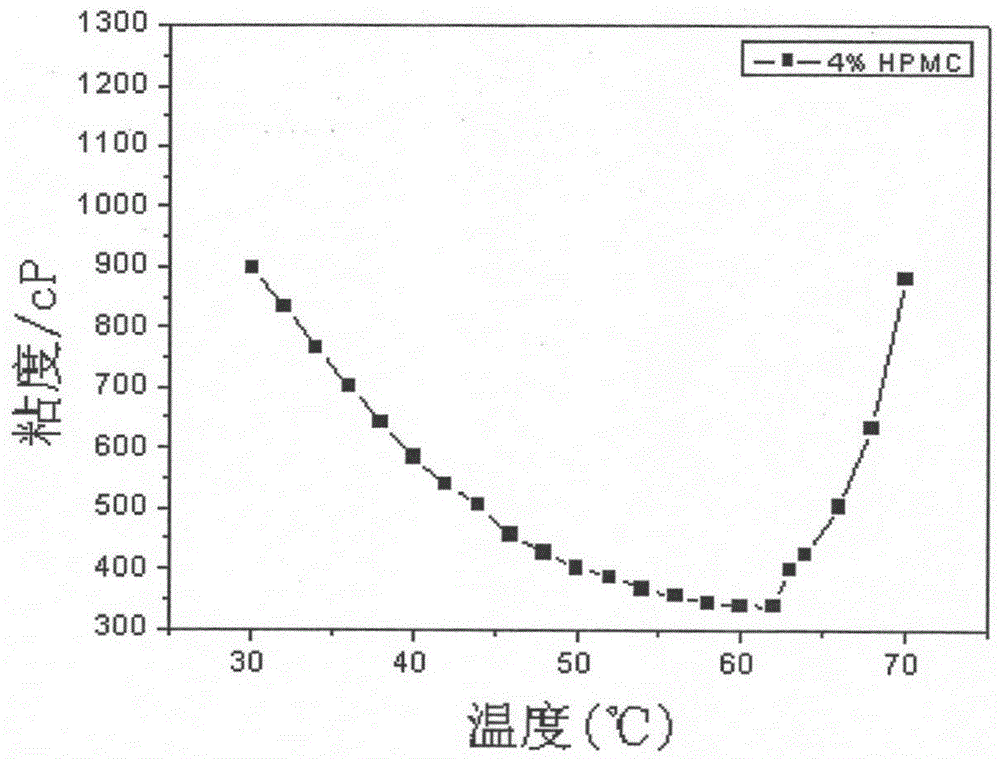
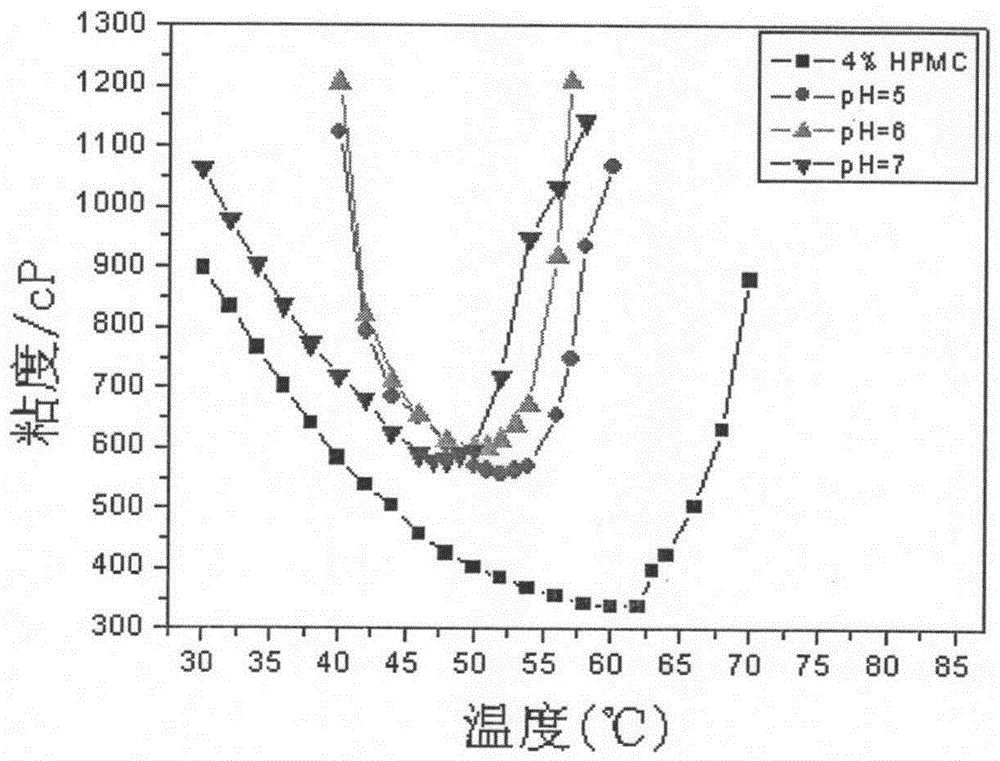
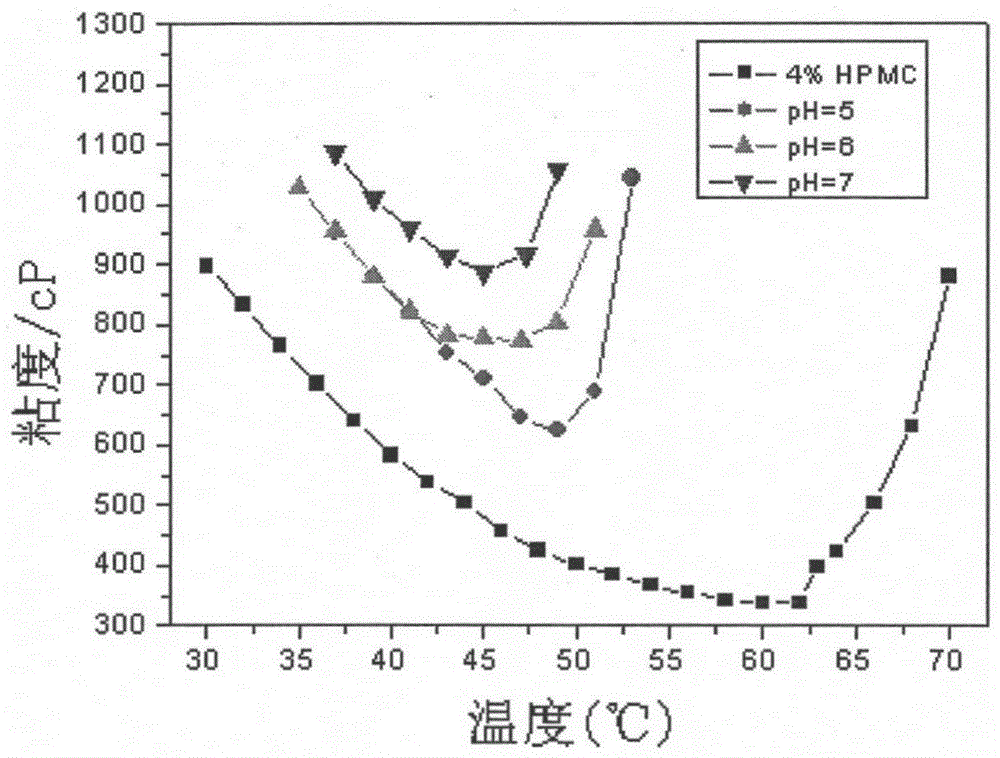
A method for adjusting the viscosity of natural heat-sensitive polymer aqueous solution
An aqueous solution viscosity and heat-sensitivity technology, applied in the field of adjusting the viscosity of natural heat-sensitive polymer aqueous solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0024] (1) Dissolve 18.00g of HPMC powder in 282.00g of deionized water at room temperature, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 3 to 6 days, and prepare a solution with a mass fraction of HPMC of 6% for subsequent use; dissolve 12.00g of HPMC powder in 288.00 g deionized water, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 3 to 6 days, and prepare a solution with a mass fraction of HPMC of 4% for testing;
[0025] (2) Weigh 6.48g of AA, add deionized water to 50.00g, stir well, and prepare 1.8mol / L AA solution.
[0026] (3) Weigh 10.00 g of the AA solution in 3 parts (2), adjust the pH to 5, 6, and 7 with NaOH solution, and dilute to 20.00 g with deionized water.
[0027] (4) Take by weighing 10.00g of the solution in (3), and 20.00g of the 6% HPMC solution in (1), and stir evenly to make a mixed solution. In this mixed solution, the concentration of MAA is 0.3mol / L, and the mass fraction of HPMC is 4 %, pH 5, 6, 7, respectively, for te...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Dissolve 18.00g of HPMC powder in 282.00g of deionized water at room temperature, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 3 to 6 days, and prepare a solution with a mass fraction of HPMC of 6% for subsequent use; dissolve 12.00g of HPMC powder in 288.00 g deionized water, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 3 to 6 days, and prepare a solution with a mass fraction of HPMC of 4% for testing;
