Antimony-base compound thin film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of solar cells and oxide thin films, applied in circuits, electrical components, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problems of toxic production process, low element content and high price, and achieve the effect of excellent photovoltaic performance and abundant resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
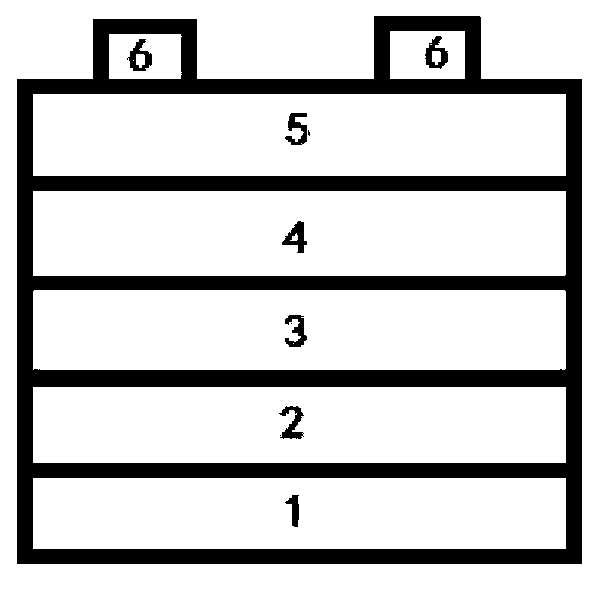
[0047] Embodiment 1, the preparation method of antimony-based compound thin-film solar cells, including the steps of depositing a back electrode layer, depositing a P-type absorber layer, depositing an N-type buffer layer, depositing an oxide film window layer, and depositing a metal gate electrode:
[0048] 1. The step of depositing the back electrode layer: depositing the back electrode layer 2 on the surface of the substrate 1 by magnetron sputtering;
[0049] The substrate is glass with a thickness of 1.8cm;
[0050] The back electrode layer is Mo with a thickness of 800nm;
[0051] 2. The step of depositing a P-type absorbing layer: using a solution coating method to deposit a P-type absorbing layer 3 on the back electrode layer 2;
[0052] The P-type absorption layer material is CuSbS 2 , with a thickness of 1.5 μm;
[0053] Cu:Sb:S was dissolved in hydrazine at a ratio of 1:1:7 by solution coating method to form CuSbS 2 precursor, CuSbS was coated with a film coater...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2, the preparation method of antimony-based compound thin-film solar cells, including the steps of depositing a back electrode layer, depositing a P-type absorber layer, depositing an N-type buffer layer, depositing an oxide film window layer, and depositing a metal gate electrode:
