Method for producing metallic iron
A manufacturing method and technology of metallic iron, applied in the field of metallic iron, can solve the problems that the separation between metallic iron and slag has not been studied.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
change example 1
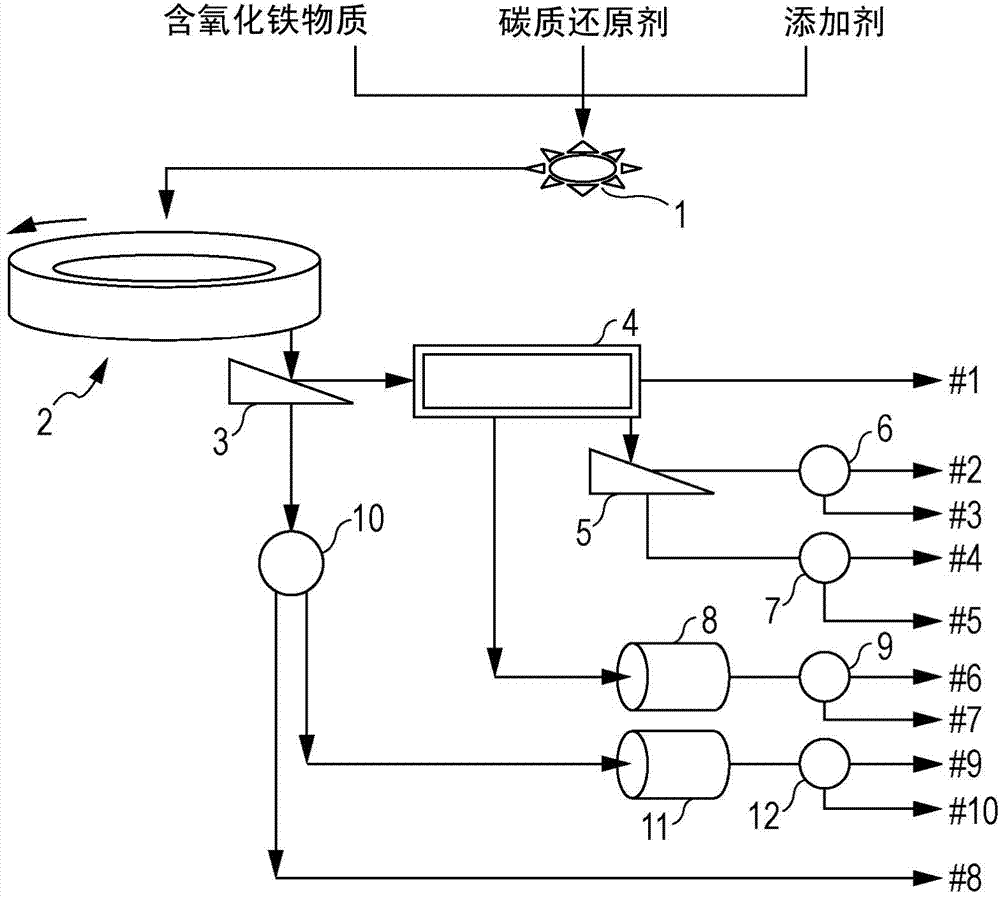
[0436] When the agglomerate is heated in a moving hearth type heating furnace, the metallic iron is melted on the hearth and coalesced with adjacent metallic iron to coarsen. Similarly, the slag melts and coalesces with neighboring slag and coarsens. The coarsened slag is crushed and made finer when discharged from the heating furnace or by subsequent treatment, and the coarsened metallic iron remains in a coarse state without being made finer. When the coarsened metallic iron is supplied to the crushing process, a load is applied to the crusher, and the consumption of the crusher is severe.