[0031] (2) Weigh 12.91g of MAA, add deionized water to 50.00g, stir well, and prepare 3mol / L MAA solution.
[0032] (3) Weigh 10.00 g of the MAA solution in 3 parts of (2), adjust the pH to 5, 6, and 7 with NaOH solution, and adjust the pH to 20.00 g with deionized water.
[0033] (4) Take by weighing 10.00g of solution in (3) and 20.00g of 6% HPMC solution in (1) respectively, stir well, and make mixed solution, MAA concentration is 0.5mol / L in this mixed solution, and HPMC mass fraction is 4 %, pH 5, 6, 7, respectively, for testing.
[0034] (5) Use Brookfield viscometer to carry out ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Dissolve 18.00g of HPMC powder in 282.00g of deionized water at room temperature, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 3 to 6 days, and prepare a solution with a mass fraction of HPMC of 6% for subsequent use; dissolve 12.00g of HPMC powder in 288.00 g deionized water, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 3 to 6 days, and prepare a solution with a mass fraction of HPMC of 4% for testing;
[0037] (2) Weigh 6.30 g of citric acid monohydrate, add deionized water to 50.00 g, and prepare a 0.6 mol / L CA solution.
[0038] (3) Weigh 10.00 g of the CA solution in 3 parts (2), adjust the pH to 5, 6, and 7 with NaOH solution, and dilute to 20.00 g with deionized water.
[0039] (4) Take by weighing 10.00g of the solution in (3) and 20.00g of the 6% HPMC solution in (1) respectively, and stir evenly to prepare a mixed solution. In this mixed solution, the CA concentration is 0.1mol / L, and the HPMC mass fraction is 4 %, pH 5, 6, 7, respectively, for testing.
[0040] (5) Use Brookfiel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com