[0064] 1. The step of depositing the back electrode layer: depositing the back electrode layer 2 on the surface of the substrate 1 by magnetron sputtering;
[0065] The substrate is glass with a thickness of 3cm;
[0066] The back electrode layer is SnO 2 : F; the thickness is 1000nm;
[0067] 2. The step of depositing a P-type absorbing layer: using a solution coating method to deposit a P-type absorbing layer 3 on the back electrode layer 2;
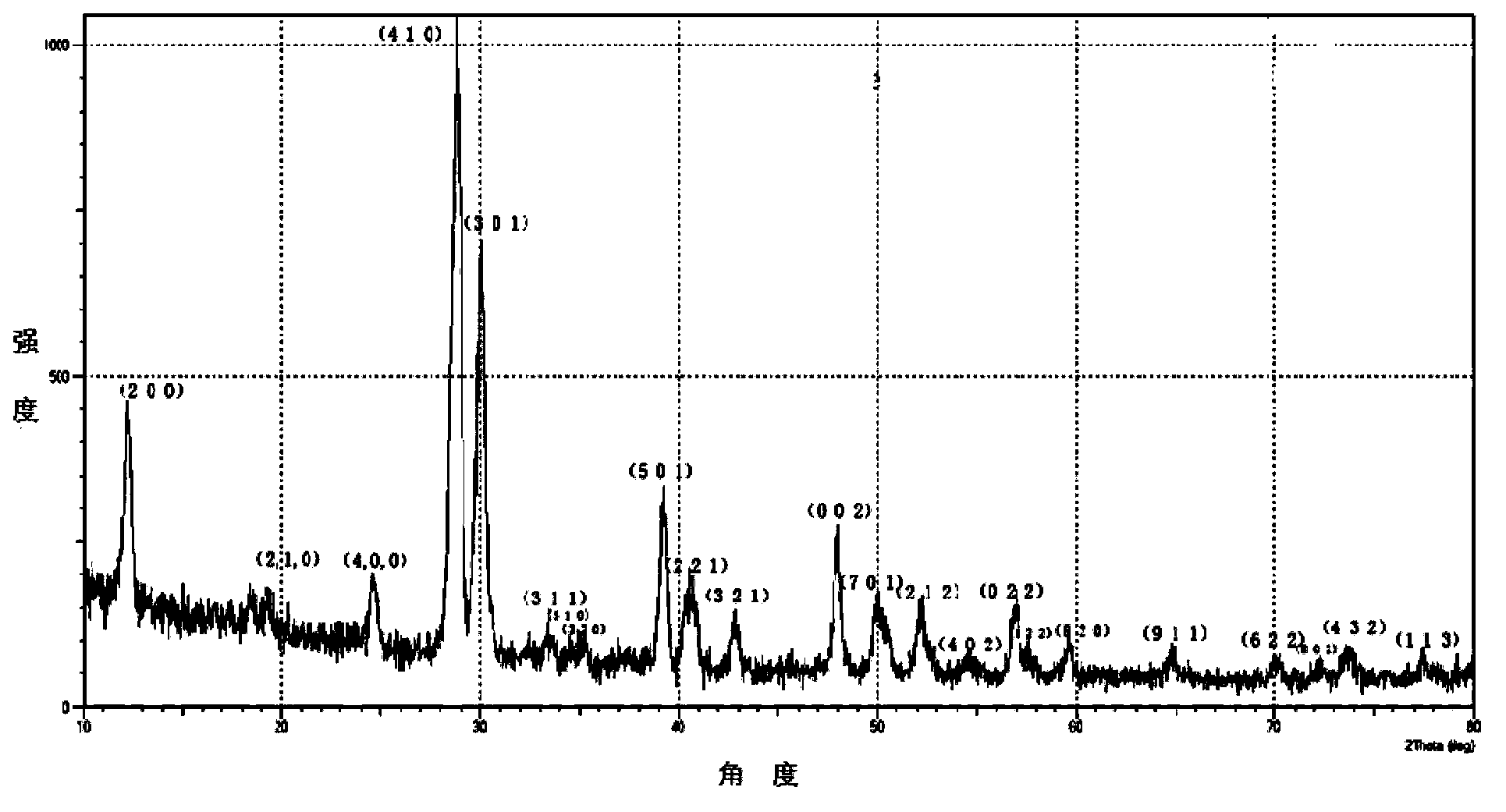
[0068] The P-type absorption layer material is CuSbS 2 , with a thickness of 1.5 μm; the surface morphology under the scanning electron microscope is as follows Figure 7 Shown; cyclic voltammetry curve as Figure 8 Shown; Raman spec...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3, the preparation method of antimony-based compound thin-film solar cells, including the steps of depositing a back electrode layer, depositing a P-type absorber layer, depositing an N-type buffer layer, depositing an oxide film window layer, and depositing a metal gate electrode:
[0077] 1. The step of depositing the back electrode layer: depositing the back electrode layer 2 on the surface of the substrate 1 by magnetron sputtering;
[0078] The substrate is polyimide with a thickness of 0.01cm;
[0079] The back electrode layer is In 2 o 3 :Sn; thickness is 100nm;
[0080] 2. The step of depositing a P-type absorbing layer: using a thermal evaporation method to deposit a P-type absorbing layer 3 on the back electrode layer 2;
[0081] The P-type absorption layer material is CuSbS 2 , with a thickness of 0.8 μm;
[0082] 3. The step of depositing an N-type buffer layer: using a chemical water bath method to deposit an N-type buffer layer 4 on the P-typ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com