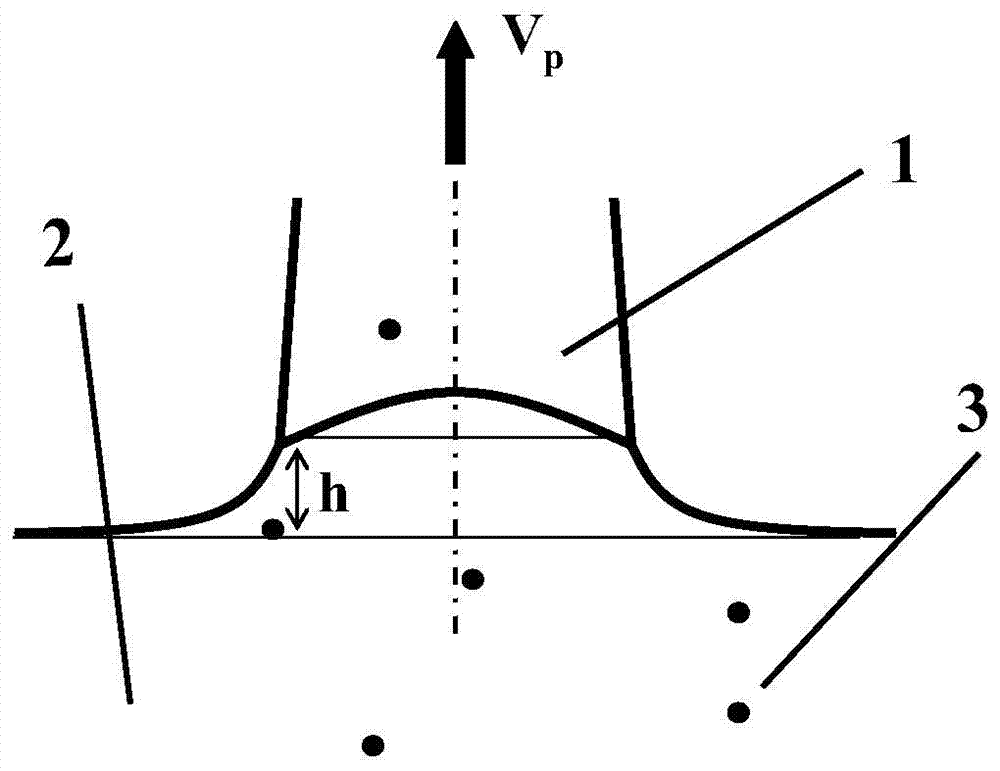
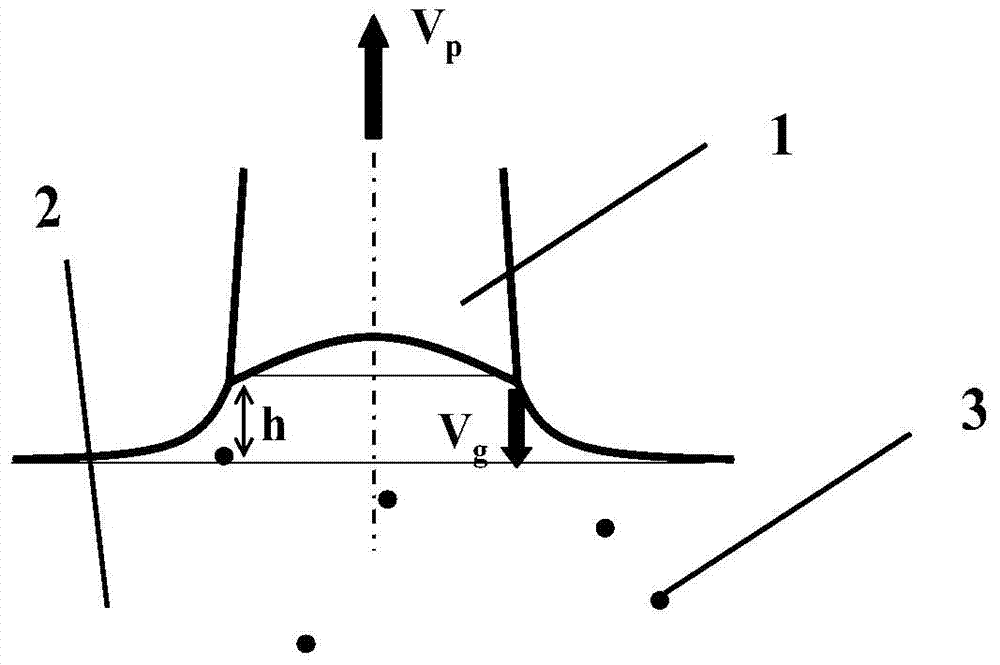
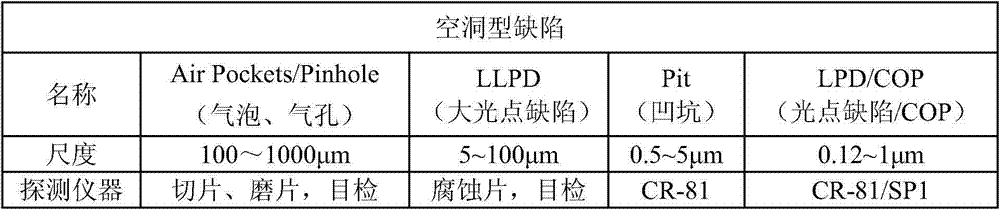
Method for reducing density of micro-pinholes in monocrystalline Czochralski silicon
A technology of Czochralski single crystal silicon and micropores, which is applied in the direction of single crystal growth, single crystal growth, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of increasing stabilization time, reducing equipment production efficiency, and high incidence of void-type defects, achieving The effect of reducing Pit and reducing the density of micropores
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In a standard Czochralski single crystal furnace, a 22-inch quartz crucible is used to load 110kg of polysilicon; the argon flow rate in the melting stage is 100 slpm, the furnace chamber pressure is 2000 Pa; the stabilization time is 60 minutes, and the rotation speed of the crucible is 1 r / min during the stabilization process.
[0029] Under the conditions of crystal rotation 12r / min, crucible rotation 8r / min, argon gas flow rate 80slpm, furnace chamber pressure 2000Pa, the Vp casting speed is 0.40~1.2mm / min; the average casting speed is 0.80mm / min to grow a diameter of 200mm, etc. A silicon single crystal with a diameter length of about 1060 mm. The crystal was subjected to processing procedures such as slicing, grinding, etching, polishing (CMP), cleaning, etc., and the number and proportion of cavity-type defect silicon wafers in the slicing, etching, and polishing inspection procedures of the branched crystal were counted, as shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 2
[0031] In a standard Czochralski single crystal furnace, a 22-inch quartz crucible is used to load 110kg of polysilicon; the argon flow rate in the melting stage is 40slpm, the furnace chamber pressure is 800Pa; the stabilization time is 120min, and the rotation speed of the crucible during the stabilization process is 1r / min to 8r / min .
