Upstream resource distribution method capable of considering both throughput capacity and fairness in TD-LTE-Advanced (Time Division-Long Term Evolution-Advanced) relay system
A technology of resource allocation and relay system, applied in electrical components, wireless communication and other directions, can solve problems such as adjacent cell interference, and achieve the effects of increased throughput, large throughput, and high fairness index
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0037] Specific implementation mode one: the uplink resource allocation method in the TD-LTE-Advanced relay system described in this implementation mode, which takes into account both throughput and fairness, includes the following steps:
[0038] Step 1. The base station dynamically allocates frequency resources for the relay and direct transmission users according to the service demands of the direct transmission users and the relay users;
[0039] Step 2. The uplink relay in the uplink subframe of the access link allocates resources for the relay users according to the priority of the proportional fairness algorithm, and at the same time, the base station on the direct transmission link adopts the proportional fairness algorithm to allocate resources for the direct transmission users;
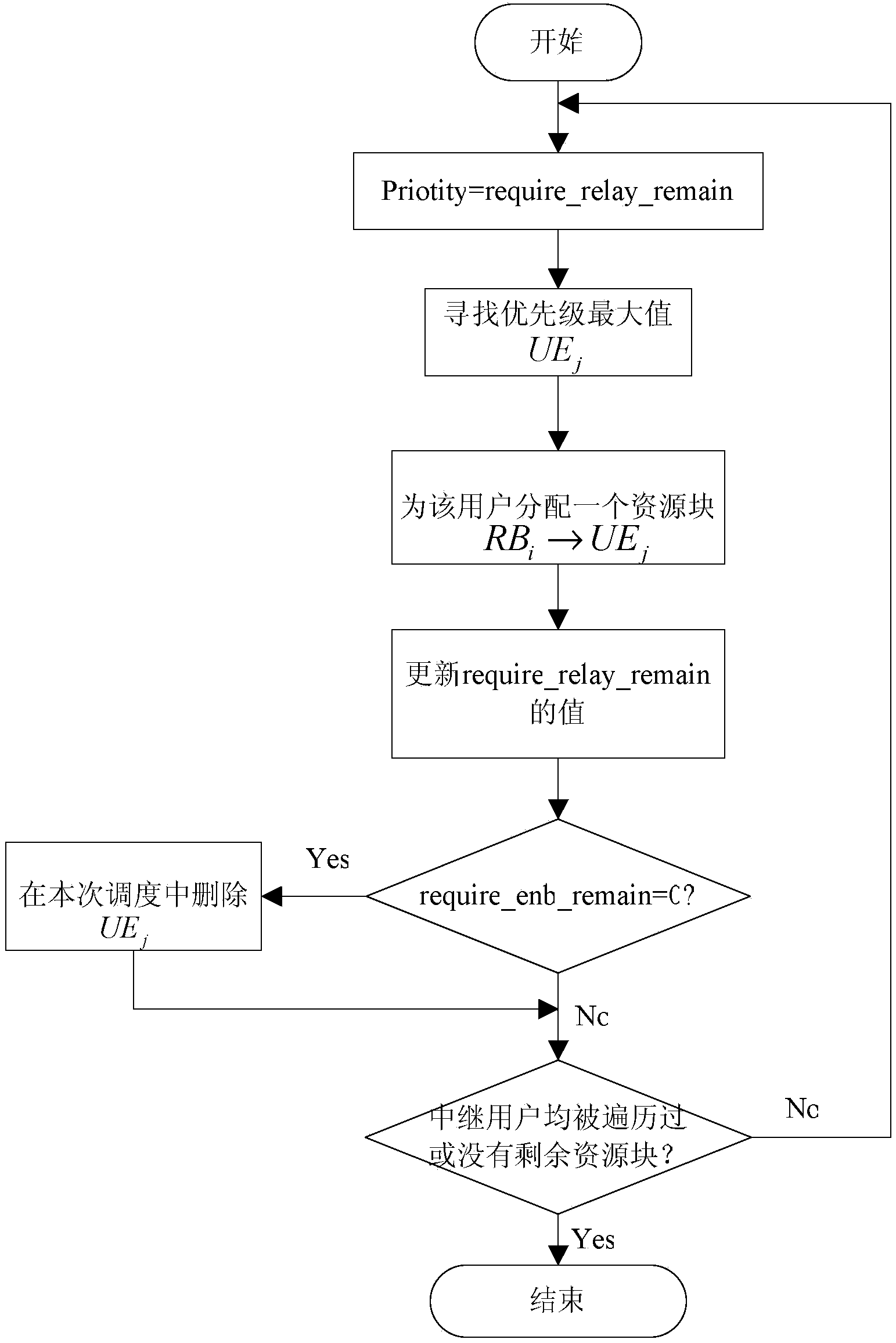
[0040] Step 3: In the uplink subframe of the backhaul link, the base station allocates resources for the relay user based on the queue information of the relay user buffered in the relay, and...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the uplink resource allocation method in the TD-LTE-Advanced relay system described in Embodiment 1, which takes into account both throughput and fairness.
