Method for preparing edible bacterial cellulose by using rice immersing water and product of method
A technology of bacterial cellulose and soaking rice water, applied in the field of food biology, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of coconut water, waste of coconut water resources, unable to meet demand, etc., and achieve the advantages of reducing production cost, improving reuse and reducing sewage discharge. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
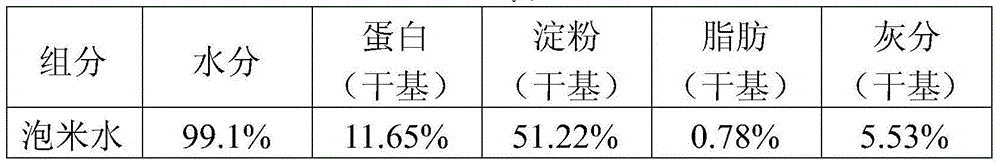
[0036] The soaked rice water obtained by soaking rice is used as the medium raw material, the soaking condition is 40°C for 4 hours, the solid content of the soaked rice water is 0.6%, the dry protein content is 11.64%, and 3% sucrose is added and then heat-sterilized at 121°C After 15 minutes, cool to 25°C, add 5% seed solution of Acetobacter xylinum, adjust the pH value to 3.0 with acetic acid, and obtain bacterial cellulose after static fermentation. The fermentation temperature in static mode is 34°C. The fermentation humidity is 55%, and the fermentation time is 6 days.
[0037] The yield of the prepared bacterial cellulose was 58%, the solid content was 15%, the hardness was 870g, the elasticity was 0.32, and the adhesiveness was 136 as measured by a texture analyzer.
Embodiment 2
[0039] The soaked rice water obtained by soaking rice is used as the medium raw material, the soaking condition is soaking at room temperature for 12 hours, the solid content of soaked rice water is 1%, the dry protein content is 12.12%, and 5% of sucrose is added and then heated at 121°C. Bacteria for 20 minutes, cooled to 30°C, added 10% gluconic acid acetobacter xylinum seed solution, adjusted the pH value to 4.0 with acetic acid, and made bacterial cellulose after static fermentation, the static fermentation temperature was 28°C , the fermentation humidity is 75%, and the fermentation time is 9 days.
[0040] The yield of the prepared bacterial cellulose was 52%, the solid content was 5%, the hardness was 550g, the elasticity was 0.25, and the adhesiveness was 89 as measured by a texture analyzer.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The soaked rice water obtained by soaking rice is used as the medium raw material, the soaking condition is 12 hours at room temperature, the solid content of the soaked rice water is 1%, the dry protein content is 12.12%, and 6% glucose is added and then heated at 121°C. Bacteria for 20 minutes, cooled to 26°C, added 10% gluconic acid acetobacter xylinum seed solution, adjusted the pH value to 4.0 with acetic acid, and made bacterial cellulose after static fermentation, the static fermentation temperature was 28°C , the fermentation humidity is 65%, and the fermentation time is 9 days.
[0043] The yield of the prepared bacterial cellulose was 49%, the solid content was 7%, the hardness was 860g, the elasticity was 0.27, and the adhesiveness was 232 as measured by the texture analyzer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com