[0032] Under the conditions of crystal rotation 12r / min, crucible rotation 8r / min, argon gas flow rate 80slpm, furnace chamber pressure 2000Pa, the Vp casting speed is 0.40~1.2mm / min; the average casting speed is 0.80mm / min to grow a diameter of 200mm, etc. Silicon single crystal with a diameter length of about 1050mm. The crystal is subjected to processing procedures such as slicing, grinding, etching, polishing (CMP), and cleaning. See Table 2 for statistics on the number and proportion of cavity-type defect silicon wafers occurring in the slicing, etching, and polishing inspection processes of the branched crystal.
Embodiment 3
[0034] In a standard Czochralski single crystal furnace, a 22-inch quartz crucible is used to load 110kg of polysilicon; the argon flow rate in the melting stage is 40slpm, the furnace chamber pressure is 800Pa; the stabilization time is 120min, and the rotation speed of the crucible during the stabilization process is 1r / min to 8r / min .
[0035] Under the conditions of crystal rotation 12r / min, crucible rotation 8r / min, argon gas flow rate 80slpm, furnace chamber pressure 2000Pa, the technical solution of the present invention is implemented in the isometric growth process, except that the upward pulling speed Vp=0.40~1.2mm / min; In addition, there is a periodic downward falling speed Vg=0.32~0.96mm / min, the cycle of oscillation operation is 12 seconds, and the frequency of oscillation operation is 1 / 11; the average pulling speed is 0.76mm / min to grow a diameter of 200mm, equal diameter A silicon single crystal with a length of about 1070mm. The crystal is subjected to proces...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com