[0042] The allocation principle of the initial division of the frequency resources of the direct transmission user and the relay user in the step 1 is:
[0043] The initial division steps are as follows:
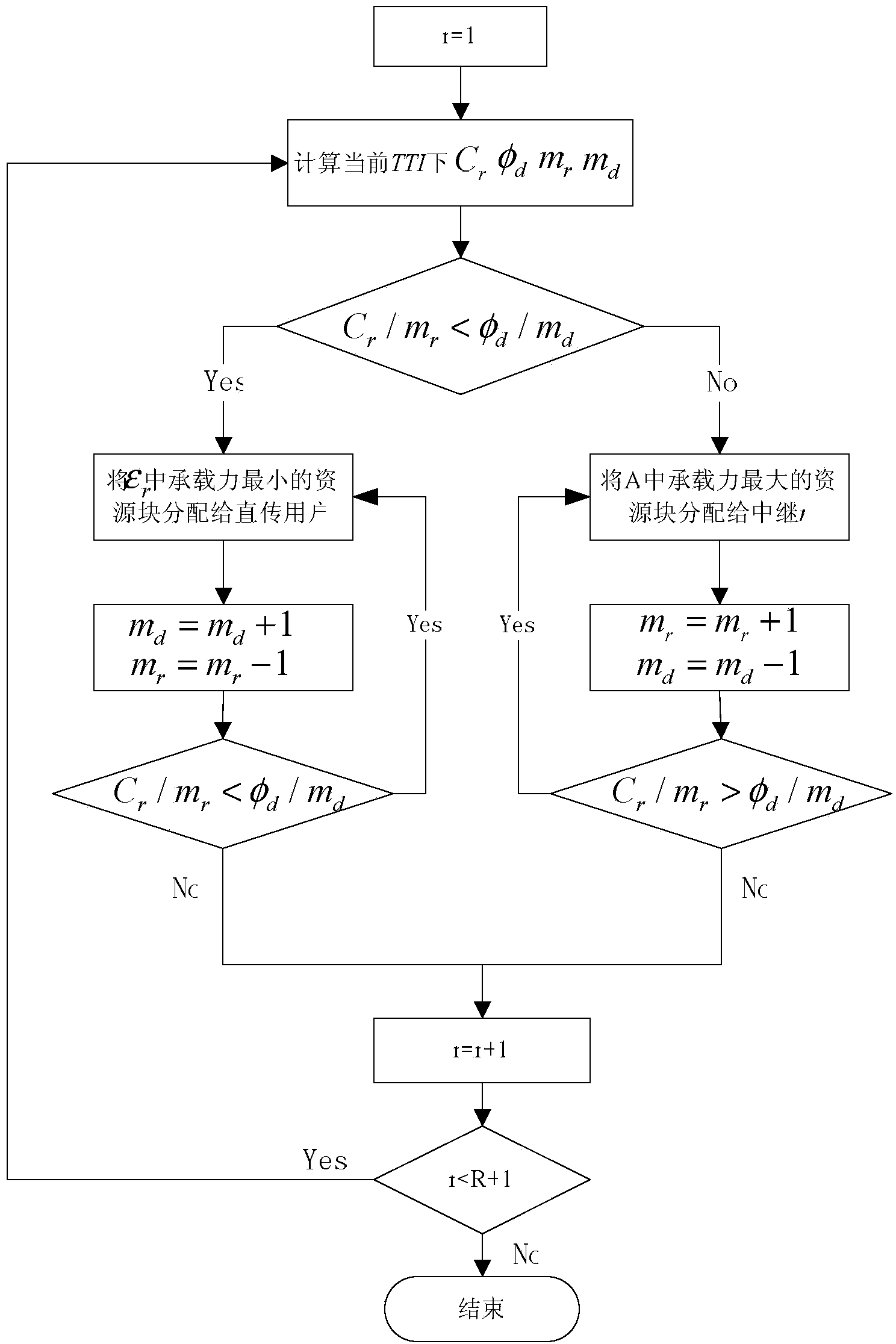
[0044] a. Parameter setting. Let A be the set of resource blocks allocated to direct transmission users, ε r is the set of resource blocks allocated to relay r, let c rn for ε r The carrying capacity of resource block n in . The initial setting is A=[1,2,…,M], C r is the sum of the service data buffered in the user queue of the relay user belonging to the relay r at the base station, φ d It is the sum of the service data buffered in the user queue of the direct transmission user at the base station.
