Function identification of antimony oxidase gene sboA in agrobacterium tumefaciens
A technology of antimony oxidase and Agrobacterium, which is applied in the field of functional identification of antimony oxidase gene in Agrobacterium tumefaciens GW4, can solve the problem that no specific antimony oxidase functional gene has been found in research, and achieve the effect of good material circulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: sboA gene knockout, complementation and over-standard experiment
[0034] 1. Knockout vector construction
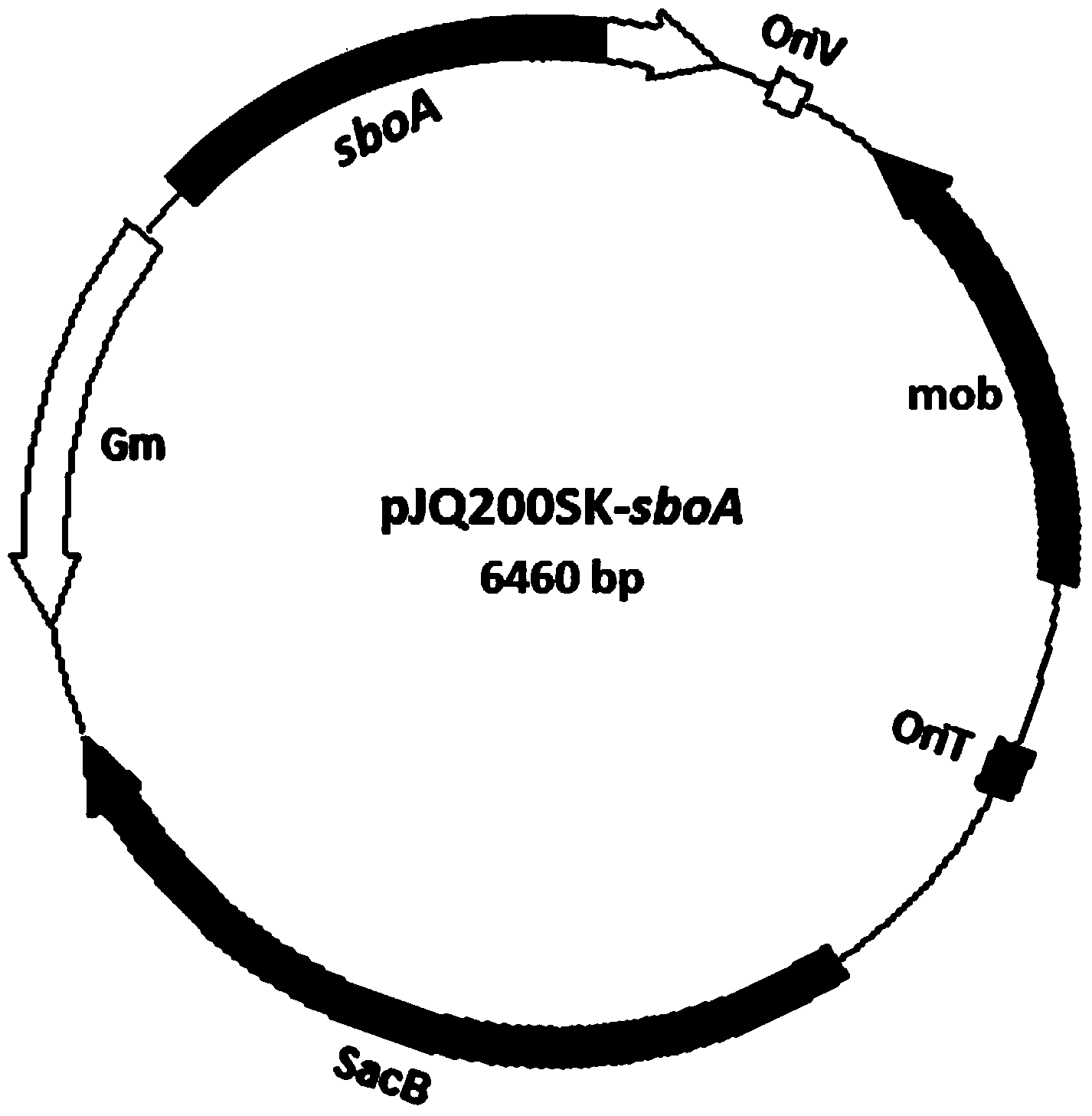
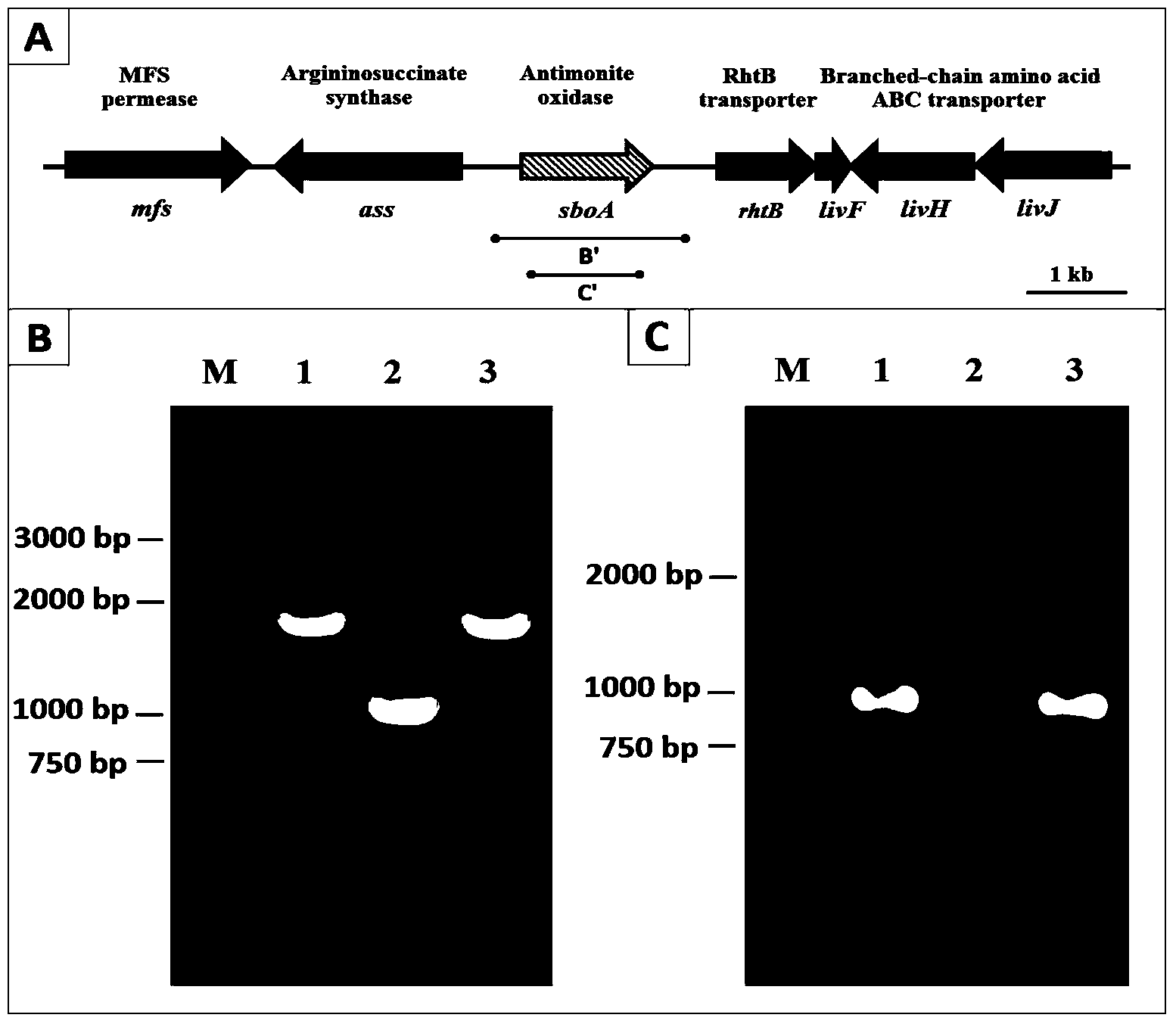
[0035] This embodiment adopts pJQ200SK (see figure 1 , Montana State University, USA, Professor Timothy R. McDermott (Professor Timothy R. McDermott) donated)) knockout vector for seamless knockout of sboA gene. The knockout vector construction process is as follows: According to the sboA gene sequence in the strain GW4, primers PsboA-1F and PsboA-1R with upstream homologous fragments of BamHI and XbaI restriction sites and primers PsboA-2F and PsboA with downstream homologous fragments were designed -2R. Then configure the PCR system: 5 μL 10×PCR buffer, 1 μL dNTPs, 1 μL each of the left and right primers, 2 μL DNA template, 0.5 μL Taq DNA polymerase, and finally add water to 50 μL. PCR program: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, denaturation at 95°C for 45 sec, annealing at 50°C for 45 sec, extension at 72°C for 30 sec, and finally extension at 72...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Growth and antimony oxidation experiments of wild strain GW4, sboA mutant strain (GW4-ΔsboA), sboA complementation strain (GW4-ΔsboA-C) and sboA overexpression strain (GW4::sboA)
[0047] Single clones of wild-type GW4, sboA mutant strain GW4-ΔsboA, sboA complementation strain GW4-ΔsboA-C and overexpression strain GW4::sboA were picked and inoculated in 5 mL of CDM medium respectively, and cultured with shaking at 28°C for 24 hours. Take 100 μL of fresh bacteria solution and inoculate them into 100 mL CDM medium containing 10 μmol / L Sb(III) and 50 μmol / L Sb(III). The culture was shaken on a shaker at 28°C, and the condition without Sb(III) was used as a control.