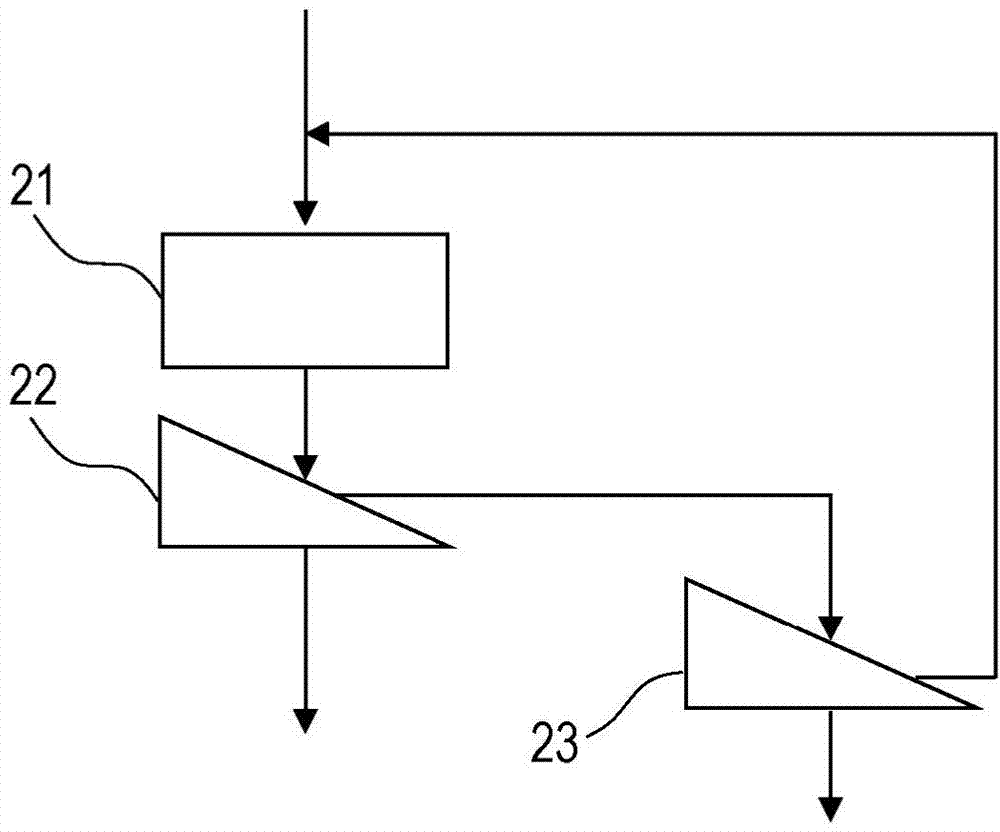
[0437] Therefore, in Modification 1, such as Figure 3-3 As shown, a sieve c ( Figure 3-3 105) for sieving. Then, the coarse particles remaining on the sieve c (on-sieve c) are supplied to the crusher 102, and crushed by impacting on the crusher 102 .
change example 2
[0439] When the agglomerate is heated at 1300°C or higher in a heating furnace, a bottom layer of material such as carbonaceous particles and refractory particles is laid to protect the hearth of the heating furnace. The particle size of the bottom charge is preferably small particles with a particle diameter of 0.5-3 mm. The bottom charge is discharged from the heating furnace together with the reduced material after the agglomerate is heated. Therefore, through the above-mentioned sieving step c, the bottom charge is included in the medium and fine particles (substances under the sieve c) that pass through the sieve c.
[0440] Therefore, in Modification 2, such as Figure 3-3 As shown, a sieve c ( Figure 3-3 105) for sieving, and for the medium and fine particles (substances under sieve c) passing through the sieve c, use a sieve b with a mesh size of 2 to 8 mm ( Figure 3-3 106) Sieving. The reason why the mesh of the sieve b used in the screening step b is 2 to 8 mm ...
change example 3
[0442] In modification example 3, as mentioned above, also can use magnetic separator ( Figure 3-3 107b) After sorting, it is supplied to the crusher 102 through a path not shown in the figure, and impacts are applied to the magnetic objects to crush them. By pre-separating nonmagnetic substances with a magnetic separator, the recovery efficiency of metallic iron obtained by crushing magnetic substances can be improved.
[0443] In addition, the medium particles recovered as the under-sieve c and the over-sieve b with a magnetic separator ( Figure 3-3 107b) After sorting, the magnetic material is supplied to the pulverizer ( Figure 3-3 108b) and pulverized, with a magnetic separator ( Figure 3-3 107e) of non-magnetic matter is sorted in advance, thus also can improve the metallic iron ( Figure 3-3 104b) Recovery efficiency.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com