[0045] b. Allocate a resource block contiguous ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0048] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 2 This embodiment is described. This embodiment is a further limitation of the uplink resource allocation method in the TD-LTE-Advanced relay system described in the first embodiment, which takes into account both throughput and fairness.
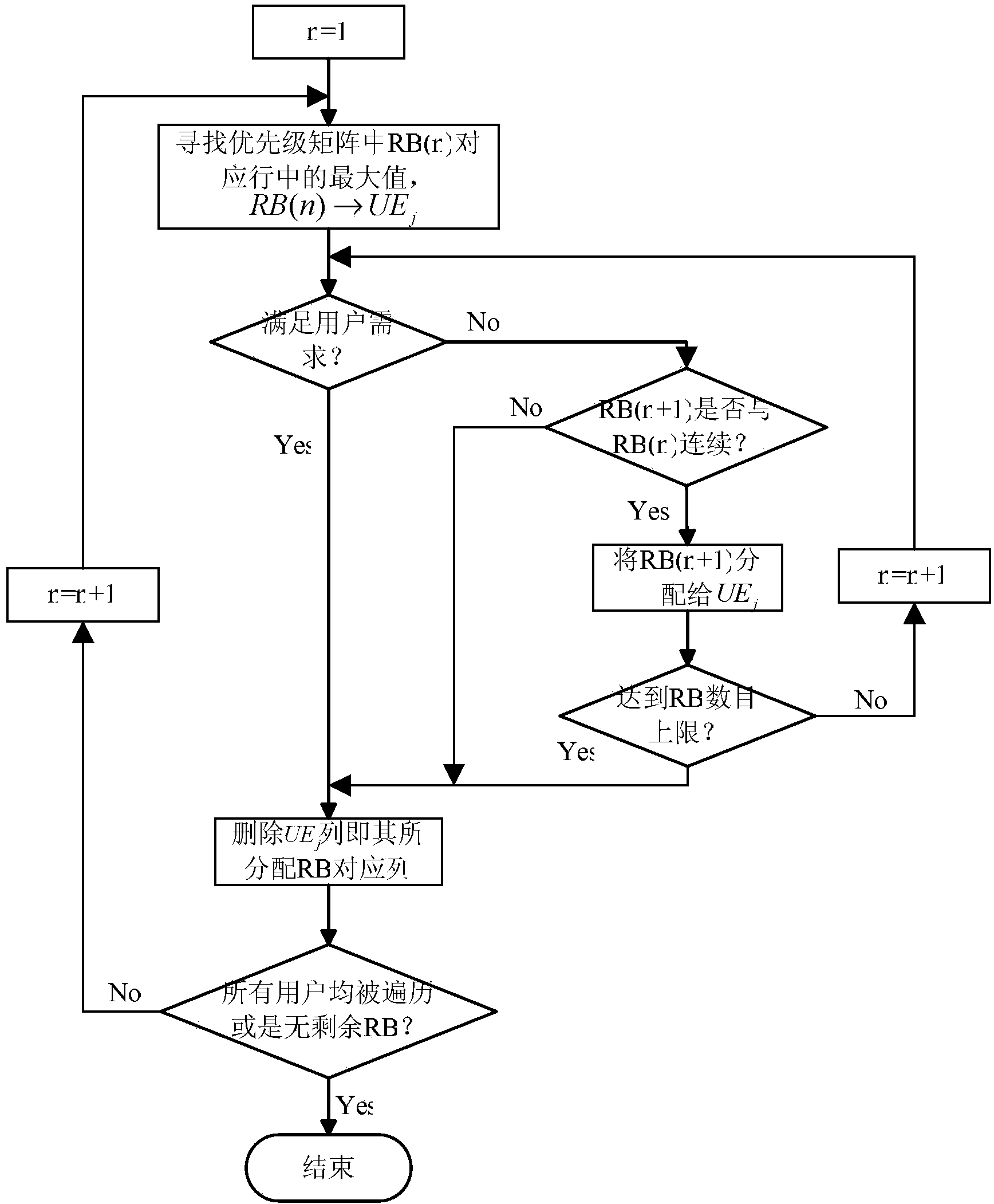
[0049] The idea of resource allocation method for access link and direct link in step 2:
[0050] Select the maximum gain in the priority matrix to complete the correspondence between UE-RB (user-resource block), and then consider the resource blocks continuous with the resource block according to the continuity requirements to meet the needs of the user as much as possible. If the user's needs can be met, the user is considered to end this resource allocation. If the wireless resources allocated to the user have reached the maximum number of resource blocks that can be obtained by each user, even if there is no resource block that can satisfy the user Requirements, it is sti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com