[0048] According to the growth status of the strain, take a sample every 8h for the determination of OD 600(absorbance value at 600nm wavelength place, DU800 type spectrophotometer) and the content of different forms of antimony in the culture medium. The content of antimony in the medium was dete...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Overexpression of SboA in Escherichia coli E.coli S17-1 and identification of antimony oxidation
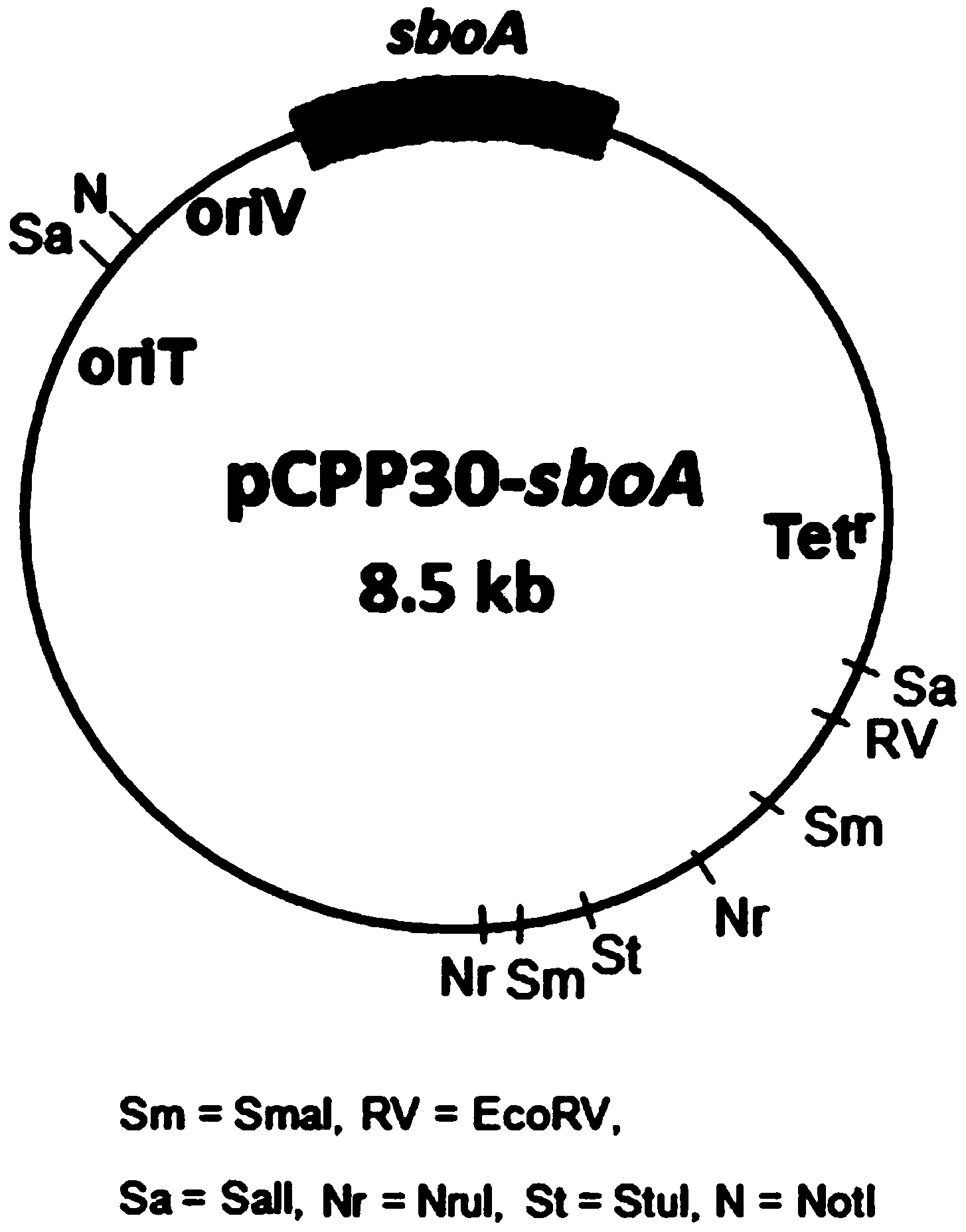
[0051] The complementary vector pCPP30-sboA in Example 1 was transformed into E. coli S17-1 without sboA gene, so that it could be expressed heterologously in E. coli. The wild-type E.coli S17-1 and E.coli S17-1 (pCPP30) transformed into pCPP30 were used as controls to detect the Sb(III) oxidation phenotype.
[0052] The activated bacterial strain S17-1 (pCPP30-sboA), S17-1 (pCPP30) and S17-1 were inoculated in LB medium for expanded culture, then low-speed centrifugation (5000rpm) was used to collect the thalline and washed with 50mM Tris-HCl (pH =8.0) and washed twice. Then inoculate in the CDM medium containing 0.02% yeast powder and 10 μ M Sb (III) and adjust the amount of bacteria to make the initial OD 600 Reached around 0.5. Place in a shaker at 37°C for incubation. Take samples at 0.5h, 1h, 1.5h and 2h to measure OD 600 and antimony content in diffe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com