Organic electroluminescence device and manufacturing method for organic electroluminescence device
An electroluminescent device and luminescent technology, applied in the direction of organic light-emitting devices, organic light-emitting device structures, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor refractive index, low light-emitting performance, total reflection loss, etc., and achieve stable luminous color, The effect of lowering the potential barrier and reducing the decay speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
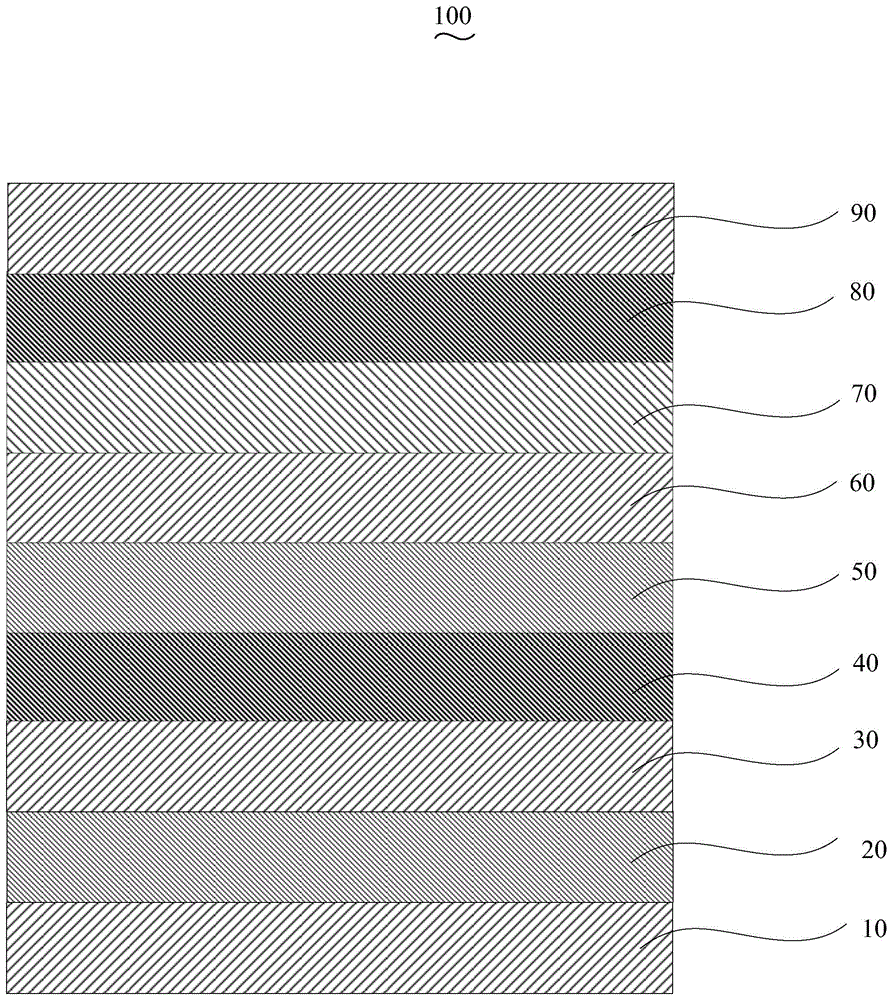
[0037] The preparation method of the organic electroluminescence device 100 of an embodiment, it comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step S110 , preparing the scattering layer 20 on the surface of the glass substrate 10 by electron beam evaporation.
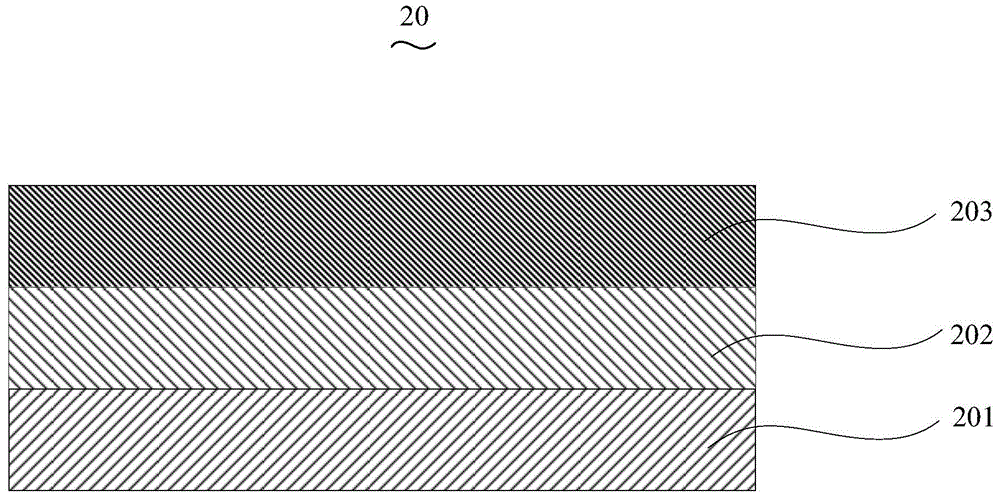
[0039] The scattering layer 20 is formed on one side surface of the glass substrate 10 . The scattering layer 20 is composed of a metal oxide layer 201, a luminescent material layer 202 and an iron salt layer 203. The metal oxide layer 201 is prepared on the surface of the glass substrate 10 by thermal resistance evaporation, and the HOMO of the material of the metal oxide layer 201 is The energy level is -5.2eV~-6.0eV, and the luminescent material layer is prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the metal oxide layer 201, and the material of the luminescent material layer 202 is 4-(dinitrile methyl)-2 -Butyl-6-(1,1,7,7-tetramethyljulodine-9-vinyl)-4H-pyran (DCJTB), 9,10-di-β-naphthylene anthracene ( AD...
Embodiment 1
[0058] The structure prepared in this example is glass substrate / MoO 3 / Alq 3 / FeCl 3 / ITO / MoO 3 / NPB / Alq 3 / TAZ / CsF / Au organic electroluminescent device, in this embodiment and the following embodiments, " / " indicates a layer, and ":" indicates doping.
[0059] The glass substrate is N-LASF44. After rinsing the glass substrate with distilled water and ethanol, soak it in isopropanol for one night. Prepare the scattering layer on the glass substrate. The scattering layer is composed of a metal oxide layer, a luminescent material layer and an iron salt layer. The metal oxide layer is prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the glass substrate. The material is MoO 3 , the thickness is 12nm, and the light-emitting layer is prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the metal oxide layer, and the material is Alq 3 , the thickness is 70nm, and the iron salt layer is prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the light-em...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The structure prepared in this example is a glass substrate / WO 3 / DCJTB / FeBr 3 / IZO / WO 3 / TCTA / ADN / CsN 3 / Al organic electroluminescent devices.
[0067] The glass substrate is N-LAF36. After rinsing the glass substrate with distilled water and ethanol, soak it in isopropanol for one night to prepare a scattering layer on the glass substrate. The scattering layer consists of a metal oxide layer, a luminescent material layer and an iron salt layer. Composition, the metal oxide layer is prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the glass substrate, and the material is WO 3 , with a thickness of 10nm. The light-emitting layer was prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the metal oxide layer. The material was DCJTB, and the thickness was 80nm. The iron salt layer was prepared by thermal resistance evaporation on the surface of the light-emitting layer. The material was FeBr 3 , with a thickness of 50nm. Then IZO is prepared on th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com