A method for rapid detection of microbial drug resistance and a dedicated microfluidic chip
A microfluidic chip and microbial technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, enzymology/microbiological devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to meet requirements, difficult to obtain bacteria, etc., to achieve rapid The effect of preparation and inspection, low cost and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1, microfluidic chip and its preparation
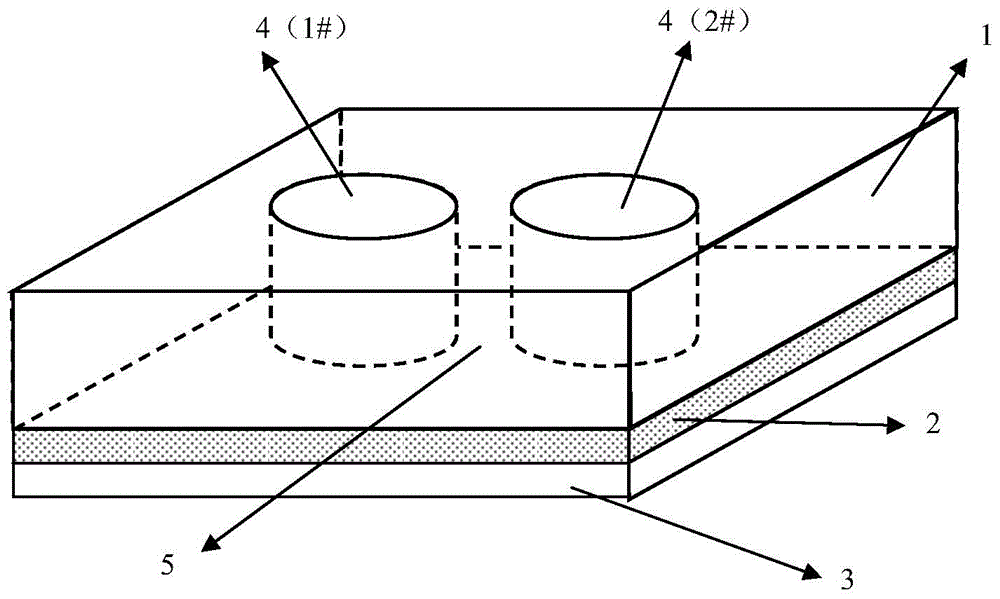
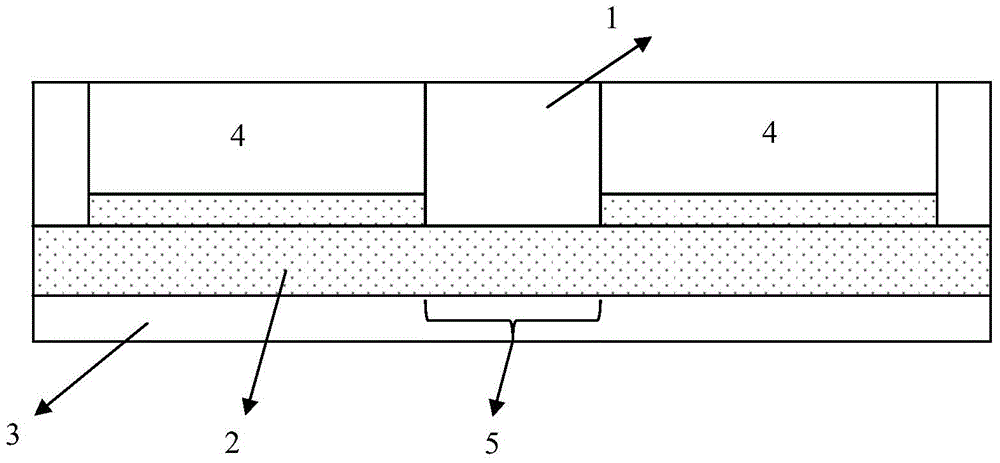
[0059] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the microfluidic chip provided by the present invention has a three-layer structure. From top to bottom, it is a polydimethylsiloxane layer (PDMS layer) 1 with a length and width of 24 mm and a thickness of 8 mm, with a thickness of 0.03 mm. ~0.05mm agarose layer 2 and cover glass 3 (24mm×24mm), PDMS layer is provided with two through holes 4 with a diameter of 5mm (as shown in the figure, the left side is marked as 1# through hole, the right side Recorded as 2# through hole), the distance between the centers of 1# through hole and 2# through hole is 6mm, that is, the shortest distance between the edges of the two through holes is 1mm, forming the observation area 5, and the agarose layer is composed of agarose Aqueous solution (3wt%) and diluted Escherichia coli suspension (OD 600 Value is about 0.2, logarithmic phase) mixed in a volume ratio of 1:1.
[0060] The m...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2, rapid detection Escherichia coli drug resistance
[0069] Prepare 10mg / L amoxicillin (molecular weight: 419.5) solution according to the standard method, with 2 times the standard concentration (referring to when the medium is prepared, the component concentration is 2 times the given standard, so that it can be diluted 1:1 with the standard culture The equal volumes of the culture medium with the same component concentration of the base were mixed to obtain the culture medium containing the actual concentration of 5 mg / L amoxicillin.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com