Permanent magnet speed controller with fixed magnetic gap
A technology of permanent magnet governor and fixed magnet, which is applied in the direction of controlling electromechanical brakes, electric brakes/clutches, electrical components, etc. It can solve the problems of high power consumption, poor torque transmission capacity, and waste of rare earth resources in magnetic circuit regulators. Achieve the effects of saving installation space, improving torque transmission capacity, and saving rare earth materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
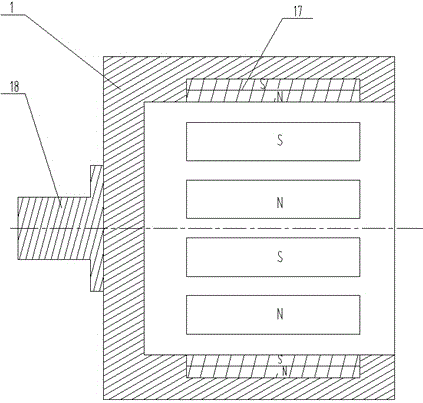
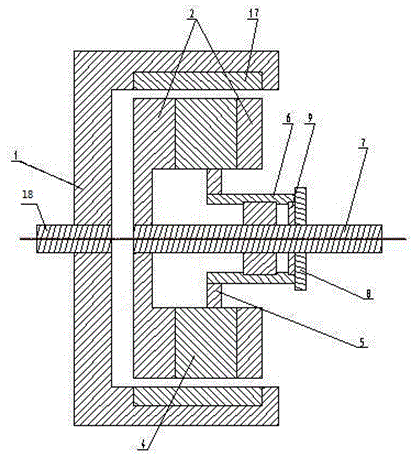
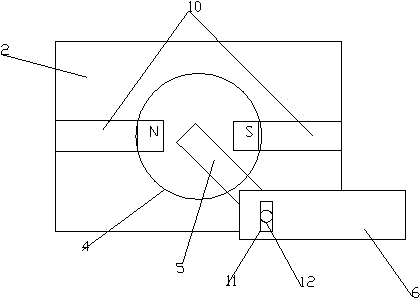
[0033] A permanent magnet governor with a fixed magnetic gap, such as figure 1 , 2As shown in . Magnets 17, the magnetic poles of the outer permanent magnets 17 are radially arranged, and the magnetic pole surfaces of the two adjacent outer permanent magnets 17 are different in magnetism; the inner magnetic rotor is distributed along its outer circumferential surface with at least one rotatable The permanent magnet 4, the rotatable permanent magnet 4 is perpendicular to the driven shaft 7. The rotatable permanent magnet 4 is cylindrical and has an N pole and an S pole along the diameter direction. The two sides of the rotatable permanent magnet 4 are wrapped with a magnetizer 2, and the two magnetizers 2 are separated by a non-magnetizer 10; In this embodiment, the number of magnets of the outer permanent magnet 17 is equal to the number of magnetic poles of the rotatable permanent magnet 4 . One end of the rotatable permanent magnet 4 is provided with a magnetic circuit re...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A permanent magnet governor with a fixed magnetic gap, such as figure 1 , 4 , 5, the rotatable permanent magnet 4 is parallel to the driven shaft 7, and other structures are the same as the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0037] A permanent magnet governor with a fixed magnetic gap, such as figure 1 , 6 As shown in . Magnets 17, the magnetic poles of the outer permanent magnets 17 are radially arranged, and the magnetic pole surfaces of the two adjacent outer permanent magnets 17 are different in magnetism; the inner magnetic rotor is distributed along its outer circumferential surface with at least one rotatable The permanent magnet 4, the rotatable permanent magnet 4 is perpendicular to the driven shaft 7. The rotatable permanent magnet 4 is cylindrical and has an N pole and an S pole along the diameter direction. The two sides of the rotatable permanent magnet 4 are wrapped with a magnetizer 2, and the two magnetizers 2 are separated by a non-magnetizer 10; Two rotatable permanent magnets 4 are provided with a fixed permanent magnet 3 side by side along the axial direction of the driven shaft 7. The fixed permanent magnet 3 is cylindrical and has N poles and S poles along the diameter dire...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com