Method for repairing thorium (IV)-polluted water body by employing facultative marine fungi living body
A marine fungus and water body technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve low cost, easy management, and no secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
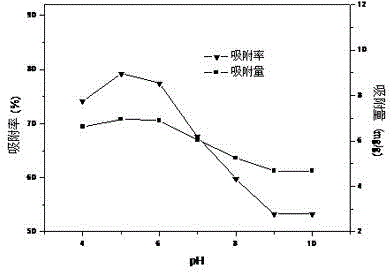
[0031] To the 7 groups with pH values of 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, and 10.0, the amount of thorium (Ⅳ) contained was 50 mg L -1 3.0 g of fungal active mycelia were added to 50 mL of water, and the content of thorium (IV) in the water was detected for 8 hours. figure 1 . It can be seen from the figure that when the pH value is 4-8, the adsorption rate of thorium (IV) by fungi exceeds 60%, and when the pH value is 5.0, the removal rate and adsorption capacity of thorium (IV) reach the maximum. 79.24% and 6.96 mg g respectively -1 , the removal effect is better.
Embodiment 2
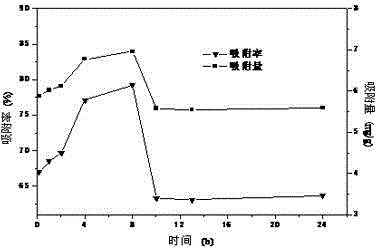
[0033] To 8 groups of pH 5.0 containing thorium (IV) amount is 50 mg L -1 3.0 g of fungal active mycelia were put into 50 mL of water, and at 0.25, 1, 2, 4, 8, 10, 13, and 24 h, the content of thorium (Ⅳ) in the water, and the adsorption of thorium (Ⅳ) The relationship between the rate and adsorption capacity with time is shown in the appendix figure 2 . When the feeding time is 8 h, the removal rate of thorium (IV) is the highest, close to 80%, and the removal effect is better.
Embodiment 3
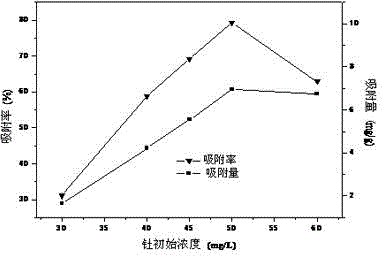
[0035] To 5 groups of pH 5.0 containing different initial concentrations of thorium (Ⅳ) (30, 40, 45, 50, 60 mg L -1 ) into 50 mL of water, and 3.0 g of fungal active mycelia were put into the water body. After 8 hours, the content of thorium (IV) in the water was detected, and the adsorption rate and adsorption capacity of thorium (IV) changed with the initial concentration of thorium (IV). see attachment image 3 . When the initial concentration of thorium(IV) is 50 mg L -1 When , the removal rate of thorium (Ⅳ) is the largest, close to 80%, and the removal effect is better.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com