Preparation for reducing mercury content in rice grains and its preparation and usage
A technology of rice grains and preparations, applied in rice cultivation, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the absorption and transport efficiency of heavy metals such as mercury, the low absorption and utilization rate, and affecting rice yield, etc., to achieve grain Effects of safe export, reduction of total mercury content, and promotion of rice growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The preparation method of the preparation for reducing the mercury content in rice grains comprises the following steps in turn: add 1L of water to the reaction kettle, adjust the water temperature to 50-60°C, add 20g of L-methionine, L-cysteine Acid 130g, L-selenomethionine 30g, glutathione 55g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 120g and sodium nitrophenolate 12g, each component was added and reacted at constant temperature (50-60°C) for 30min until it was used as the final One component of sodium nitrophenolate was added and reacted at a constant temperature of 50-60°C for 30 minutes. After the reaction product is cooled to room temperature, filtered (filtered through a 2500-mesh filter), sterilized (heated at 121° C. for 20 minutes), and filled, the finished product is a preparation for reducing mercury content in rice grains.
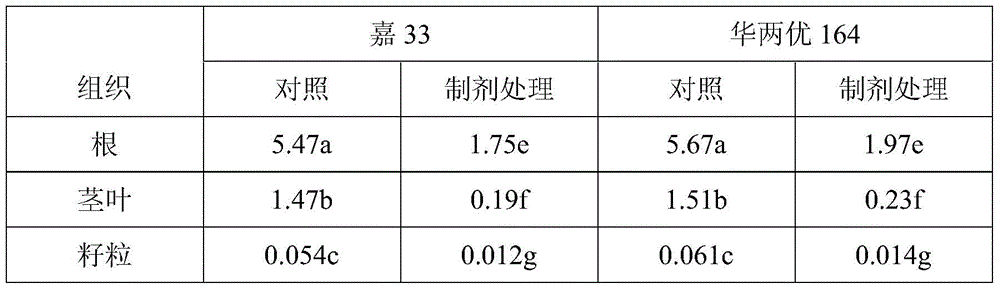
[0034] The above-mentioned preparations were used to carry out the plot test. The contaminated soil test plot [volume, 1m (length) × 1m (width)...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The preparation method of the preparation for reducing the mercury content in rice grains comprises the following steps in turn: add 1L of water to the reaction kettle, adjust the water temperature to 50-60°C, add 15g of L-methionine, L-cysteine Acid 100g, L-selenomethionine 25g, glutathione 50g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 150g and sodium nitrophenolate 10g, each component was added and reacted at constant temperature (50-60°C) for 30min until it was used as the final One component of sodium nitrophenolate was added and reacted at a constant temperature of 50-60°C for 30 minutes. The reaction product is cooled to room temperature, filtered (passed through a 2500-mesh filter), sterilized (heated at 121° C. for 20 minutes), and filled to obtain a finished product—a preparation for reducing mercury content in rice grains.
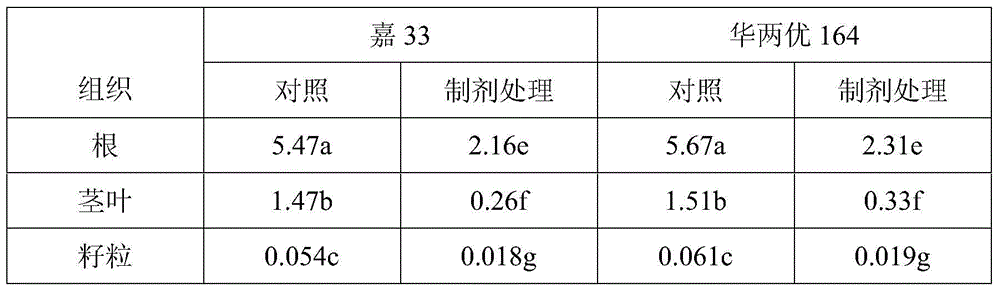
[0045] The above-mentioned preparations were used to carry out the plot test. The contaminated soil test plot [volume, 1m (length) × 1m (width) × 0...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The preparation method of the preparation for reducing the mercury content in rice grains comprises the following steps in sequence: add 1L of water to the reaction kettle, adjust the water temperature to 50-60°C, add 18g of L-methionine, L-cysteine Acid 107g, L-selenomethionine 25g, glutathione 50g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 150g and sodium nitrophenolate 15g, each component was added and reacted at constant temperature (50-60°C) for 30min until it was used as the final One component of sodium nitrophenolate was added and reacted at a constant temperature of 50-60°C for 30 minutes. The reaction product is cooled to room temperature, filtered (passed through a 2500-mesh filter), sterilized (heated at 121° C. for 20 minutes), and filled to obtain a finished product—a preparation for reducing mercury content in rice grains.
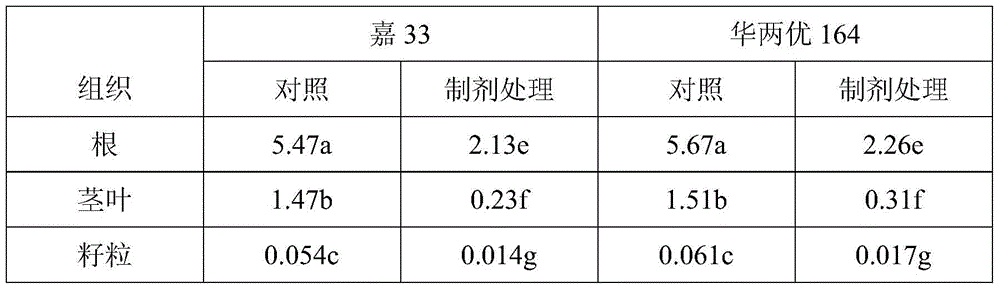
[0053] The above-mentioned preparations were used to carry out the plot test. The contaminated soil test plot [volume, 1m (length) × 1m (width)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com