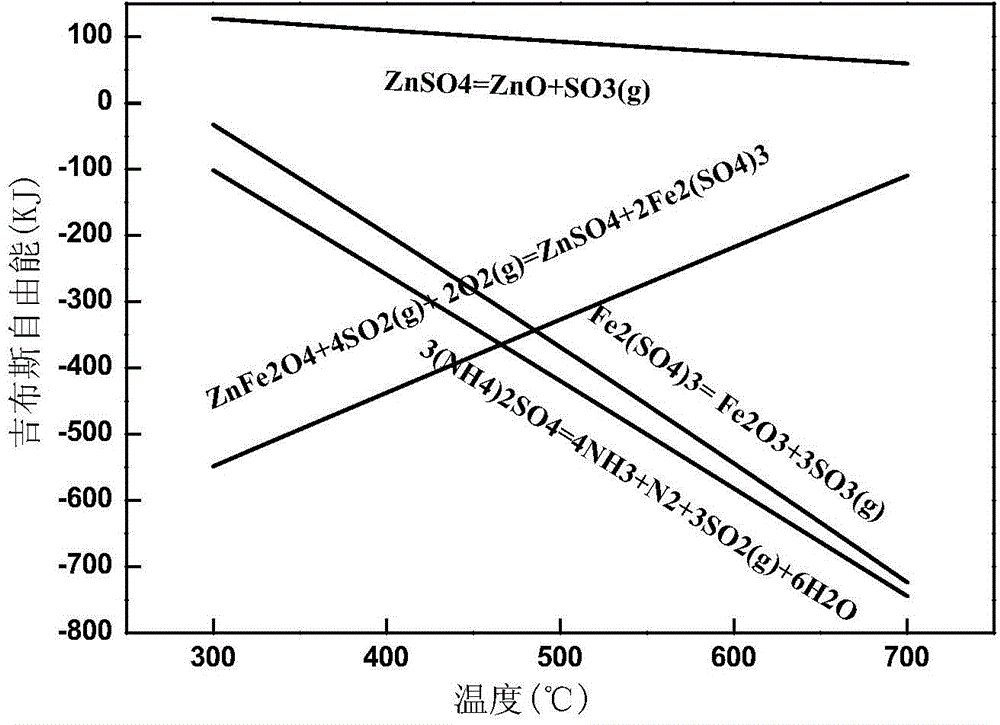
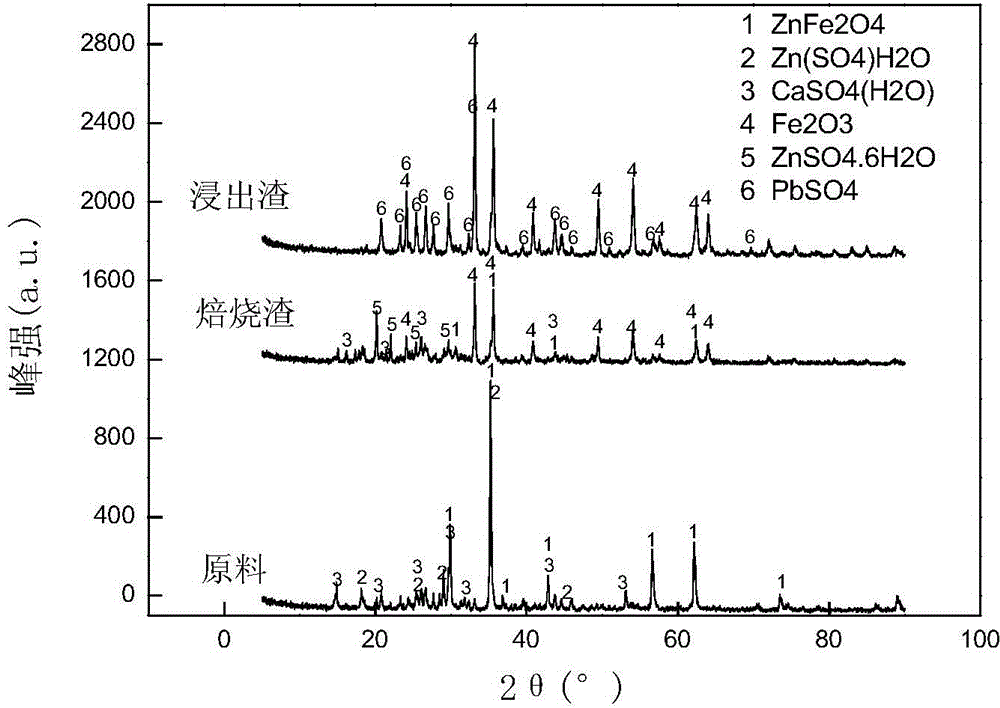
Method for zinc-iron separation by carrying out activated roasting and phase control on zinc ferrite
A zinc ferrite and roasting technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of zinc ferrite decomposition and zinc-iron separation without a good solution, zinc and iron resources cannot be effectively utilized, etc., to achieve roasting The effect of low temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Grind 100g of acid leaching residue containing zinc ferrite to -200 mesh (74um) and account for more than 90%. Total Zinc 64.97%. Add 25g of ammonium sulfate and mix evenly, roast at 400°C for 1h, then raise the temperature of the roaster to 600°C for 30min, take it out and cool.
[0036]The roasted slag is leached with water at room temperature, the pH of the leaching solution is 5, the liquid-solid ratio is 6 / 1, and the leaching time is 15 minutes. After the leaching is completed, it is filtered and separated to obtain zinc-rich liquid and iron-rich slag. The zinc-enriched solution contained 19.7g / L of zinc and 0.31g / L of iron; the leaching rate of zinc was 91.52%, and the leaching rate of iron was 0.8%; the iron-rich slag contained 1.96% of zinc and 42.10% of iron.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Grind 100 g of mixed slag containing zinc ferrite until -200 mesh (74um) accounts for more than 90%. The contents of Zn and Fe in the slag are 14.96% and 23.06% respectively, and the content of zinc ferrite is 5.76%. Add 20g of ammonium sulfate and mix evenly, roast at 400°C for 1h, then raise the temperature of the roaster to 600°C for 30min, take it out and cool.
[0039] The roasted slag is leached with water at room temperature, the pH of the leaching solution is 7, the liquid-solid ratio is 8 / 1, and the leaching time is 15 minutes. After the leaching is completed, it is filtered and separated to obtain zinc-rich liquid and iron-rich slag. The zinc-enriched solution contained 18.05g / L of zinc and 0.24g / L of iron; the leaching rate of zinc was 87.25%, and the leaching rate of iron was 0.57%; the iron-rich slag contained 2.37% of zinc and 48.07% of iron.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Grind 100 g of goethite slag containing zinc ferrite until -200 mesh (74um) accounts for more than 90%. The contents of Zn and Fe in the slag are 9.56% and 35.42%, respectively, and the content of zinc ferrite is 5.52%. Add 30g of ammonium sulfate and mix evenly, roast at 400°C for 1h, then heat up the roasting furnace to 600°C for 30min, take it out and cool.
[0042] The roasted slag is leached with water at room temperature, the pH of the leaching solution is 7, the liquid-solid ratio is 5 / 1, and the leaching time is 20 minutes. After the leaching is completed, it is filtered and separated to obtain zinc-rich liquid and iron-rich slag. The zinc-enriched solution contained 23.51g / L of zinc and 0.46g / L of iron; the leaching rate of zinc was 92.76%, and the leaching rate of iron was 0.81%; the iron-rich slag contained 1.82% of zinc and 57.03% of iron.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com