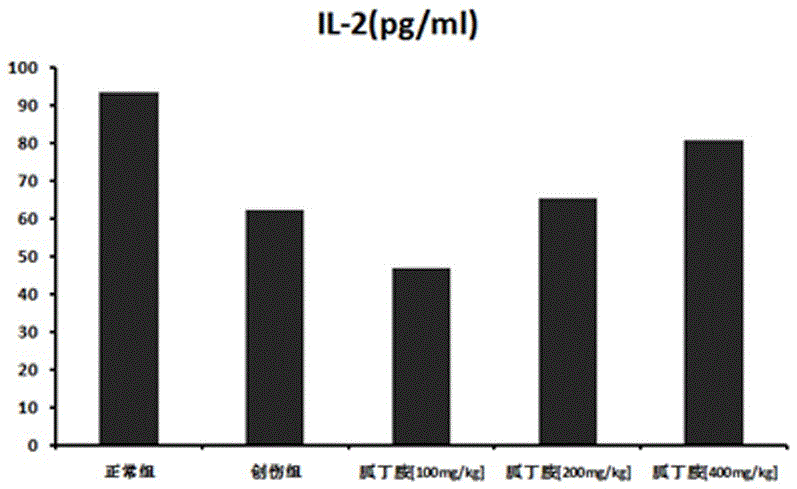
[0029] C57BL / 6 mice were subjected to double hindlimb femur fracture combined with 40% orbital bleeding to construct a severe traumatic blood loss model. Compared with the control group, the immune function of the mice after severe trauma was suppressed, and the proliferation ability of splenocytes was significantly reduced, and the secretion of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) was significantly reduced.
[0030] Agmatine was administered retroperitoneally to severely traumatized mice, and 100mg / kg, 200mg / kg, and 400mg / kg agmatine were given immediately after injury (once a day, the treatment time was 1 day). After treatment, the severe injury was significantly improved. Trauma-induced immunosuppression, manifested in a dose-dependent increase in the ability of splenocytes to proliferate and secrete IFN-γ and IL-2 (see figure 1 ,2).
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Effect of agmatine on secretion function of splenic macrophages and peritoneal macrophages in traumatized mice
[0032] The model preparation and agmatine treatment of traumatized mice were the same as in Example 1.
[0033] Compared with the control group, the secretion of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) in the spleen macrophages and peritoneal macrophages of severely traumatized mice stimulated by endotoxin (LPS) in vitro was significantly reduced , treated with agmatine (100mg / kg, 200mg / kg and 400mg / kg) (once a day for 1 day), after treatment, can significantly up-regulate the secretion of splenic macrophages and peritoneal macrophages in traumatized mice function (see Figure 3, 4).
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 Effect of Agmatine on Mortality of Traumatized Mice After LPS Challenge
[0035] The trauma mouse model is the same as in Example 1. Agmatine (100mg / kg, 200mg / kg and 400mg / kg immediately after injury) was administered retroperitoneally to severely traumatized mice (once a day, the treatment time was 1 day), and LPS challenge was performed 24 hours after injury (LPS 25mg / kg, retroperitoneal injection), and additional agmatine (400mg / kg, retroperitoneal injection) treatment (once a day, the treatment time is 1 day). The results showed that compared with the simple LPS challenge group, severe trauma could significantly increase the mortality of LPS challenge model mice (trauma + LPS vs LPS, 80% vs 20%), and agmatine intervention treatment (100mg / kg , 200mg / kg and 400mg / kg) can dose-dependently reduce the mortality of LPS-challenged mice (40%, 33.33%, 25%, see Figure 5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com